Page 2 :
DISADVANTAGES OF MARGINAL COSTING
Page 3 :
1. It is based on an unrealistic assumption that all costs can be segregated into fixed and variable costs. In the long term sales price, fixed cost and variable cost per unit may vary., , 2. All costs are not divisible into fixed and variable. There are certain costs which are semi-variable in nature. The separation of costs into fixed and variable is difficult and sometimes gives misleading results., , 3. Under marginal costing, stocks and work in progress are understated. The exclusion of fixed costs from Stock Valuation affects profit, and true and fair view of financial affairs of an organization.
Page 5 :
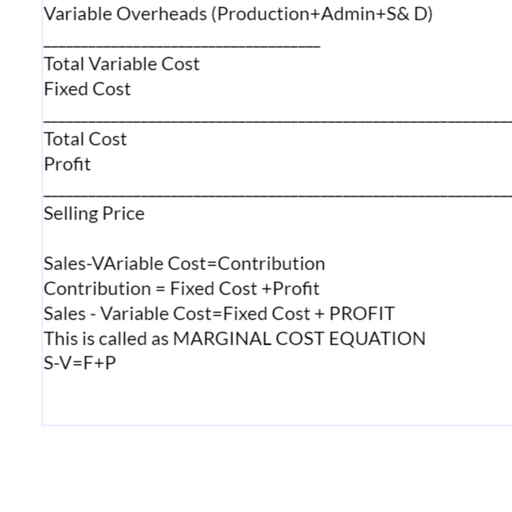
CONTRIBUTION, Contribution or the contributory margin is the difference between sales value and the marginal cost , Contribution (C) = Sales (S) – Variable Cost. , It is obtained by subtracting marginal cost from sales revenue of a given activity. , It can also be defined as excess of sales revenue over the variable cost. , The contribution concept is based on the theory that the profit and fixed expenses of a business is a ‘joint cost’ which cannot be equitably apportioned to different segments of the business., In view of this difficulty the contribution serves as a measure of efficiency of operations of various segments of the business.
Page 6 :
EXAMPLE
Page 7 :
Some of the facts about marginal costing are depicted below, Marginal costing is not a distinct method of costing like job costing, process costing, operating costing, etc., but a special technique used for managerial decision making. , Marginal costing is used to provide a basis for the interpretation of cost data to measure the profitability of different products, processes and cost centres in the course of decision making., It can, therefore, be used in conjunction with the different methods of costing such as job costing, process costing, etc., or even with other techniques such as standard costing or budgetary control.
Page 8 :
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MARGINAL COSTING AND ABSORPTION COSTING
Page 10 :
It is a managerial tool showing the relationship between various ingredients of profit planning viz., cost, selling price and volume of activity. , As the name suggests, cost volume profit (CVP) analysis is the analysis of three variables cost, volume and profit. , Such an analysis explores the relationship between costs, revenue, activity levels and the resulting profit. It aims at measuring variations in cost and volume., Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Page 11 :
TO BE CONTINUED