Page 1 :
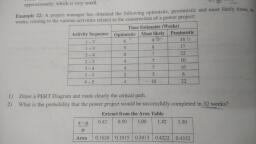
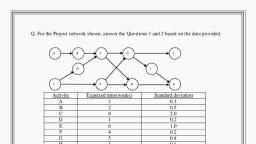
A laDefine specifications, Identify customers, , Interview 10 customers, Interpret requirements, Benchmark products, Define target PDS, Target PDS released, Generate concepts, Review comp products, Search patents, Brainstorm concepts, Select top 2 concepts, MQ presented, Profile, Design test, Build test, , ey, a, , , , a =a ee, Ale, , , , , , 5 ee a tStst=~—<S~*~S, Figure 16.2: Gantt chart, , as that path,, , , , , In this, the main focus is on critical path activities, determines the minimum a moult i, , e entire project., The network path, which is not critical create ‘float’ or slack slack., Float is the total amount of time when related activities on non, critical may be delayed without changing the overall project, completion. In other words, the non Critical path is defined as, that series ivities that may be delayed without, ‘ol ‘of time for the related activities on non, , is not going to effect on completion of project as for as the time is, , conce!, Thus if we want to shorten the time to complete the project,, , then you need to cut ors! e OF lements in the crit, path., aa, , Programme Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT), , Programme Evaluation and Review Technique or commonly, abbrevi Pl is a model designed to analyze and represent, he task involved in completion of a given project or programme., {was developed in 1958 by Booz Allen Hamilton, te under, , he special project office of US Navy as a part of the Polaris, , , , nobile submarine launched ballistic missile. It is also based on, , ener anal, , , , most likely duration, and most pessimistic duration. . Hence, , PERT r uncertainty is s attached i in scheduling time estimatesta, , playa major role in this ‘type of net work. The network paid, , PERT as depicted in Figure 16.3 is as follow:, , © The CIRCLES mark the beginnings and ends of TASKS tote, , done in the project. Also called NODES., , The ARROWS are the tasks themselves, , The NUMBERS after the task names are the DURATIONS¢, , the task, , © When a node has two or more tasks branching from ££, means those tasks can be done concurrently (at the som, time.), , * When a node has incoming arrows, it means the incom, task must be completed before progress may continue fo, arrows heading away from the node e.g. Task A must &, completed before tasks B or G may begin., , — re,, , G2, , H5, , , , Figure 16.3: The PERT