Page 1 :
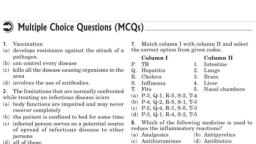
Chapter 13: “Why do we fall ill?”, KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept], CONCEPTS, , RATING, , Significance of Health, , **, , Disease and Its causes, , ***, , Infectious diseases, , *****, , Principles of prevention of diseases, , ****, , 1.”Health” is a state of being well enough to function well physically, mentally, and socially., 2.”Disease”( disturbed ease) means being uncomfortable. One or more systems of the body, will change, give rise to “Symptoms” ( Cough, loose motions, pus formation, headache,, fever, breathlessness, vomiting, fits, unconsciousness, inflammation , swelling and general, effects - a Doctor look for the basis of symptoms). Diseases are basically two types- Acute, Disease & Chronic Disease, 3. Acute Disease: The disease which lasts for only a short period of time is called Acute, Disease Ex. Common Cold., 4.Chronic Disease: The disease which lasts for long period of time is called Chronic Disease, Ex. Tuberculosis., Acute Disease, , Chronic Disease, , They are short duration disease, , They are long lasting disease, , Patient recovers completely after the cure, , Patient does not recover completely, , There is no loss of weight or feeling of tiredness There is often loss of weight of feeling of, afterward, , tiredness, , There is short duration loss of work and There is a prolonged loss of work and efficiency, efficiency, , 5. Causes of Diseases : Most of the diseases have many causes, rather than one single, cause, like unclean water, nourishment, genetic differences, genetic abnormalities e.g., Based on the causes diseases are of two types: Non-Infectious Diseases and Infectious, Diseases., , 78
Page 2 :
6. Non-Infectious Diseases: Not caused by infectious agents, mostly internal and noninfectious cause. Ex. Cancer, 7. Infectious Diseases: Caused by infectious agents., SN, , Type Of Disease, , Example, , 1, , Bacterial diseases, , - Typhoid, Cholera, Tuberculosis, Acne, Anthrax,, , 2, , Viral diseases, , - Common Cold, Influenza, Dengue fever, AIDS, Japanese, encephalitis or brain fever, , 3, , Fungal diseases, , Skin diseases, , 4, , Protozoan diseases, , -Malaria ( Plasmodium), Kalaazar (Leishmania), Sleeping, sickness( Trypanosomes), , 5, , Worm diseases, , - Ascariosis ( Round worm), Elephantiasis(Wuchereria ), , (Please refer Fig. 13.1 (a-e), NCERT Text Book Page- 181)., , a)The infectious diseases spread by agents are called as Communicable Diseases., SN, , Type of Disease, , Example, , 1, , Air born Diseases, , - Pneumonia, common cold, Tuberculosis;, , 2, , Water born diseases, , - Cholera, hepatitis, , 3, , Sexual Diseases, , - HIV, Syphilis., , 4, , Animal born Disease, , - Rabbis., *(Vector- the animal carrying infectious agent from a sick, person to another potential host without getting affected Ex., Mosquito carrying Malaria Parasite)., , (Please refer Fig. 13.2 & 13.3, NCERT Text Book Page- 183)., , 9. Principles of Treatment:, 1. Antibiotics- many bacteria make a cell wall to protect themselves, the antibiotic, (Penicillin) blocks the bacterial process that builds cell wall and blocks the, biochemical pathways. Antibiotics do not work against viral infections. Antiviral, medicine is harder than making Antibacterial medicine because Virus has only few, biochemical mechanisms of their own. Other medicines bring down fever, reduce, pain or loose motions. We can take bed rest to conserve energy., 79
Page 3 :
10 Principles of Prevention : Following three limitation are normally confronted while, treating an infectious disease:, , , , , Once someone has disease, their body functions are damaged and may never, recover completely., Treatment will take time, which means that someone suffering from a disease is, likely to be bedridden for some time even if we can give proper treatment., The person suffering from an infectious disease can serve as the source from where, the infection may spread to other people., , General ways of preventing infectious disease :, , , , , Air-borne – We can prevent exposure by providing living condition that are not, overcrowded., Water-borne – prevent by providing safe drinking water. This is done by treating the, water to kill any microbial contamination., Vector-borne – We can provide clean environment, which would not allow mosquito, breeding., , 11. Immunity: Even in cells there is repair mechanism called” Immunity”. Immune cells, manage to kill off the infectious agents. Smallpox disease is eliminated by developing, memory cells for particular infection by mimics the microbes, called” Vaccine”. The basis of, Immunization- if you had smallpox once, there was no chance of suffering from it again., Proper nutrition is essential to maintain body immunity. There are vaccines against tetanus,, diphtheria, whooping cough, measles, polio and many other diseases., 12. Prevention of disease is better than cure. Hygiene is the basic key to maintain good, health., QUESTION BANK:, 1. Define Health……. (It is astate of being well enough to function well physically, mentally,, and socially), 2. Name any two Symptoms of diseases………………………. (Cough& loose motions), 3. The disease which last for only a short period of time is called……………….( Acute Disease), 4. State whether Tuberculosis is aChronic Disease or Acute Disease…… (Chronic Disease), 5. Mention the causal organism for Sleeping sickness ………… (Trypanosoma), 6.Cholera is a waterborne disease, mention TRUE/ FALSE ……….. (TRUE), 7. Antibiotics do not work against viral infections, mention TRUE/ FALSE ……….. (TRUE), 8. Write short notes on Immunity, 80
Page 4 :
(Even in cells there is repair mechanism called” Immunity”. Immune cells manage to kill off, the infectious agents.), 9. Explain with an example the term Vaccine. ( Smallpox disease is eliminated by developing, memory cells for particular infection by mimics the microbes, called” Vaccine”)., 10. State reasons to support “Prevention of disease is better than cure”., , QUESTION PAPER:FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT – I (For Practice), Marks- 40, , Time: 90 minutes, , * General Instructions, 1. Questions 1-5 (1 Mark each), , 2. Questions 6-10 ( 2 Mark each), , 3. Questions 11-15 (3Mark each), , 4. . Questions 16-17 (5Mark each), , Q.1 Define Health, Q.2 Mention any two symptoms of diseases., Q.3 Typhoid is a bacterial disease. Mention True/ False……………., Q.4 Sleeping sickness is caused by……………………………………………, Q.5 Elephantiasis is caused by……………………………………………………., Q.6. Mention two Air born diseases1…………………………..2…………………., Q.7 Mention two Sexually Transmitted Diseaes1………………..2………………., Q.8 Mention two Viral Diseaes1………………..2………………., Q.9 What is called vector. Give one example., Q.10 Give two examples of Chronic diseases., Q.11 Distinguish between Infectious and Non-infectious diseases., Q.12 Write a short notes on Small Pox., Q.13 What is immunity? Write short notes on it., Q.14 What is Vaccination? Give the details, how it works in human body., Q.15 Write three reasons for Cancers., Q.16 What are the basic five principles of treatment for diseases., Q.17 How Hygiene could help you to maintain good health and mention five situations to, take care about health., , ----------------X--------------81