Page 2 :
What is Standard Cost ?, A measure of acceptable performance in regard to cost., ICWA- predetermined cost which is calculated from management’s standards of efficient operations and the relevant necessary expenditure., Dr. Sumedha Naik, 2
Page 3 :
Features of Standard Cost, Predetermined , Based on past experience, For measuring efficiency of future production, In terms of money or quantity, What cost should be, Recorded in books of accounts, For controlling cost, For each elements of cost, normal, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 3
Page 4 :
What is Standard Costing?, A system of cost accounting, ICWA- the preparation and use of Standard cost, comparison with actual, variance analysis, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 4
Page 5 :
Applicability, Standard product , Sufficient volume of production, Standard processes, methods of production, Controllable cost, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 5
Page 6 :
Distinction, Standard Cost, Should be , Planned cost, Where Standard Costing is used , Recorded in books, Serves control purpose, Estimated Cost, Will be, Expected actual, Where historical costing is used, Not recorded in books, No, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 6
Page 7 :
Distinction, Standard Costing, Scientific basis, Deals with Manufacturing of product or process, Concerned with production and distribution expenses, No help in projection of Financial statements , Variance analysis is done, Should be cost, Budgetary Control, Past performance and future trends, Deals with whole operation/department , Concerned with all types of incomes and expenses , , Helps in projection of financial statements , No variance analysis , Would be cost, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 7
Page 8 :
Benefits of Standard Costing, Aid to management – planning, organizing, coordinating, motivating, controlling, etc., Yardstick for efficiency, Formulation of production and pricing policies, Quick reports, Less cost of operation, Covers limitations of historical costing, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 8
Page 9 :
Benefits of Standard Costing, Improves efficiency, Simplifies valuation of inventory, Cost consciousness in employees, Effective delegation of authority, Reduces waste of material and idle time, Management by exception based on variances, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 9
Page 10 :
Limitations of Standard Costing, Unsuitable for small concerns- higher cost, Technical skill required, Causes of variances-controllable or uncontrollable, Revision of Standards is difficult, Realistic Standard?, Higher Standards-stress for employees, Costly, Analysis of past events, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 10
Page 12 :
Cost Centres, Location of item or equipment, Personal or impersonal, Necessary to determine responsibilities, delegation of authority, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 12
Page 13 :
Classification of Accounts, Assigning Codes, Code=symbol of a particular item, Example- Direct Material 01-05, Direct Labour 06-10, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 13
Page 14 :
Types of Standards, Basic Standard –, For indefinite period, Unchanged for longer period, Established and operated for a number of years, Not useful for cost control, Suitable for fixed costs like rent, Salaries, etc., Dr. Sumedha Naik, 14
Page 15 :
Types of Standards, Current Standard:, For limited period, Relevant to current conditions, Revised at regular intervals, Three types, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 15
Page 16 :
Types of Current Standard, Ideal Standard: , theoretical, difficult to attain, Assumes that performance is perfect, Don’t consider wastage, Unrealistic, Adverse variance, Discourages employees, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 16
Page 17 :
Types of Current Standard, 2. Expected Standard:, Time bound, Based on expected performance, Considers wastage, Meaningful and realistic, Useful for cost control, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 17
Page 18 :
Types of Current Standard, 3. Normal Standard:, Past performance Standard, Based on Average past performance, Eliminates the cost variations caused due to trade cycle, Useful for planning and decision making, Difficult to apply in practice, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 18
Page 19 :
Setting Standards, Standard Committee, Need cooperation and co ordination, All functional heads, Important role of Cost Accountant, Collection of cost data for accuracy, Standard for each element of cost, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 19
Page 20 :
Standard Direct Material Cost, Standard Material Specifications-design, quality, availability, Standard Material Usage- normal loss, unavoidable loss, finished goods volume, help of production engineer, Standard Material Price-average price of materials, discounts, freight, other handling charges, future trends,, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 20
Page 21 :
Standard Direct Labour Cost, Operations involved, skill required, volume of work, availability of labour, help of personnel department , Standard Hours: time and motion study, systematic time setting, estimates, past performances of labour, use of stop watch, waste and Idle Time, help of cost accountant, Standard wage rates: past rates, expected increase, wage board recommendations, overtime, incentives, bonus plans, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 21
Page 22 :
Standard Direct Expenses, Matter of common sense, Past expenses, Future expectations, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 22
Page 23 :
Standard Overheads, Complex procedure, Estimation of indirect material, indirect labour and indirect expenses is difficult, Setting Standard overheads for estimated production is difficult, Estimates depend upon efficient budgetary control, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 23
Page 24 :
Standard selling prices, Marketing department , In consultation with Managing Director, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 24
Page 25 :
Revision of Standards, If incorrect Standards are applied, If changes in Government policies, laws, etc., If change in tax, duty by authorities, If change in price by authorities, If change in minimum wages, If outdated, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 25
Page 26 :
Variance Analysis, Variance is the difference between the Standard cost and actual cost, Variance Analysis is the process of analysing variances, Variances are subdivided, So as to fix responsibility for a particular performance, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 26
Page 27 :
Variance Analysis, Favourable or unfavourable, Favourable = F, Adverse=A, Cost control through variance analysis, Where occurred, Which cost elements, What are causes, Who are responsible, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 27
Page 28 :
Benefits of Variance Analysis, To evaluate individual performance, To assign responsibilities, To motivate individuals, To find out causes, To take corrective action, To reveal difficulties, To ensure cost control, To manage by exceptions, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 28
Page 29 :
Two Categories, Price Variance, Volume or Usage Variance, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 29
Page 30 :
Price Variance, Material Price Variance, Labour Rate Variance, Variable overhead Variance, Fixed overhead Expenditure Variance, Sales Price Variance, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 30
Page 31 :
Usage Variance, Material Usage Variance, Labour Efficiency Variance, Fixed overhead Volume Variance, Sales Volume Variance, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 31
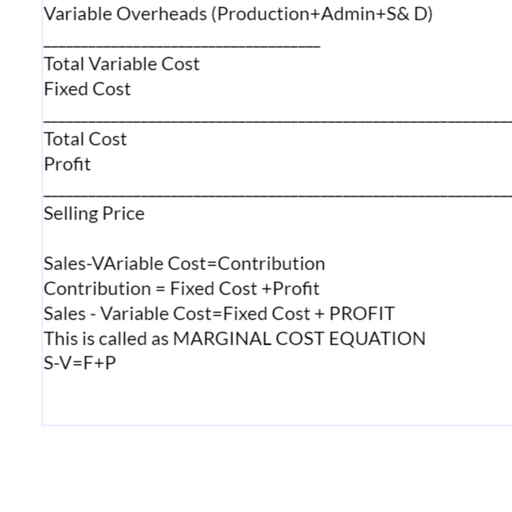
Page 33 :
Material Price Variance, Part of MCV caused due to difference between Standard Price of Material and Actual Price of Material used., MPV=(SP-AP) × AQ, AQ= Actual qty used, SP=Standard Price, AP= Actual Price, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 33
Page 34 :
Causes of MPV, Changes in Purchase Price, Delivery Cost, Landing Cost, Qty of Materials, Tax Policy, Failure to get discount, Use of cheaper substitute, Fraud in Purchasing, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 34
Page 35 :
Material Usage Variance, Part of MCV caused due to difference between Standard Qty of Material and Actual Qty of Material used., MUV=(SP-AP) × AQ, AQ= Actual qty used, SP=Standard Price, AP= Actual Price, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 35
Page 36 :
Causes of MUV, Use of different grade of Materials, Design change of product, Change in labour performance, Wastage of scrap, Defects, Rejected Material, Pilferage, Non Standard Material, Incorrect booking of Material usage, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 36
Page 38 :
Labour Rate Variance, The portion of LCV caused due to difference between Standard Wage Rate and Actual Wage Rate, LRV= (SR-AR) ×AH, SR= Standard Rate, AR= Actual Rate, AH= Actual Hours, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 38
Page 39 :
Causes of LRV, Higher wage rates, Change in grade of labour, Addition to workers, Change in method of payment of wages, Trade union pressure, Casual Workers, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 39
Page 40 :
Labour Efficiency Variance, It is portion of LCV caused by difference between the Standard Hours for actual output and Actual hours, LEV=(SH-AH) ×SR, SH=Standard Hours, AH=Actual Hours, SR=Standard Rate, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 40
Page 41 :
Causes of LEV, Slow workers, Factors beyond control, Poor working conditions, Workers restrict to output, Abnormal length of run, Quality of supervision, Change in production method, Change in tools, Change in quality of materials, Incorrect booking of labour time/hours, Dr. Sumedha Naik, 41