Page 1 :
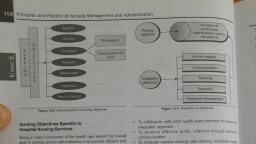
f nursing officer/Nursing, jperintendent/Matrons, , , , , , Top level, , , , , , , , , [ Nursing sisters/ward, sisters/Sister grade |, , , , , , , urses/Sister, grade Il, , soe, , i Titles of positions, , , , , , Levels, , , , Figure 2.3: Levels of nursing management in hospitals ae, , } planning and coordinating functions. They are accountable for, the nursing services for which they are serving. They issue the, instructions for the lower levels. In the hospital setting they are, assisted by deputy nursing superintendent, assistant nursing, superintendents or assistant matrons. They control all the activities, of the hospital nursing services., , Middle Level, , Middle management in nursing is usually the heads of nursing, units in the hospitals and they are at supervisory level. They are, responsible for the top management for the functioning of their, departments and designated as ward sisters or sister grade I., They make duty plans of the nursing personnel of lower or, operational level, divide the work to them. They follow and, implement the policies and guidelines issued to them by the top, nursing management. They evaluate the performance of, Operative level nurses and coordinate with other departments, and team to ensure that the best possible patient care. They, arrange for necessary materials, equipments for the operative, level nurses and provide them with the necessary working and, therapeutic environment. They supervise and guide them and, also solve their problems. They maintain good human relation, in the unit and communicate their problems to the higher level, , management., , , , Operative Level, , Operative level management comprise of nurses at the, operational level designated as staff nurses or sister grade II., They are responsible for the patient care. They plan and take the, decision for care of their assigned patients. They carry out the, instructions given by their superiors and team members in, relation to patient care. They are also known as the first line, management., , , , , , , , , , , , CIPLES OF MANAGEMENT IN NURSING, , are statements of fundamental, , Pee ees an, ent principles in nursing tec eervelns guidelines, , _ truth related to nursing field. These princip, , , , , , Nursing Management and Administration Wis, , for decisions, , and actions of nurse manager: i, arial Ss workin,, level in differe; coun, , nt settings. They are derived through ob i, a ¢ I igh observation, on snevele of events which nurse managers have to face in S, ane Practice in clinical, educational institutions or in any areas [Sy, ever they are working. The Principles of nursing a, , sae aoe can be derived and applied from the principles, = n by Henry Fayol who is known as the father of functional, anagement or management process, as he has given more, , sume on functions of managers and showed regard to human, elements with wider Perspectives:, , Division of Work, , This principle implies that every employee should be assigned, , only one type of work so as to bring about specialization in, , every activity. The specialization will help in creating specific, personal and professional development among the nurses and, therefore increasing their efficiency. This principle is applicable, to nurses working at Operational, supervisory as well as, managerial level. This principle of management is also called, principle of specialization., , Authority and Responsibility, , Authority means the right to give order by a superior to her, subordinates; responsibility means the obligation for, performance. This principle suggests that there must be parity, between authority and responsibilty. They are co-existent and, go together, and are two sides of the same coin., , Discipline, , Discipline refers to getting obedience to the rules and regulation, of the organization, proper conduct in relation to others, respect, of authority or for superior, etc. It is essential for the smooth, functioning of all organizations., , Unity of Command, , Every subordinate must receive orders and instructions and be, accountable to one and only to one superior. This will improve, the performance of employee. If an employee receives orders, from more than one superior; it is likely to have the overlapping, of orders and instructions and create confusion and conflict., Dual command generates tension, confusion and conflict, and, results diluted responsibility and blurred communication., , It will be very difficult to maintain discipline in the organization., Unity of Command also makes it easier to fix responsibility for, mistakes and there will be harmonious relationship between, the superior and subordinates., , Unity of Direction, , Unity of direction means that one head should give the direction., All the activities of a work unit or group should be directed, towards the same goal and those working in the same line of, activity must understand and pursue the same objectives. There