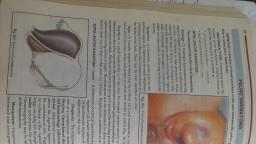
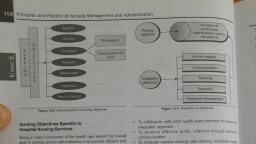
Page 1 :
Principles and Practice of Nursing Management, , , , In Indian scenario, the nurse administrators are not directly, involved in planning budget. Above mentioned steps are being, exercised where they are involved in planning nursing services., The data also revealed that there is no separate budget for nursing, services in Indian hospital and most of the nurse administrators, were unaware of the weightage given to the expenditure on, nursing services is the hospital budget. Few of them reported, that budget for nursing services is allocated on salary of nursing, personnel, their education and equipment, however the, weightage in percentage of total budget is not fixed., , ZERO-BASED BUDGETING a, , Zero-base budgeting was adopted in India in 1986 as a technique, for determining expenditure budgets. Accordingly the Ministry, of Finance instructed all the administrative ministries to review, their respective programmes and activities in order to prepare, expenditure budget estimates based on the principles of zerobase budgeting. Although this budgeting system has not yet, been fully implemented in India., , Meaning, , It is a technique of planning and decision-making which reverses, the working process of traditional budgeting. In traditional, incremental budgeting, departmental managers justify only, increases over the previous year budget and what has been, already spent is automatically sanctioned. No reference is made, to the previous level of expenditure. By contrast, in zero-based, budgeting, every department function is reviewed comprehensively and all expenditures must be approved, rather than only, increases., , Zero-based budgeting requires the budget request be justified, in complete detail by each division manager starting from the, zero-base. The zero-base is indifferent to whether the total budget, is increasing or decreasing., , Thus this budget process is labor intensive for nurse manager., The use of a decision package to set funding priorities is a key, feature of zero based key components decision packages are, listing of all current and proposed objectives or activities in the, department alternative plans for carrying out these activities cost, for each alternative., , Steps, , Following steps are followed in zero base budgeting:, Q Identify organizational program, Divide the program into packages, pack ould have its goals, activities and needed, , , , , , , , , ‘each package from the base zero, , , , , , , , , and Administration, , Avoids the common tendency in budgeting of looking =, changes from a previous period., Efficient allocation of resources, as it is based on needs and, benefits. :, , * Cost effective ways to improve operations., , * Detects inflated budgets., , * Useful for service departments where the output is difficult to, , identify. A, * Increases staff motivation by providing greater initiative ang, , responsibility in decision-making. aL, * Increases communication and coordination within the, , organization., Identifies and eliminates wasteful and obsolete operations, , * They force managers to set priorities and use resources ros., , efficiently. ;, Identifies opportunities for outsourcing., * Forces cost centers to identify their mission and their, , relationship to overall goals., , Disadvantages, , * Difficult to define decision units and decision packa, is time-consuming and exhaustive., , * Forced to justify every detail related to expenditure, , * Necessary to train managers. Zero-based budgeting m, clearly understood by managers at various leve, successfully implemented., , * Difficult to administer and communicate the budgeting, because more managers are involved in the process, , ¢ Ina large organization, the volume of forms may be so large, that no one person could read it all., , * Compressing the information down to a usable size, remove critically important details., , ¢ Honesty of the managers must be reliable and uniform. Any, manager that exaggerates skews the results., , , , , , , , PERFORMANCE BUDGETING, , Meaning, , Itis a system of presentation of expenditure in terms of functions, , Programmes, performance units, reflecting primarily, the output, and its cost. It emphasizes accountability, efficiently and economy, by emphasizing outcomes and results instead of activities oF, outputs. Thus the manager would budget as needed to achieve, specific outcomes and would evaluate budgetary success, accordingly., , Steps, , The following steps are being taken:, 1 Identify and analyze the work of organization into functions,, sub functions; programmes, sub programmes; activities, sub, _ activities in results, O Lay down the targets of each scheme, function, programs, Performance norms or standards for each activity, , ee