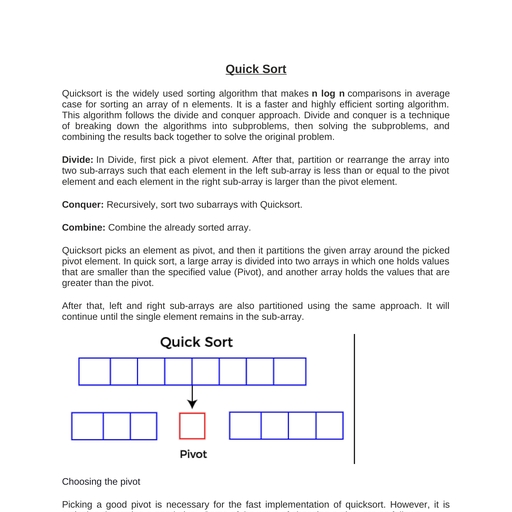
Page 1 :
Introdudion- Decision theory is a systematic procedure, to identify the best posible decision, the various available alternatives., among, Decision theoy which is cdefined as the process of, logical and quantitative analysis of all factors that, influences the cdeciston problem, assists the, decisien -maker in analysing these poroblems with, several cowues of action and s., consequences, Complete Uncestainty, Decision-Maktng, under uncertainty, Complate Certainty, Decision, making, under, Certainty, Degree ot., Certainty, Decision, Making, under Risk, Decision Making Situations, Accasiding to fishbun, solving the decision model, consists of finding a, exxpected related value of which is atleast as great, as the expected seelative value of any ather, stratogy in a, of a, strategy for action, the, specified set. The perspective coriteria, strategy will be maxcimisation of alecision, maker's total expected relative value.", Elements in Decision Making-, D Decision - Makey, 2) Goals, 3) Beference or Value System, 4) Acts/Courses of Action, 5) States ob Nature, 6) Payott, 1) Payoff Table, 8) Opporitunity loss Table/Regset Table
Page 2 :
steps of Decision Making Psroces -, ) Define the Psroblem - The firet actiou a olecision, ů to, makei has to take, clearly define the peroblem., "A prioblem well dlefined half -solved "., 2) List all possible alternative - Once the problem, a, ů clearly defined, decision maker must take is to list all the, possible alternative that can be considered iu, the decision., then the next actiou, 3) Identify the expected future events, The third step tor the decision maker is to, list all the future events that, these future eveuts, nature in decision theoy, occur ., may, are termed as, states of, 4) Coutruct a payoff table -, The decision makes, now construct, a, payoft table (table eepresenting profit., benefit , ete.) for each possible conubination, of altirnative course of actiou and state, nature ., of, 5) Select optủmum decisionacriterion, decision' maker coustructs, then he she will choose criterion, sresults, Once the, payofs table, in largest payoft, quantitative, which, The crite on, ar qualitative., Decision-, be economič,, may, 6) Apply the model cnd make, Fenally the decision maker applies the, selected model to the data, to make the decisiom., which helps, De