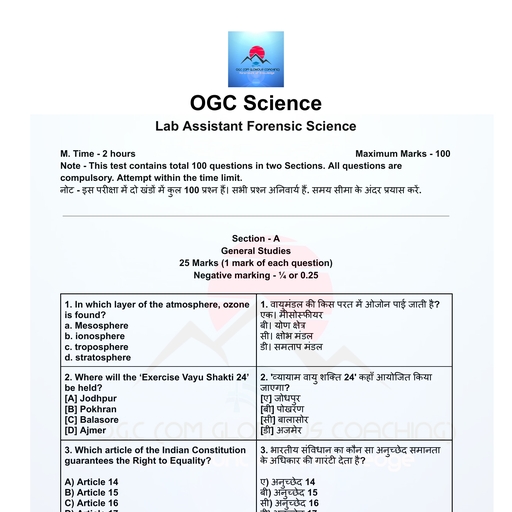
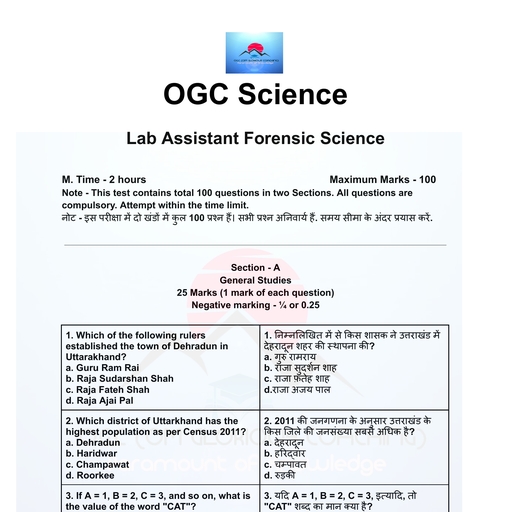
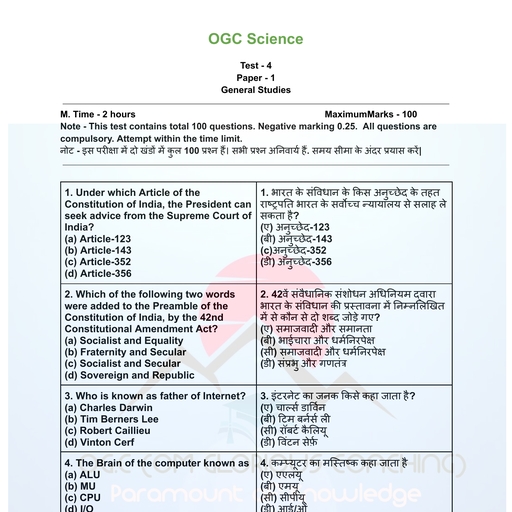
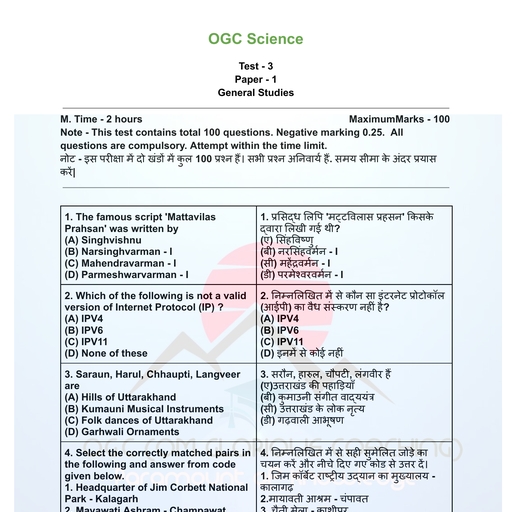
Page 1 :
6, , Silicones and Phosphazenes, , Syllabus: Silicones and phosphazenes as examples of inorganic, polymers, nature of bonding in triphosphazenes., , 6.1. Silicones, Silicones are the, , synthetic organic, , repeated R, SiO units. These, , linkageThese, , are, , units, , are, , silicone, held, , polymers containing, together by Si-0-Si, , also called as polysiloxanes. They, have the, where R is an alkyl or aryl group The, , general, , formula (R, Sio),, empirical, formula of these polymers, i.e., R, Sio is similar to that of a ketone, , R, CO, therefore, they are called as silicones. However, they are, altogether different from ketones as they do not contain doubly bound, oxygen. These polymers may be linear, cross linked orcyclic. They have, very high thermal stability and, therefore, they are also called as high, , temperature polymers., 6.2. Classification, Silicones have different nature due to the difference in the lengthof, chain structure, size of alkyl and aryl groups etc. On this basis silicones, , are classified as, the, , ) Linear or straight chain silicones: These are obtained by, or diaryl, hydrolysis and condensation polymerization of dialkyl, substituted silicon chlorides (R,SiCl, or Ar, SiCl,)., , R, , R, , R, , -0-Si-0-Si-0-Si-0-, , R, , R, Linear silicone., , (204), , R
Page 4 :
Silicones a n d P h o s p h a z e n e s, , 207, , R, , R, , Cl-Si-CI +3H,o, , -3HCI HO, , CI, , Si -OH, OH, , Alkyl silane triol, R, R, , R, , R, , -0-Si-0-Si-0-Si-, , Condensation, nHO-SiOH, , Polymerization, -H20, OH, , -0-Si-0-Si-0-SiR, , R, R, Cross linked silicone, , 6.4. Properties, 1. The nature of a silicone polymer depends upon the length ofthe, chain, siz, of the alkyl or aryl groups present and the extent of cross, lower silicones are oily liquids, those having chains are, inking, , The, , viscous dits, jellies and greases while those having long chains are rubber, , like elastomers and resins., 2., , They are highly sáble towards heat., , 3. The lower silicones, , are, , soluble in organic solvents like ether,, , carbon tetrachloride, benzene etc., , However, when heated in air, , at, , They are resistant to oxidation., oxidized and this leads to cross linking., 550400°C, they are rapidly, most of the, are not affected by, and, inert, S. They are chemically, chemical reagents., 4., , 6.5 Uses, 1. Silicone oils, , baths,high vacuum, , are, , used in high temperatureoil, , pumps etc., used to form, , These polymers are, wool etc., paper, glass, wood., clothes,, ., , used, , Ven, , are, These polymers, at very low temperature., are, , water resistant coatings, , as greases,, , used, , varnishes, , as excellent, , Silicone rubbers, appliances., motors and other electrical, , and, , insulators, , can, , be, , on, , used, , for electric
Page 6 :
aionesand Phosphazenes, , (i) A better method involves the, amounts in, , quimolar, , a, , rachloro ethane., , nPCL +nNH,, , and, 160°C inPC,the, , (PNCI,),, , 6.8 Properties, , 209, , reaction of, , sealed tube at, , +, , 4n, , NH,Cl in, , presence, , of, , HCI, , white crystalline solid, M.Pt., benzene, CCl, and ether. 114C and BP., 256°C.k, crystalline solid, M.Pt. 123.5, B.Pt. 328.5°C and (PNCl,), is alsoo, has lower, the above solvents. These, solubility, compounds, are, imitating, and, poisonous., 2., of heat: On, is, , 1,, , a, , is soluble in, , a, , Action, , heating, , nolymerizes give, to, , a, , rubber like, , ofhigh molecular weight., these, , polymers, , are, , reactions, , very reactive and, , mucleophiles, , such, , mechanism., , These reactions, , (), , 250°C, (PNCI,),, , or, , (PNCL, ),, , elastic product or amixture of chlorides, , Nucleophilic substitution, , 3., , at, , :, , The chlorine atoms of, , can be replaced by, , many, , as-OH,-NH,-OR,C,H, SCN, F" by S, given as, , are, , Hydrolysis : The chlorine atoms in these compounds are quite, , reactive. Hence, on hydrolysis some or all the chlorine atoms can be, , by-OH groups. The hydrolysis of trimer is slow.However, it, Teplaced, Can be completely hydrolysed by using aqueous ether., Cl, , CI, , HO OH, , N, , CL, , C+6H20 6HCI, , CI, , CI, , N, HO, , OH, , HO, , OH, , Tri phospho nitrilic, , OH, , chloride, , NH, , HN, , Isomerizes HO, OH, NH, , The, , hydrolysis of, , tetramer, , takes, , place, , rapidly, , by boiling, , water.
Page 11 :
214, , Inorganic Chemistry-I, 4., , Basic, , Properties:, , The, , nitrogen, , atoms, , of, nitrilio, chlorides contain lone pair of electron, hence they actphospho, as a base., Thevy, react with SO,, HCIO, or AICI, to form addition, compounds., a, , (PNCI,), +3SO,>(PNCI,), .3S0,, (PNCI,), +HCIO, (PNCI,), .HCIO,, , (PNCI,) +2HCIO,, , (PNCI,), +2AICI,, , », , (PNCI,), .2HCIO,, , (PNCI,),.2AICI,, , 6.9. Usees, They are used:, i) As catalyst in the manufacture of silicones., , ii) In flame proofing fabrics, oil additives etc., 6.10. Structure of Triphospho Nitrilic Chloride, Electron diffraction measurements show that, triphospho nitrilic, chloride, (PNCI,), has a planar six membered ring structure. The ring, contains phosphorus and nitrogen atoms in alternate, positions having, equal bond distance of 1.60 A. It has a resonance structure similar to, benzene and possesses an aromatic character., , CI, , CI, , C, C, , C, , Ci, N, , C, , CI, , ,Cl, , CI, , The nitrogen atomns, in the ring are Sp, , hybridized, , CI, , N, , CI, , 160A, , whereas, , phosphorus atoms are, , sp hybridized. Thebond, tengths and bond angles, , C, , CI, , CR120C, , shown in figure, Fig. 6.1. Structure of Triphospho nitrilic chloride, below, This structure is supported by Raman and infrared spectr, , are, , Triphospho nitrilic chloride involves p, - d, bonding unlike benzene, which involves p. - P, bonding. The extent of T-bonding 1s, , appreciable as the P-N bond distance in triphospho nitrilic chloride, shorter (1.60 A) than normal PN single bond distance 1.78 A.
Page 12 :
SiliconesandPhosphazenes, , 215, , Exercises, Objective Questions, , Which of the, , 1, , following statement is not, , (a) Silicones are also called as, b) The properties of silicones are, (b), , correct about, , polysiloxanes., , silicones?, , to those of, Silicones are high temperauresimilar, nes., ketones., polymers, , very high thermal stability., (d) Silicones have the general, , because, , of their, , formula, The high temperature polymers of (R, Sio), , 2., , silicon are called-, , (a) Silicates, cSilicones, , (b) Silanes, , (d) Silicon halides., Silicones have the structural unit-, , 3., , O, , (a)-Si-Si, R, , -Si-0, , R, , R, R, , c), , (d)-Si=0|, , Si-, , R, , R, , T h e hydrolysis and condensation polymerization of alkyl or, , aryl tri chloro silanes give, (a) Linear silicones, , (b) Cyclic silicones., e ) Cross linked silicones, (d) None of these., 5., , elemental, n e chloro alkanes react with, presence, , of copper to give chloro, , silanes., , as, a) Rochow Muller process, (c) Dewar processS, 6., , uch of the following, 2), , They are used in high, , b) They are, , as, h e y are used, , (b) Craig process., (d) Mitchell process, , statement, , polymers?, , is not, , temperature, , excellent, , silicon at 300°C in the, The process is known, , silicone, correct about, , Oil, , insulators, , batns., , for electric, , motos.
Page 13 :
216, , Inorganic Chemistry-ll, (c) They, , are, , used to form water resistant, , coatings on paper., clothes etc., d) They are used in the manufacture of fire, proof clothes., The basic unit of, , 7., , (a) PNCI, , polyphosphonitrilic.chlorideisPNCl, , (c) PN2 Cl, 8., , The, , replacement, , (d) PNCl3, , of -Cl atom from, , phosphazene takes place by mechanism, , (& S, , 6) S, , ) Se, 9., , P-CI part of, , Phospham is-, , (a) PNg Cls, , brNg (NH3, , (c)Pg Ng (NH2 )3, 10., , (d) PNg (NH26, , Which is used in the manufacture of fire, proof clothes ?, , (a) Borazine, (b) Silicone, (c) Silane, , (d Phosphonitrilic chloride, 11. Most,of the cyclo triphosphazenes have -, , aplanar structure, (b) tetrahedral structure, (c) puckered ring structure, (d) chain structure., 12. In the structure of triphospho nitrilic, and phosphorus atoms in the ring are, , chloride, the nitrogen, hybridized, respectively, , as, , (a) sp, sp, , b),sp, , s p , sp3, , d) sp, sp, , II. Fill in the Blanks, 1., , Silicones are very high molecular weight polymers which, contain ., , 2., , linkage., , The hydrolysis and condensation polymerization ofdialky, or diaryl substituted silicon chloride gives, silicone.
Page 14 :
Silicones and Phosphazenes, , 3., , 4., , Silicone, , .., , i s used in sealing of, , 217, , joints of jet air craft., , Phosphazenes have the general formula, , 4., , 5., Phospham is...., 5., Most ofthe cyclo triphosphazenes have . . Structure., 6., chloride involve, 7. Triphosphonitrilic, bonding., is (PNCl2 )ai is, bond, length, P-N, 8., ., , ., , True/False Statements, , 1., , The silicone polymers are highly stable towards heat., , 9The viscosity of silicone oils is much affected by a variation in, temperature., , 3., 4., , Silicones are chemically very reactive., Silicone rubbers are mixed in the paints to make them damp, resistant., , 5., 6., 7., , Polysiloxanes are isoelectronic to polyphosazenes., to, Triphosphonitrilic chloride on heating at 250°C polymerizes, give a rubber like elastic product., useful products, Phosphazenes give a variety of industrially, , with the, 88., , The, , help of nucleophilic addition, , structure, , of, , F, , reactions., , cyclo triphosphazene, , is stabilized, , by, , resonance., , Answers, I. Objective Questions, , 1., 5., 9., , (b), (a), , 2., , (c), , 6., , (d), , 7., , b), , 10., , (d), , 11., , Il. Fill in the, , Blanks, , 1. Si-0-Si, 3. rubber, , 5. PN (NH)3, 7. pTdr, , (b), (b), , 4., , (c), , 8., , (c), , (a), , 12., , (c), , 2. linear, 4.(PNX2n, 6. planar, 8. 1.60 A
Page 15 :
Inorganic Chemistry-ll, , 218, II. True/False Statements, , 3., , False, , 1, , True, , 2., , False, , 5., , True, , 6., , True 7.False, , 4., , True, , 8. True, O00