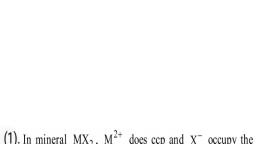Question 1 :
The pattern of successive layers of ccp arrangement can be designated as:
Question 3 :
In a crystalline solid, anions $B$ are arranged in ccp lattice and cations $A$ occupy $50$% of the octahedral voids and $50$% of the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the solid?
Question 4 :
A crystalline solid between A and B has the following arrangement of atoms: <br/>(i) Atoms A are arranged in a CCP array.<br/>(ii) Atoms B occupy all the octahedral voids and half of the tetrahedral voids.<br/>What is the formula of the compound?<br/>
Question 5 :
A compound is formed by cation $C$ and anion $A$. The anions form hexagonal close packed (hcp) lattice and the cations occupy $75\%$ of octahedral voids. The formula of the compound is :
Question 6 :
Assertion: It occupies certain holes of this type but not the other holes of the same type?
Reason: The proximity of two cations $(A^{2+ }\,\,and \,\,B^{4+})$ would be electrostatically unfavourable.
Question 7 :
Aluminium crystallizes in a cubic close packed structure. Its metallic radius is $125$ pm. The edge length (in pm) of the unit cell and number of unit cells per cc of aluminium, respectively, are :
Question 8 :
$CsCl$ crystallizes in a cubic lattice that has a $Cl^-$ at each corner and $Cs^+$ at the centre of the unit cell. If $(r_{Cs^+})=1.69\overset{o}{A}$ and $(r_{Cl^-})=1.81\overset{o}{A}$, what is the value of edge length a of the cube?<br>
Question 9 :
Gold is plated with rhodium to give a base for mounting diamonds in modern jewellery. The rhodium-gold alloy consists of gold atoms in fcc structure with half the face centers being replaced by rhodium atoms. Formula of this alloy is :<br/>
Question 10 :
The ratio of the volume of a tetragonal lattice unit cell to that of a hexagonal lattice unit cell is: <div>(both having same respective lengths)</div>
Question 11 :
$AB$ crystallises in a bcc lattice with edge length an equal to 387 pm. The distance between two oppositely charged ions in the lattice is:<br/>
Question 12 :
In a solid $AB$ having $NaCl$ structure atoms, occupy the corners of the unit cell. If all the face centred atoms along one of the axis are removed, then the resultant stoichiometry of the solid is:<br>
Question 13 :
Iron crystallizes in several modifications, At about $910^o$C, the body centred $\alpha$-form undergoes transition to the face centred cubic $\gamma$-form. Assuming that the distance between nearest neighbours is same in the two forms at the transition temperature. Calculate the ratio of density of $\gamma$-iron to that of $\alpha$-iron at the transition temperature.
Question 14 :
A solid has three types of atoms $X,\ Y$ and $Z$. $X$ forms an $FCC$ lattice with $Y$ atoms occupying all the tetrahedral voids and $Z$ atoms occupying half of the octahedral voids. The formula of the solid is
Question 15 :
Radii of $A^+$ and that of $X^-$ and $Y^-$ have been given as<br/>$A^+=1.00$ pm<br/>$X^-=1.00$ pm<br/>$Y^-=2.00$ pm<br/>Determine the volume of unit cells of AX and AY crystals.<br/>