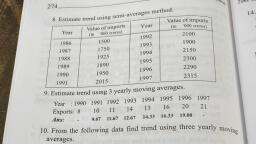
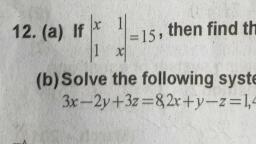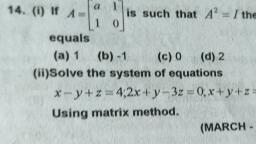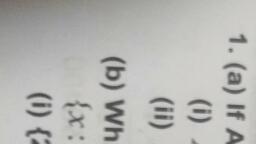Page 1 :
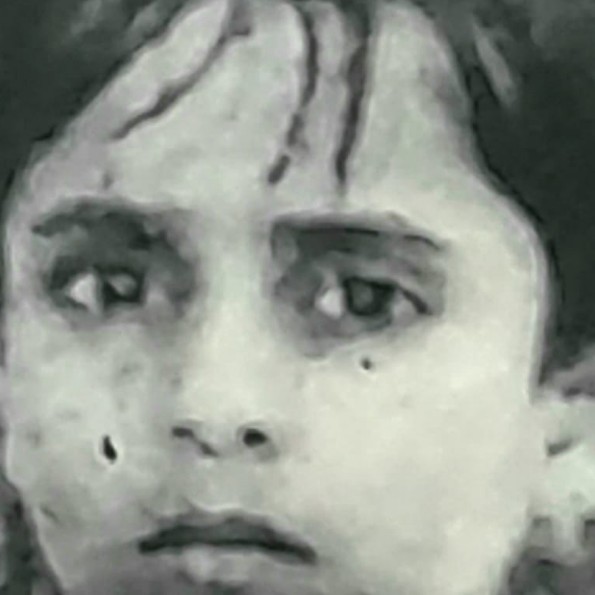
Wessels ANSWERS, , Qn. 2, , , , Se yat is the basic theme of organisation In the, periodic table? (2), Ww The basic theme of organisation of elements inthe, periodic table is to facilitate the study of the properties |, of all the elements and their compounds. On the |, basis of similarities in chemical properties, the various |, elements have been divided into different groups. This |, has made the study of elements simple because |, their properties are now studied inthe form of groups |, rather than individually. |, , What is the basic difference in approach between, Mendeleev’s Periodic Law and the Modern Periodic, Law? (2), Mendeleev Periodic Law states that the properties, of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic, weights whereas Modern Periodic Law states that, the properties of elements are a periodic function of, their atomic numbers. Thus, the basic difference in, approach between Mendeleev's Periodic Law and, Modern Periodic Law is the change in basis of, arrangements of elements from atomic weight to, atomic number., , ; Qn.3, , Consider the following species. N*, O*, F, Na’,, Mg* and Al** (2), a) What is common in them?, , b) Arrange them in order of increasing ionic radii., , "Xs ®) Each one of these ions contains 10 electrons and, , Qn. 4, , , , hence these are isoelectronic ions., b) The ionic radii of isoelectronic ions decrease with, the increase in the magnitude of the nuclear, charge. Among the isoelectronic ions: N*, O*,, F, Nat, Mg®* and Al’*, nuclear charge increase, in the order:, , N*< O*< F< Na*< Mg** < Al*, Therefore, the ionic radii decrease in the order:, , N* > QO? >F>Na*>Mg*>Al*, , Anything that influences the valence electrons will, affect the chemistry of the element. Which one of, the following factors does not affect the valence shell?, (a) Valence principal quantum number (n), , (0) Nuclear charge (Z), , (c) Nuclear mass, , (@) Number of core electrons (1), Nuclear mass does not affect the valence shell. Thus,, , e option (c) is the correct answer., , Qn., Considering the elements F, Cl, O and N, the correct, order of their chemical reactivity in terms of oxidising, , property is: (1), a) F>Cl>O>N b) F>O>CI>N, c) Cl>F>O>N d) O>F>N>Cl, , Na) F>Cl>O>N, , Across a period, the oxidising character increases, from left to right. Therefore, among F, O and N,, oxidising power decreases in the order : F > O > N,, However, within a group, oxidising power decreases, from top to bottom. Thus, F is a stronger oxidising, agent than Cl. Thus, overall decreasing order of, oxidising power is F > Cl > O > N and the choice (a), is correct., , PREVIOUS YEARS, QUESTIONS & ANSWERS, , , , Qn. 1 [4 Mark Question], a) Who introduced the periodic law of elements for, the first time? State the law. (2), b) State the modern periodic law of elements. (2), NW a) Mendeleev’s Periodic law : The physical and, chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic mass., b) Modern Periodic law : The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic function, of their atomic numbers., , , , , [4 Mark Question], , Qn. 2, , Account for the following:, , a) lonization enthalpy of nitrogen is greater than that, of oxygen., , b) Atomic radius decreases from left to right in a, period., , c) Electron gain enthalpy of F is less negative than, that of Cl., , XY 4) lonisation enthalpy of nitrogen is greater than that, of oxygen. This arises because in nitrogen atom,, three 2p electrons reside in different atomic, orbitals. (Hund’s rule) whereas in the oxygen, atom, two of the four 2p electrons must occupy, the same 2p orbitals resulting in an increased, electron repulsion. Consequently it is easier to, remove the fourth 2p electrons from oxygen than, it is, to remove one of the three 2p electrons from, nitrogen., , (Mgrrimam \Pudtiskers