Page 1 :
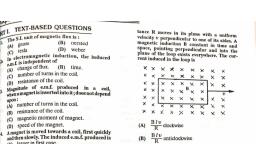
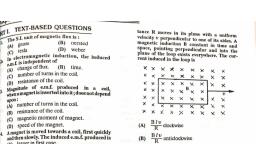
| aaa, rExT-BASED QUESTIONS, , <j anit of magnetic flux is :, Tbe, @), , , , , , , (B) oersted, gauss (D) weber, , tic induction, the induced, In clectrofipendent of ’, emt ange offiux. (B) time., a) number of turns in the coil., (9 ssstance of the coil, i of emf, 5 Maret, number of turns in the coil., (B) resistance of the coil., (C) magnetic moment of magnet., (D) speed of the magnet., 4 Amagnet is moved towards a coil, first quickly, snd then slowly. The induced e.m.f. produced is, (A) larger in first case., (8) smaller in first case., (C) equal in both cases., (D) larger or smaller, depending upon resistance of the coil., , S Refer to the figure. Deflection in the galYunometer (G) occurs, when :, , fg), , luced in a_ coil,, into it;doesnotdepend, , , , , , oma, , R MAGNET, , , , , , ~ the magnet is pushed into the coil., ( ) the magnet is rotated into the coil, 9 = Magnet is stationary at the centre of, , ) the number of turns in the coil is reduced., , ep (Karnataka Entrance, 1992, 1990), , Telatew 3 law of electromagentic induction is, ted to the law of a of, , (A), ) cha 4B) energy, , © Ne, (CET. 1998), , 0), wd cong at momentum., ‘“cting square loop of side L and resis, 10., , tance R moves in its plane with a uniform, velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A, magnetic induction B constant in time and, space, pointing perpendicular and into the, plane of the loop exists everywhere. The current induced in the loop is, , , , , , , , , , HM PR Me, ee Se ak ne, xX x x xX xX xX X X, Cue ue MM Mie, KMIMOM % 8, a, A RIM <M 4. MH MK se, SX RM Moat fed ie, , mM KM Mm RM Me, , (A) BEY clockwise, , (B) BT” anticlockwise, , (c) 2B 1 anticlockwise, , (D) zero (LLT. 1989), , Asquare shaped coil of side 10 cm and number, of turns 500 is placed perpendicular to mag, netic flux lines, which is changing at the rate of, , 1-0 Ts”, The e.m-f. induced in the coil is, , (A) 0-1V (B) 0-5V, (Cc) 1:0V (@) 5:0V, (C.P.M.T..1990), , A magnetic field of 2 x 107? T acts at right, , angles to a coil of area 100 cm? with 50 turns., The average e.m.f. induced in the coil is 0-1 V,, when it is removed from the field in the time ¢., , The value of ¢ is, (B) 001s, , (A) O-1s, (c) is (D) 10s, , (C.B.S.E, 1992), Magnetic flux ¢ (in weber) in a closed circuit of, resistance 10 {2 varies with time é (in seconds), according to the equation :, , o=5P-4641., , The magnitude of the induced e.m.f. in the, circuit at ¢ = 0-2 sis:, , (A) 0-4V (), (Cc) -2V (D), , -0:4V, na.
Page 2 :
11. Lenz's law is a consequence of the law of conservation of :, (A) charge only. (B) momentum only., €(C) energy only., (D) energy and momentum., (Pre-degree Kerala, 1992), 12. The direction of induced e.m.f. is given by, (A) . Fleming's left hand rule., (B) Fleming's right hand rule., (C) Lenz's law., (D) Biot Savart’s law., ly A straight conductor of length 0-4 m is moved, with a speed of 7 m s”! perpendicular to a, , magnetic field of intensity 0-9 Wb m7, The, induced e.m.f. across the conductor is :, , (A) 5:04V (B) ‘1:26V, (C) 2°52V (D) 25:2V, (Roorkee, 1982), , 14. A piece of wire is passed through the gap between the poles of a magnet in 0-1s. An emf, , of 4 x 107? Vis induced inthe wire. The magnetic flux between the poles of the magnet is, (A) 10 Wb (B) 4x 107 Wb, , (C) 4x10°?Wb = (D)_-:0-1 Wb, 15. Aconductor of length / is moved perpendicular, “to uniform, magnetic field, , Bwunicity 2 - pot *, vasshownin ~ % *||% xy*, figure. The x *xifeo x, emf, induced x ,, across the xxix x x, length of the ARK KK MK, conductor is, , (A) zero (B) Blv, , (C) Blu/2 (D) BPv/2, , (C.P.M.T. 1993), , 16. Anaeroplane in which the distance between the, tips of the wings is 50 m is flying horizontally, , with a speed of 360 km h™? over a place, where, , the vertical component of earth’s magnetic, , field is 2-0 x 10~* T. The potential difference, between the tips of the wings would be, , (A) O-1V (B) 1-0V, (©) 0-2V (D) 0-01V, (C.P.M.T. 1990), , 17. Acarmoveson a plane road. The induced e.m.f., in the axle connecting the two wheels is maximum, when it moves , (A) eastwards at the equator., (B) westwards at the equator., (C) eastwards in the latitude 45°,, (D) at the poles., , 18, The two rnils of a track insulated from, each other and the ground are connected to mil, Pains tN, , 19., , 20., , 21., , livoltmeter. What is the 7, livoltmeter, when a train pees the my., , 180 kmh! along th, , vertical component of earth's » Riven thar, 0-2 x 107° Wb m “and rails, lm? iy OTe Separatey, (A) 107?V (B) 10mv, , (Cc) 1V (D) Imv, , LL., , Two rails of a railway track 1 a <i, insulated from each other and the ty, connected to a millivoltmeter, What ae, reading on the millivoltmeter, when a nwt, travels at a speed of 20ms "al, Given that the horizontal componestofengt, magnetic field is 0-2 x 107‘ T., (A) 4mV (B) 0-4mv, (C) zero (D) 10mV, Eddy currents are, (A) — currents due to a changing magne:, (B) induced currents due to a high magnetic, , flux., , (C) induced currents in a inhomogeneous, , material., , (D) unstable currents ina conductor., , (Karnataka Entrance, 199!), , When a sheet of metal is placed in magoetic, , field, which changes from zero to 4 maximum, , value, induced currents are set up in the direc, tion shown in the diagram. What is the dire, tion of the magnetic field ?, , 4, , (A) Into the plane of paper., , (B) Out of the plane of the paper:, (C) East to west., (D) North to south. dé, An induction furnace works on the vein e |, (A) selfinduction (B) mutual at, , (C) eddycurrents () Pres el, , ‘The SI unit of inductance, the ben"?, written as, , (A) weber ampere™?, (@) volt second ampere, (C) jouleampere™? (D) came |