Page 1 :
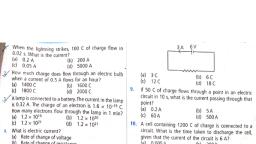
a Foundation Scien, , , , , , "Jas 10, physics for Class 1, e: Phy, , are connected in series with, , are resistors is 2A, that in the.“, 4, Three res each resistor 1M the eg), “arrent in & lly, 2. he kilowat the curre, I ilowatt hour is the unit of be ‘ are connected in paralle|, 3. The equivalent resistance of two equal resistances 5, Three restore current in each resistor is 2 4 wit, each ’ 2 Nat, onnected varallel the value of eac pattery- “Il be, resistance, ie i i‘ the battery will be, » ANSWERS *, 14,400) 20. 180 J or 43 ca), : a @ 22. 0.5 W, 509, 1. 200 V 202) 3. 1500 C 21. 6 24,0.25A 25.1.6W,3.2W, 4.15 x10” electrons 5.3A 2.132259 37.012 kWh, 6.124 7,.6€02,01A 8.42 26. 14.4.W,7.2W g i A, 9. (a) 15.71 m (b) 4: 1 (4 times) 28. (a) 4422 (b) 30.8 kWh 29. (a) 2880 J (b) rx, 10,42 11. R/4, 12. (a) 27 Q (b) 3 2 (c) one resistor connected in tive Questions, series & a combination of two resistors in E ta r i © 3,(c) 4. (b) 5. (, paralle E12) Fd Gis) 9.08) 1, 13. 822 resistor connected in series to a parallel 6. (d), combination of 69 and 3 m) 2 ep aT 5, 14.0.2 A,4V fe Ler . :, 15. (a) 102) 0.6A()02A 16.054 6.F, 17. 1250, 192A 18.2A,1A, , + POSTSCRIPT «, , , , ver, silver, iron, etc., are conductors of, € contain a large number of free, electrons. Rubber, glass, wood, etc., are insulators as, they have almost no free electrons. In between the, two, there are materials such as silicon and, germanium in which the number of free electrons is, much greater than that in insulators and much smaller, than that in conductors. Such materials are called, semiconductors. Their resistivity decreases as the, temperature increases. Also the resistivity can be, drastically changed by putting some ‘impurity’ in the, semiconductor. By controlling the amount of impurity, and its distribution, very useful electronic devices are, formed from semiconductors. Such semiconductor, devices are used in computers, digital watches,, tronic calculators, etc, , , , tricity, , , , , , , , You know about many applications of electric current,, but can you name one application of electric charge?, Most photocopying machines are based on the, properties of electric charges. A photocopying, machine has a powerful light source and a system of, mirrors and lenses which forms an image of the, original document on a roller made of a special, , Original, , , , Fig. 4.A1, , material. The roller is initially positively charged, material of the roller has the property of losing, charge when exposed to light. Light reflected fron, white portions of the original document falls on, roller and these portions of the drum lose, charge. The dark portions of the original do not ref, light and, therefore, the corresponding areas on, roller retain positive charge. For printing, a negat, charged ‘toner’ (special type of ink) is used, Positively charged areas on the roller attract, negatively charged toner, As the drum rotates, toner gets transferred to the paper, which passes, contact with the drum. This way, the dark portions, the original document are imaged on the pst