Page 1 :
Chapter - 3, , Reaction Intermediate
Page 3 :
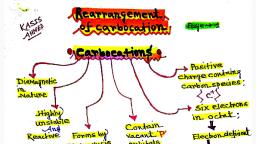
CHEM ACADEMY, Reaction intermediates are generated by the breaking of covalent bond of the substrate. They are, short-lived species and are highly reactive. There are six types of reaction-intermediates., , (1) Carbocation (2) Carbanion (3) Free radical, (4) Carbene (5) Benzyne (6) Nitrene, Generation of Reaction intermediates:, , Organic Molecule, , Acid Base Ally, , Carbocation Carbanion Free Radical, CARBOCATIONS, , An organic species which has a carbon atom bearing six electrons in its outermost orbit and has a, positive charge is called a carbocation. , Characteristics of Carbocations (except vinyl carbocation), (i) It has three bond pairs with empty p-orbital. Its hybridisation is sp”., (ii) Shape of carbocation is trigonal planar., , 0, , 0, Note: Triphenylmethy! carbocation has propeller shape., , (iii) There are six electrons in the outermost orbit of carbocationic carbon hence its octet is incomplete., All the six electrons are paired., , (iv) It isa charged electrophile., , (v) It is diamagnetic in character., , (vi) It is formed by heterolytic bond fission., , (vii) It reacts with nucleophiles., , Generation of Carbocation, , Carbocations are usually generated in one oftwo general ways., , ‘ \, (a) Through direct ionisation of Sy bond where X leaves the molecule with bonding pair., 6+ (x @ Pr), R—CH,—X: <——*+R—CH, + X:, , (b) When a proton or other positive species adds to one atom of an unsaturated system, leaving the, adjacent carbon atom with a positive charge., , \ \o 5 H, OK. Fo wo Prt par —y + H,0, , Reaction Intermediate 3