Page 1 :
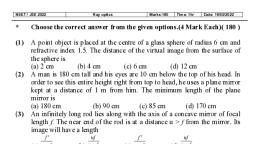
When a pencil is partially immersed into water, inclined to the surface of water, it appears to be shortened and bent at, coming from A' and the apparent position of the immersed part is seen to be as CA', Hence, the pencil immersed in, the surface of water as shown in fig. The rays of light starting from A bends away from the normal and appear to be, (Application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation based questions), 1. Read the following and answer the questions from 1.I to 1.4:, water appears to be bent in water., A., 1.I The refractive index of glass is 3/2, What will be the speed of light in glass?, (a) 2 x 10 m/s, (b) 2.25 x 10 m/s, (c) 1.5 x 10 m/s, (d) 1.33 x 10 m/s, 1.2 Ifa ray of light falls normally on a glass slab then the angle of refraction in glass slab is:, (a) 90°, (b) 45°, (c) 30°, 1.3 Twinkling of stars is due to:, (d) 0°, (b) partial absorption of light in the atmosphere, (d) refractive index fluctuations in the atmosphere, (a) periodic bursts of light from the star, (c) interference between light coming from various, 1.4 A stick partially immersed in water appears broken due to :, (a) reflection, (b) refraction, (c) total internal reflection, (d) dispersion, 2. Read the following and answer the questions from 2.1 to 2.4:, Table: Image formation by a convex lens, Position of the object, Position of the image, Size of the image, Nature of the image, At infinity, At the focus F2, Highly diminished, Real and inverted, Beyond 2F,, Between F, and 2F2, Diminished, Real and inverted, At 2F,, At 2F2, Same size, Real and inverted, Between F, and 2F,, Beyond 2F2, Magnified, Real and inverted, At F1, At infinity, Highly magnified, Real and inverted, Between O and F,, On the side of the object, Magnified, Virtual and erect
Page 2 :
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal, DEEPAK CBSE Sample Papers Science 10, to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus., The lenses forms different types of images when object placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel, 2.1 Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the same size of the object?, A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor's head, 2.3 A convex lens forms an image of magnification-2 of height 6 cm. The height of object is :, 4.1 When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is:, 80, (a) At the principal focus of the lens, (c) At infinity, (b) At twice the focal length, focus., 2.2 Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?, (a) Water, (c) Plastic, (b) Glass, (d) Clay, (a) 4 cm, (c) 2 cm, (b) 3 cm, (d) 6 cm, 2.4 If an object is placed at 2F in front of a convex lens, the image lies:, (a) at F, (c) between F and 2F, (b) at 2F, (d) beyond 2F, 3. Read the following and answer the questions from 3.1 to 3.4:, When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between, focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed., As me object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens, from focus to infinity. Also the size of image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted., A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective to the position of the object., 3.1 The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is:, (a) at focus, (b) at 2F, (c) at optical center, 3.2 When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is :, (d) between F and 2F, (a) real and smaller, (b) virtual and inverted, (c) virtual and smaller, (d) real and erect, 3.3 The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is:, (b) point in size, (d) same as that of object, (a) small, (c) highly magnified, 3.4 When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is :, (b) at 2 F on the other side, (d) between F and optical center, (a) at F, (c) at infinity, 4. Read the following and answer the questions from 4.l to 4.4:, The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image, is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual, When the two, reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual, A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is, placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect., mirrer to focus light on body parts like eyes, cars, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified, ofthe obiect. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and, erect image of an object., (a) larger than the object, (c) same size as that of the object, (b) smaller than the object, (d) highly enlarged.
Page 3 :
81, 4.2 No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be -, (a) plane, (b) concave, (c) convex, (d) either plane or convex, 4.3 A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body, of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic from the top., (a) Plane, convex and concave, (b) Convex, concave and plane, (d) Convex, plane and concave, (c) Concave, plane and convex, 4.4 To get an image larger than the object, one can use:, (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror, (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror, (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror, (d) a plane mirror.