Page 1 :
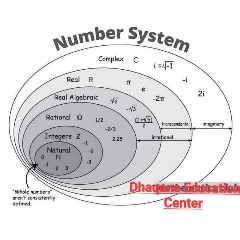
Paper Code: GE3B-03, Basic Mathematics and Statistics, Total Credit: 6, Total hours of lectures: 60 hours, Course Objective: The course is designed to provide a basic applied knowledge of mathematics. The, students will be to apply the number system & basic algebra, set theory, determinants and matrices, limits,, continuity, differentiation & Integration, data frequency & distribution and measures of central tendency, and measures of dispersion for solving business problems., statistical problems, Sl, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, , Course Outcome, Remembering, Understanding the course, Applying the general problem, Analyse the problems, Evaluate the problems after analysing, Create using the evaluation process, , Module, Number, , Content, , Mapped modules, M1,M2,M3,M4,M5,M6, M1,M2,M3,M4,M5,M6, M1,M2,M3,M4,M5,M6, , Total, Hours, , %age of, questions, , Blooms, Level, (if, applicable), , M1, , The Number System and Basic, Algebra, , 8, , 10, , 1,2, , M2, , Set Theory and Permutation, and Combination, , 10, , 15, , 1,2, , M3, , Determinants and Matrices, , 10, , 15, , 1,2, , M4, , Limits,, Continuity,, Differentiation and Integration, , 16, , 35, , 1,2,3, , M5, M6, , Data, Frequency Distribution, Measures of Central Tendency, and Measures of Dispersion, , 6, , 10, 15, , 1,2,3, 1,2,3, , 10, 60, , Sl., 1., , 2., , Remarks (If any), , 100, , Topic/Module, Hour, Module 1 : The Number System – Positive and Negative Integers, Fractions, Rational and 8, Irrational Numbers, Real Numbers, Problems Involving the Concept of Real Numbers., Basic Algebra – Algebraic Identities, Simple Factorizations; Equations: Linear and Quadratic (in, Single Variable and Simultaneous Equations). Surds and Indices; Logarithms and Their Properties, (Including Change of Base); Problems Based on Logarithms., Module 2 : Set Theory-Introduction; Representation of sets; Subsets and supersets; Universal and 7, Null sets; Basic operations on sets; Laws of set algebra; Cardinal number of a set; Venn Diagrams;, Application of set theory to the solution of problems, Permutations and Combinations – Fundamental principle of counting; Factorial notation., Permutation: Permutation of n different things; of things not all different; restricted, permutations; circular permutations. Combination: different formulas on combination;
Page 2 :
3., , 4, , 5., , 5., , 6., , complementary combination; restricted combination; Division into groups. Mixed problems on, permutation and combination, Module 3: Determinants- Determinants of order 2 and 3; minors and cofactors; expansion of 7, determinants; properties of determinants; Cramer’s rule for solving simultaneous equations in two, or three variables, Matrices- Different types of matrices; Matrix Algebra – addition, subtraction and multiplication of, matrices; Singular and non-singular matrices; adjoint and inverse of a matrix; elementary row /, column operations; Solution of a system of linear equations using matrix algebra., Concept of Eigen Value, Eigenvector., Module 4: Differentiation: Meaning & geometrical interpretation of differentiation; standard 4, derivatives (excluding trigonometric functions); rules for calculating derivatives; logarithmic, differentiation., Integration: Meaning, Standard formulas, Substitution, Integration by parts (Excluding, Trigonometric functions), Module 5: Data-Collection, Editing and Presentation of Data: Primary data and secondary data; 7, Methods of collection; Scrutiny of data. Presentation of data: textual and tabular presentations;, Construction of a table and the different components of a table. Diagrammatic representation of, data: Line diagrams, Bar diagrams, Pie charts and divided-bar diagrams., Module 5 : Frequency Distributions- Attribute and variable; Frequency distribution of an 7, attribute; Discrete and continuous variables; Frequency distributions of discrete and continuous, variables; Bivariate and Multivariate Frequency Distributions. Diagrammatic representation of a, frequency distribution: case of an attribute; case of a discrete variable: column diagram, frequency, polygon and step diagram; case of a continuous variable: histogram and ogive., Module 6 : Measures of Central Tendency- Definition and utility; Characteristics of a good 10, average; Different measures of average; Arithmetic Mean; Median; Other positional measures –, quartiles, deciles, percentiles; Mode; Relation between Mean, Median and Mode; Geometric and, Harmonic Mean. Choice of a suitable measure of central tendency., , 7, , Module 7: Measures of Dispersion- Meaning and objective of dispersion; Characteristics of a good 10, measure of dispersion; Different measures of dispersion – Range, Quartile deviation, Mean, deviation, Mean Absolute deviation, Standard deviation; Comparison of the different measures of, dispersion. Measures of relative dispersion – Coefficient of Variation. Combined mean and standard, deviation, Combined mean and standard deviation., Introduction to Skewness, Kurtosis, Moments., Suggested Readings, 1. H. S. Hall & S. R. Knight – Higher Algebra; Radha Publishing House., 2. Reena Garg, Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishing House., 3. Sancheti& Kapoor – Business Mathematics; Sultan Chand & Company., 4. R. S. Soni – Business Mathematics – Pitambar Publishing House., 5. N G Das, Statistical Methods (Combined edition volume 1 & 2), McGraw Hill Education., 6. J K Sharma: Business Statistics, fifth edition, Vikas Publishing house.