Page 1 :
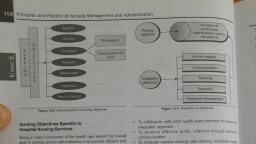
»ment and Adr, , , , ‘i Manage, Principles and Practice of Nur sing, { give, yt but do no!, administrators, and other staff who suPPO!, direct service, /, arvices ina Yeal, Time available for Nursing Services aie, s » to provide, To determine whether the current staff Is ap ee ine, amount of service needed or if additional sta ' . | much time |S, desired services, it is necessary to estimate 108 | tated, , y 4 is can be Ce, available with the staf to provide the care: This fan We avg, by multiplying the staff available for services, , per nurse per year, , Daily Activities, ng care should make brief, , Each staff that provides direct nursit, ee ae fe basic information, , account of activities daily in order to provic, for planning and evaluating the services, necessary for estimating amount and type, for determining the average amount of services one, , These amounts are, , of services given and, nurse can, , provide in a day., , Time Required per unit of Activity, This information is necessary to determine the number of staff, needed for each activity during the year. Time requirements are, Nel obtained by periodic time studies of nursing activities The, average time required per unit of activity is calculated by dividing, the total time spent in each activity by the number of times the, , fe) activity is performed., , Services Provided, , Nursing services provided is determined on the information, obtained from the nurses’ record and reports of daily activities,, estimation of time required per unit of service and calculation of, number of staff available for service., , Enumeration of Service Requirements, , It includes number of patients to receive nursing service during, the year and estimation of nursing service required., , Staff Required for Intended Service, , By summarizing the total amount of staff time necessary to provide, the nursing services proposed and relating these requirements, to the amount of service that the present staff can give, determinations can be made as to whether additions or changes in, the staffing pattern are needed., , STAFFING NORMS, LT, , Norm is a standard, model, or pattern. It a standard of, achievement or behaviour that is required, desired, or designated, as normal. These are standards that guide, control and i ater, individuals and communities. For estimating the enna gulate, pur ganenpover. various committees, nursing ae ;, associations have been recommended staffing no; ncil,, hospitals, community both rural and urban: tee TMs for, in India. Norms are according to: : ig institutions, , , , , , ninistration, alth Survey and Developme, =, , , , , , , , , , , , art of the Hoe ey, Rep nittoo (BNO? Committee 1946) con e 19 ;, Fe to Bhore committee recommer ono! ie401-70, According | er nurse population ratio j pend ould be, required as pt ‘ted for 30 years) Propose 1 oI oe are °, sulations (targeté re | qh be ee, por se of time to international 4, } eter a, reach in due cour 39 valty dep’ cha, to 2% beds F : } a5 ter i, nue Be Report (Shetty Committee 1 954) or one siewatient c, ei eewith the initiation of Union Mir gach OF art, commit Amrit Kaut, Govt. of India, constitu —, eek May 1954 to review conditions, emol rape #2, on Tq Profession. The recommendation r ’, t 3S, NUTS ng 1 nurse (also qualified in midwifery | a, staffing 16 © vices) including students t —eopen?, maternity Serr ning of nurses and midw, j nue qursing Sut, hospitals used for training Bee inci Ms ep a0, and administrative staff will not be includec eta", nurses ', One nurse (also qualified in midwifery, e luding students to a eieiaae, maternity services) inc’ ag, hospitals. One superintendent for nursing servic peparne!, is also recommended by this committee, The above mentioned recommendations o', have been endorsed by the Mudaliar Committe i wards, ‘ ds, , surgical 2", Central Council of Health Meeting oytnopaedic wa, 7 ric ward, In a meeting held at Bombay on 16th and 17th 0; Paediatt ‘, under the agenda No.13, resolution (No.120 pa: | Ore 4, nursing manpower that in conformity with the rec Maternity Si, of Health Survey and Planning Committe« (including nev", committees appointed by Govt. of India, ie. q intensive care, midwife in a teaching hospital should be in the Coronary care, Pp, Nephrology (2, , , , nurse to 3 patients while in other hospitals ir, nurse to 5 patients. For determining the nurse patient, , nursing staff engaged in teaching and administration etc., , not be taken into consideration. \, , , , Staffing Pattern Recommended by |, Government of India, 1977, , ‘For 100 beds, there should be 1 Matron, 6 Sisters and 25 St! J, Nurses; and for 300 beds, 1 Matron, 1 Assistant Matr, Nursing Sisters and 81 Staff Nurses’, , Indian Nursing Council Recommendation, , ee Nursing Council has also recommended nurse, an in 1965, 1975 for hospitals and the revised recom ., Stating norms for teaching hospi By are depicted!, Table 32.1. ing hospitals (1986), , , , ‘For every 100 beds and to cover a 24 hours period, the saf, should be in the proportion of one sister to 25 beds and 2, staff nurse to 3 beds in teaching hospitals and one staff ae, to'5 beds in non teaching hospitals. In addition to ™, , Superintendent, there should be one assistant when j, Cont!, , ine, , , , Neurology ar, (24 hrs), , Special war, ete (24 hrs), , , , Operation 1