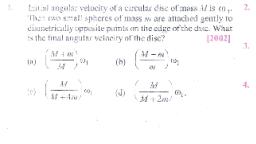Question 1 :
A loop of area 0.1 <img style='object-fit:contain' width='19' height='20' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5ea28ae23c680714de9a88a8"> rotates with a speed of 60 rps perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.4 T. If there are 100 turns in the loop, maximum voltage induced in the loop is
Question 2 :
Two identical coaxial circular loops carry current <img style='object-fit:contain' width='5' height='20' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5ea289153c680714de9a8390"> each circulating in the clockwise direction. If the loops are approaching each other, then
Question 3 :
A conducting ring is placed around the core of an electromagnet as shown in fig. when key <img style='object-fit:contain' width='11' height='20' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5ea289773c680714de9a84f8"> is pressed, the ring<br>
Question 4 :
In an <i>R-C</i> circuit while charging, the graph of ln<i>I versus</i> time is as shown by the dotted line in the adjoining diagram where <i>I</i> is the current. When the value of the resistance is doubled, which of the solid curves best represents the variation of ln <i>I</i> <i>versus</i> time?<br> <img style='object-fit:contain' width=182 height=140 src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5ea2a1288ab67a08eba561cf">
Question 5 :
The inductance between {tex} A {/tex} and {tex} D {/tex} is <br><img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5d60f0bdd3eb695bc07eb5bd" />
Question 6 :
A metal disc of radius {tex} \mathrm {100 cm } {/tex} is rotated at a constant angular speed of {tex} \mathrm {60rad } / \mathrm { s } {/tex} in a plane at right angles to an external field of magnetic induction {tex}0.05 \ \mathrm { Wb } / \mathrm { m } ^ { 2 } {/tex} . The emf induced between the centre and a point on the rim will be
Question 7 :
A cylindrical bar magnet is kept along the axis of a circular coil. If the magnet is rotated about its axis, then
Question 8 :
A metallic ring connected to a rod oscillates freely like a pendulum. If now a magnetic field is applied in horizontal direction so that the pendulum now swings through the field, the pendulum will<br>
Question 9 :
Which of the following components of a <i>L C R </i>circuit, with AC supply, dissipates energy?
Question 10 :
A coil of inductance 300{tex} \mathrm { mH } {/tex} and resistance 2{tex} \Omega {/tex} is connected to a source of voltage 2{tex} \mathrm { V } {/tex} . The current reaches half of its steady state value in
Question 12 :
A wave has wavelength $50A^o$. Which of the following is a use of this wave?<br/>
Question 13 :
Assertion: The phenomenon of $X-$ ray production is basically inverse of photoelectric effect.
Reason: $X-$ are electromagnetic waves.
Question 15 :
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given.<br>Which of the following ray are not electromagnetic waves
Question 16 :
Find $V_{ba}$ if $12$ $J$ of work has to be done against an electric field to take a charge of $10^{-2}$ $C$ from $a$ to $b$.
Question 18 :
If a positive charge is shifted from a low potential region to a high potential region, the electric potential energy:
Question 20 :
The work done to transport $20 C$ charge from points $A$ to another point $B$ over distance of $0.2 m$ is $2$ joule The potential difference across $AB$ is
Question 21 :
A particle with a charge of 3 coulombs is taken from a point at a potential of 50 V to another point at a potential of 120 V. Calculate the work done.
Question 22 :
A spark is produced between two insulated surfaces maintained at a potential difference of $5 \times 10^6 V$. If the energy output is $10^{-5} J$, the charge transferred during the spark is :
Question 23 :
When a 2$\mu$C charge is carried from point A to point B, the amount of work done by the electric field is 50 $\mu$J. What is the potential difference and which point is at a higher potential?
Question 24 :
The work done by the electric field on a charge of 2.50 n C that travels from point B to point A is
Question 25 :
In transferring $1.5 C$ charge through a wire, $9 J$ of work is needed. The potential difference across the wire will be:
Question 26 :
A particle of charge {tex} q {/tex} and mass {tex} m {/tex} moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed {tex} \omega . {/tex} The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on
Question 27 :
A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field exist in a region in the same direction. An electron is projected with a velocity pointed in the same direction. Then the electron will
Question 28 :
The radius of the coil of a tangent galvanometer which has 10 turns is 0.1 m. The current required to produce a deflection of <img style='object-fit:contain' width='142' height='20' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5ea285ea3c680714de9a7d41"> is
Question 29 :
A current flows in a conductor from east to west. The direction of the magnetic field at a point above the conductor is
Question 30 :
A compass needle whose magnetic moment is {tex} 60 \mathrm { Am } ^ { 2 } , {/tex} is directed towards geographical north at any place experiencing moment of force of {tex} 1.2 \times 10 ^ { - 3 } \mathrm { Nm } {/tex} . At that place the horizontal component of earth field is 40{tex} \mathrm { micro } \mathrm { W } / \mathrm { m } ^ { 2 } {/tex} . What is the value of dip angle at that place?
Question 31 :
A loosely wound helix made of stiff wire is mounted vertically with the lower end just touching a dish of mercury. When a current from a battery is started in the coil through the mercury
Question 32 :
In sum and difference method vibration magnetometer, the time period is more if
Question 33 :
A closely wound solenoid of 2000 turns and area of cross- section {tex} 1.5 \times 10 ^ { - 4 } \mathrm { m } ^ { 2 } {/tex} carries a current of 2.0{tex} \mathrm { A } {/tex} . It is suspended through its centre and perpendicular to its length, allowing it to turn in a horizontal plane in a uniform magnetic field {tex} 5 \times 10 ^ { - 2 } {/tex} tesla making an angle of {tex} 30 ^ { \circ } {/tex} with the axis of the solenoid. The torque on the solenoid will be:<br>
Question 34 :
Three identical bars A, B and C are made of different magnetic
materials. When kept in a uniform magnetic field, the field
lines around them look as follows: <br> <img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://data-screenshots.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/5d60fb149c699b6d4e700306.jpg" /> <br> Make the correspondence of these bars with their material being diamagnetic (D), ferromagnetic (F) and paramagnetic (P):
Question 35 :
Two wires with currents 2{tex} \mathrm { A } {/tex} and {tex}1{/tex} A are enclosed in a circular loop. Another wire with current 3{tex} \mathrm { A } {/tex} is situated outside the loop as shown. The {tex} \oint \overrightarrow { \mathrm { B } } \cdot \mathrm { d } \vec { l } {/tex} around the loop is<br><img style='object-fit:contain' src="https://storage.googleapis.com/teachmint/question_assets/NEET/5d60ef0de5db655bbf10a47d"><br>
Question 36 :
8 similar charged drops combine to form a bigger drop. The ratio of the capacitance of bigger drop to that of smaller drop will be:
Question 37 :
A spherical condenser has inner and outer spheres of radii a and b respectively. The space between the two is filled with air. The difference between the capacities of two condensers formed when outer sphere is earthed and when inner sphere is earthed will be :<br/>
Question 38 :
Two conducting spheres of radii $r_1$ and $r_2$ are at the same potential. What is the ratio of the charges on them?
Question 39 :
The ratio of the radius of two spherical conductors is $1:2$ then the ratio of their capacitance will be:
Question 40 :
Two spheres of $3 \mu F$ and $5 \mu F$ are charged to a potential of $300V$ and $500V$ respectively The common potential will be :
Question 41 :
Three condenser of capacitance $C(\mu F)$ are connected in parallel to which a condenser of capacitance $C$ is connected in series. Effective capacitance is $3.75$, then capacity of each condenser is <br>
Question 42 :
Three capacitors, $3\mu F, 6\mu F$ and $6\mu F$ are connected in series to a source of 120V. The potential difference, in volts, across the $3\mu F$ capacitor will be
Question 43 :
Two capacitors of $10\ pF$ and $20\ pF$ are connected to $200\ V$ and $100\ V$ sources respectively. If they are connected in parallel by the wire, what is the common potential of the capacitors?
Question 44 :
Two connected bodies having respectively capacitances ${\text{C}}_{\text{1}} \,{\text{and}}\,{\text{C}}_{\text{2}} $ are charged with a total charge Q. The potentials of the two bodies are.<br>
Question 45 :
A capacitor of capacity $C_1$, is charged by connecting it across a battery of e.m.f. $V_0$. The battery is then removed and the capacitor is connected in parallel with an uncharged capacitor of capacity $C_{2}$. The potential difference across this combination is :<br/>