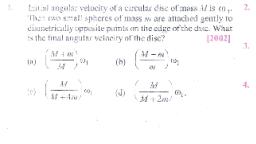Question 1 :
The displacement {tex} ( x ) {/tex} of a particle depends on time {tex} ( t ) {/tex} as {tex} x = \alpha t ^ { 2 } - \beta t ^ { 3 } {/tex}
Question 2 :
A bob of mass {tex} M {/tex} is suspended by a massless string of length {tex} L . {/tex} The horizontal velocity {tex} v {/tex} at position {tex} A {/tex} is just sufficient to make it reach the point {tex} B {/tex}. The angle {tex} \theta {/tex} at which the speed of the bob is half of that at {tex} A {/tex}, satisfies<br><img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/JEE%20Advanced/5e37f6488e34721b52b49319"><br>
Question 3 :
A projectile can have the same range {tex} R {/tex} for two angles of projection. It {tex} t _ { 1 } {/tex} and {tex} t _ { 2 } {/tex} are the times of flight in the two cases, then what is the product of two times of flight?
Question 4 :
A motor cyclist is trying to jump across a path as shown in fig by driving horizontally off a cliff {tex} A {/tex} at a speed of {tex} 5 \mathrm { ms } ^ { - 1 } {/tex}. Ignore air resistance and take {tex} \mathrm { g } = 10 \mathrm { ms } ^ { - 2 } {/tex}. The speed with which he touches peak {tex} B {/tex} is<br><img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/JEE%20Advanced/5e37f4f420c6cd1b2246532d"><br>
Question 5 :
Figure show that particle {tex} A {/tex} is projected from point {tex} P {/tex} with velocity {tex} u {/tex} along the plane and simultaneously another particle {tex} B {/tex} with velocity {tex} v {/tex} at an angle {tex} \alpha {/tex} with vertical. The particles collide at point {tex} Q {/tex} on the plane. Then<br><img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/JEE%20Advanced/5e37f59c8e34721b52b492dc"><br>
Question 6 :
A particle moves under the effect of a force $ F =Cx $ from $ x = 0 $ to $ x =x_1 $ The work done process is
Question 7 :
A force $ F = K(yi + xj ) $ ( where $ K $ is a positive constant) acts on a particle moving in the xy-plane. Starting from the origin, the particle is taken along the positive x-axis to the point (a, 0) and then parallel to the y-axis to the point (a, a). The total work done by the force F on the particles is
Question 8 :
Assertion: An object projected with same velocity on the paths of different rough surfaces are brought to rest in different distances.
Reason: The workdone against the friction depends on the path travelled by the object.
Question 10 :
When work is done on a body by an external force, its
Question 11 :
Potential energy associated with a conservative force is given by <em>U</em> = <em>Ax</em><sup>2</sup> where <em>A</em> is a constant then
Question 12 :
The energy which an $ e^- $ acquires when accelerated through a potential difference of $ 1 $volt is called
Question 13 :
A particle moves along the x-axis from $x=0$ to $x=5$ m under the influence of a force given by $F=7-2x+3x^2$. The work done in the process is
Question 14 :
A body of mass starts moving from rest along x-axis so that its velocity varies as $v = a\sqrt {s}$ where $a$ is a constant and $s$ is the distance covered by the body. The total work done by all the forces acting on the body in the first seconds after the start of the motion is:
Question 15 :
In position A kinetic energy of a particle is 60 joule and potential energy is -20 joule. In position B, kinetic energy is 100 joule and potential energy is 40 joule. Then in moving the particle from A to B - <br>
Question 16 :
A wire suspended vertically from one of its ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200 N to the lower end. The weight stretches the wire by 1 mm. Then the energy stored in the wire is
Question 17 :
A wire is clamped horizontally between two rigid support and a small mass is hanged from middle of the wire. The mass is displaced a little in vertical direction -<br>
Question 18 :
A uniform chain of length L and mass M lying on a smooth table and one-third of its length is hanging vertically down over the edge of the table. If g is the acceleration due to gravity, the work required to pull the hanging part on to the table is
Question 19 :
The ring R in the arrangement shown can slide along a smooth, fixed, horizontal rod XY. It is attached to the block B by a light string. The block is released from rest, with the string horizontal.<br> <img style='object-fit:contain' src='https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/JEE%20Advanced/5ead222c381c2135355c6b78' class="uploaded-image" />
Question 20 :
A block of mass 2 kg rests on a rough inclned plane making am angle of $30^o$ with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plans is 0.7. The frictional force on the block is $(g = 9.8 m/s^2)$ :
Question 21 :
A body is rolling on the ground with a velocity of $1\ m/s$. After travelling a distance of $5\ m$, the body stops. The coefficient of friction is:
Question 22 :
To avoid slipping while walking on ice, one should take smaller steps because:<br>
Question 23 :
A body slipping on a tough horizontal plane moves With a deceleration of 4.0 m/${ s }^{ 2 }$ . What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane ?
Question 24 :
The upper half of an inclined plane of inclination $\theta$ is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough $A$ body starting from the rest at top come back to rest at the bottom, then the coefficient of friction for the lower half is given by _______.
Question 25 :
A body of mass 40 gram is moving with a constant velocity of 20 $ms^{-}$ $^{1}$ on a horizontal frictionless table. The force acting on the body in horizontal direction is: