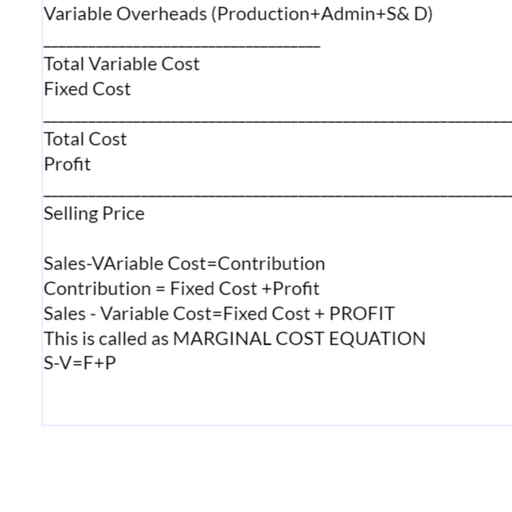
Page 2 :
WHAT WE ARE GOING TO LEARN, • Overtime- Meaning, Approval, Causes, , • Cost of Overtime, • Disadvantages of overtime, • Controlling overtime, • Leave Salary, • Time and Motion Study
Page 3 :
MEANING, It is the extra time worked by a worker over and above the normal working hours., Worker is paid higher rate of wages for this overtime. It can be paid for extra shift, work, hazardous work and working beyond normal working hours.
Page 4 :
APPROVAL, Overtime work should be authorised by the, designated authority, generally works, manager. The list of workers doing, overtime is approved and sent to payroll, department. The extra wages are paid, according to workers’ time card.
Page 5 :
CAUSES OF OVERTIME, 1., , To achieve scheduled production., , 2., , To complete rush orders., , 3., , Seasonal production and heavy demand in season.
Page 6 :
FOR HIGHER WAGES, , Labour Shortage, , Machine Breakdown
Page 7 :
WHAT’S IN DEMAND NOW?
Page 8 :
OVERTIME COST, • 1. Direct Cost Method- under this method overtime cost is directly charged to the, job concerned., , • 2. Overhead Method- under this method overtime cost is treated as overheads. This, cost can be charged to a. department causing delay or b. department where work is, done or c. standing order number as works overheads., • 3. Costing Profit & Loss A/c – overtime required to due to abnormal causes is, charged to Costing Profit & Loss A/c.
Page 9 :
DISADVANTAGES OF OVERTIME:, 1., , Causes extra labour cost, , 2., , Overall productivity of a worker can be lowered due to exertion., , 3., , Health concerns for workers., , 4., , Workers may feel not getting equal opportunity to do overtime.
Page 10 :
Causes extra light cost for night, hours., , Increases wear and tear of Plant and, Machinery.
Page 12 :
CONTROL OF OVERTIME, • 1. Appoint competent officer to authorize overtime, , • 2. Prepare Statement showing overtime requirement Departmentwise., • 3. Fix up higher limit of overtime, • 4. Do not allow overtime without sanction, • 5. Compare output in normal hours and overtime hours, • 6. Send periodic report to top management.
Page 13 :
LEAVE SALARY, • The Factories Act provides for annual leave with full pay for a certain number of, days. Workers also entitled for medical leave, casual leave, special leave, etc., • These leaves can be encashed, if not exercised. However in some cases it is not, allowed., , • Under Direct Cost method leave salary is added to labour cost., • Under overheads method, leave salary is added to overheads.
Page 14 :
TIME AND MOTION STUDY, • Time study decides the time spent on each element of a job., , • Total time for all the stages for a job is called as Standard Time., • Standard time is the time taken by an average worker to complete a job under, normal working conditions.
Page 15 :
TIME AND MOTION STUDY, • Motion Study divides the work into basic operations of a job or a process. It, eliminates unnecessary operations. Motion study finds the most scientific and, systematic method to perform a job. Both are complementary to each other.
Page 16 :
Assembly line at Ford, Motors
Page 17 :
BENEFITS OF TIME AND MOTION STUDY, • 1. Optimum utilization of resources, , • 2. Helps in deciding labour requirements, standard labour cost, fair wages, and, incentive wages., • 3. Helps in finding best method of operation., , • 4. Facilitates improvement in work methods., • 5. Facilitates budget, • 6. Assists in proper planning and control.
Page 18 :
THANK YOU