Page 1 :
New Education Society’s, , Arts, Commerce and Science College, Lanja, Department of Botany, Class: S.Y.B.Sc. Semester - 4, , Unit – II Pteridophyta and Paleobotany
Page 2 :
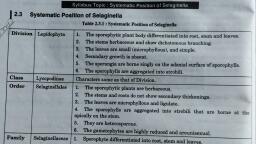
Systematic Position of Sellaginella, Division: Lepidophyta; The Sporophytic Plant Differentiated into Root, Stem and Leaves, , The stems herbaceous and shows dichotomous branching., The leaves are small (microphyllous) and simple., , Secondary growth is absent., The Sporangia are born singly on the adaxial surface of sporophylls., , The sporophylls are aggregated into strobili ., Class: Lycopodinae;, , As Above., , Oder: Selaginellales;, , The Sporophytic plants are herbaceous., The stem and root do not show secondary thickening., , The leaves are microphyllous and ligulate., The sporophylls are aggregated into strobili born at the apex of the, stem, Family: Selaginallaceae; Sporophyte differentiated into Root, Stem and Leaves., Female gametophyte released from the megesporangium during, some stage of development
Page 3 :
External Morphology, The Plant itself is Sporophyte., , It is divided into two sub genera – Homeophyllum and Heterophyllum, In Homeophyllum stem is Erect and in Heterophullum stem is Prostrate with short erect, , branches., The leaves are dimorphic and are arranged in pairs in four longitudinal rows along the, , stem., Stem – It is herbaceous, branched, prostrate sub-erect or erect. It is green, smooth and, glabrous., Leaves – Small, sessile, ovate – lanceolate or cordate, with entire or serrate margine, apex acute, with prominent midrib. On adaxial surface present small scally laminar, outgrowth called Ligule. Matured broad base of ligule is called Glossopodium. Function, of ligule is to retain water.
Page 4 :
Rhizophore –, , Long slender root like structure arising from bifurcating region of stem., It is cylindrical and leafless, bears tufts of adventitious roots., , Root –, , Primary roots are short lived and all roots are born are adventitious., These roots arises from tip of rhizophore or may be developed directly, from stem., , Strobilus –, , Reproductive structure called as Strobili are developed at the apices of, the branches. It is a compact structure consisting of central axis around, which the sporophylls are compactly arranged. Each sporophyll bears a, ligule at the base and a singled stalked sporangium. The sporangia are, of two types – Microsporangia and Megasporangia. The sporophyll, , bearing microsporangia are called Microsporophyll and the one with, megasporangia are called Megasporophyll. Both microsporangia and, , megasporangia are found in the same strobilus or in different strobilus.
Page 6 :
Internal Morphology, T.S. of Stem, T.S. of Stem shows following structures., , 1. Epidermis – I t is outermost layer made of single layer compactly arranged tubular cells. It, shows presence of Cuticle on its outer wall., , 2. Cortex – It is heterogeneous and made of many layers. Outer 2-3 layers are composed of, Sclerenchymatous cells and called hypodermis. The rest part of cortex is made of, parenchymatous cells intercellular spaces., 3. Endodermis – It is single and continuous in younger plant but in older plant endodermal cells, get elongated and separated from each other and called as Trabeculae. It maintain the, contact between cortex and stele., 4. Stele – Stele is monostelic (single Stele) Protostele or polystelic (two or more stele). Each, , stele in polystelic condition is protostelic and consists of a single layer of pericycle enclosing, a single Vanscular Bundle. The VB consists of a central core of Xylem surrounded by Phloem, , i.e. Amphicribal. Xylem is exarch and diarch. Xylem consist of xylem tracheids and xylem, parenchyma, while phloem is made of sieve tube and phloem parenchyma.