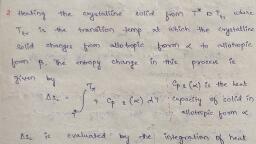Page 1 :
1, DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, OSMANIA UNIVERSITY, (Effective from academic year 2016-2017 for Campus and Constituent colleges, [UNDER CBCS Scheme], Semester I, Hrs. /week internal assessment Semester exam, CH101T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH102T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH103T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH104T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH151P (IC LAB*) 6, CH152P (OC LAB*) (4h + 2T), CH153P (PC LAB*) 6, Total, , Total, 100 marks, 100 marks, 100 marks, 100 marks, 75 marks, 50 marks, 75 marks, 600 marks, , Credits, 4, 4, 4, 4, 3, 2, 3, 24, , (*Core= compulsory papers common to all students admitted to M.Sc Chemistry, OU), , Semester II, Hrs. /week internal assessment Semester exam, CH201T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH202T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH203T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH204T (*), 4, 20 marks, 80 marks, CH251P (IC LAB*) 6, CH252P (OC LAB*) 6, CH253P (PC LAB*) (4h + 2T), Total, , Total, Credits, 100 marks, 4, 100 marks, 4, 100 marks, 4, 100 marks, 4, 75 marks, 3, 75 marks, 3, 50 marks, 2, 600 marks, , 24, , (*= compulsory papers common to all students admitted to M.Sc Chemistry, OU), , 1
Page 2 :
2, M.Sc CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS, (Effective from academic year 2016-2017 for Campus and Constituent colleges., SEMESTER –I, Semester-I and Semester-II syllabus is common for all specializations i.e., InorganicAnalytical, Organic, Physical, Physical- Organic and Chemistry (Pharmacoinformatics)., Paper 1 CH 101 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY), IC 01: Symmetry of molecules, IC 02: Bonding in Metal Complexes - I, IC 03: Coordination equilibria, IC 04: Ligational aspects of diatomic molecules, Teaching hours-4/week, Marks-80, IC-01: Symmetry of Molecules:, 15 hrs, Concept of Symmetry in Chemistry – Symmetry Operations – Symmetry Elements:, Rotational Axis of Symmetry and Types of Rotational Axes, Plane of Symmetry and types of, Planes, Improper Rotational Axis of Symmetry , Inversion Center and Identity Element –, More about Symmetry Elements – Molecular Point Groups: Definition and Notation of Point, Groups, Classification Molecules in to C1, Cs, Ci, Cn,Cnv, Cnh, C∞v, Dn, Dnh, Dnd, D∞h, Sn, (n=even), Td, Oh, Ih, Kh Groups. Descent in Symmetry with Substitution – Exercises in, Molecular Point Groups – Symmetry and Dipole moment – Symmetry criteria for Optical, activity., IC – 02: Bonding in metal complexes – I:, 15 hrs, Crystal Field Theory: Salient features of CFT. d-orbital splitting patterns in regular, Octahedral, tetragonally distorted octahedral, Jahn-Tellar theorem , trigonal bipyramidal,, trigonal planar, Pentagonal bipyramidal, and linear geometries. Concept of weak field and, strong fields. - Calculation of crystal field stabilization energies (CFSE’s) in six and four, coordinate complexes., Types of magnetic behaviour – magnetic susceptibility – calculation of magnetic moment, from magnetic susceptibility spin only formula ,- Quenching of orbital angular momentum –, Determination of magnetic moment from Guoy’s method.. Applications of magnetic moment, data for the determination of oxidation states, bond type and stereochemistry. Spin crossover:, High spin, low spin cross over phenomenon in [Fe(Ophen)2(NCS)2] and [Fe(R2NCS2)3]., Spinels., IC-03: Coordination Equilibria:, 15 hrs, Solvation of metal ions- Metal complex formation in solution-Binary metal complexes., Stability constants (types and relationships between them). – Factors influencing the stability, constants: (i) Metal ion effects (charge/size, IP, crystal field effect, John-Teller effect, Pearson, theory of hard and soft acids and bases (HSAB), elecronegativity and hardness and softness,, symbiosis. (ii) Ligand effects (Basicity , Substituent effect , Steric , Chelate(size and number, of chelate rings), Macrocyclic and Cryptate effects- crown ethers , crypton, size match, selectivity or concept of hole size, limitations, Macrocycles with pendent groups– Methods, used for the determination of Stability constants (Basic Principles only): pH metric,, Spectrophotometric and Polarographic methods., 2
Page 3 :
3, Ternary Metal Complexes – definition – Formation of ternary metal complexes – Step-wise, and simultaneous equilibria with simple examples., IC – 04: Ligational Aspects of Diatomic molecules, 15 hrs, Metal Carbonyls:- Carbon monoxide as a ligand – Molecular orbitals of CO - Donor and, Acceptor molecular orbitals of CO; Bonding modes of CO- Terminal and Bridging; Evidence, for multiple bonding from Bond lengths and Stretching frequencies; 18 Valence electron rule, and its application., Metal Nitrosyls: - NO as a ligand – Molecular orbitals of NO – Donor and Acceptor, components; Bonding modes of NO – Terminal (Linear, Bent) and Bridging; Structural, aspects of [IrCl(PPh3)2(CO)(NO)]+ and [RuCl(PPh3)2(NO)2]+., Stereo chemical control of valence in [Co(diars)2(NO)]2+ and [Co(diars)2(NO)(SCN)]+., Metal Dinitrogen complexes: - N2 as aligand – Molecular orbitals of N2; Bonding modes –, Terminal and Bridging; Stretching frequencies; Structures of Ru (II) and Os(II) dinitrogen, complexes; Chemical fixation of dinitrogen., Suggested References:, 1. Symmetry and Group theory in Chemistry, Mark Ladd, Marwood Publishers, London, (2000)., 2. Molecular Symmetry and Group Theory, Robert L.Carter, John Wiley & Son (1998)., 3. Symmetry and Spectroscopy of Molecules. K.Veera Reddy, New Age International (P), Limited (1999)., 4. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. F.A.Cotton, G.Wilkinson, C.A.Murillo and M.Bochmann,, 6th Edition, Wiley Interscience, N.Y (1999, 5. Inorganic Chemistry, J.E. Huheey, K.A.Keiter and R.L.Keiter 4 th Edition Harper Cottens, College Publications (1993)., 6. Homogeneous Catalysis by Metal complexes Vol I, M M Taqui Khan and A E Martell,, Academic Press NY (1974)., 7. Inorganic Chemistry, Keith F.Purcell and John C.Kotz, Holt-Saunders International, Editions, London (1977)., , Paper-II: CH 102 T (Organic Chemistry), OC-01: Stereochemistry, OC-02: Reaction mechanism-1, OC-03: Conformational analysis (Acyclic systems), OC-04: Heterocyclic compounds & Natural products, OC-01: Stereochemistry, 15 hrs, Molecular representations: Wedge, Fischer, Newman and Saw-horse formulae, their, description and interconversions., Molecular Symmetry & Chirality: Symmetry operations and symmetry elements (Cn &, Sn). Criteria for Chirality. Desymmetrization., Axial, planar and helical chirality: Axially chiral allenes,spiranes,alkylidene cycloalkanes,, chiral biaryls, atropisomerism, planar chiral ansa compounds and trans- cyclooctene, helically, chiral compounds and their configurational nomenclature, Relative and absolute configuration: Determination of configuration by chemical, correlation methods., 3
Page 5 :
5, rd, , 5.Heterocyclic Chemistry, 3, Edn J.A.Joule, K.Mills and G..F.Smith, Stanley Thornes, Ltd,UK, (1998), 6.The Chemistry of Indole, R.J. Sunderberg, Academic Press, New York (1970)., 7.An introduction to the chemistry of heterocyclic compounds, 2nd Edn.R.M.Acheson,, Interscience Publishers, New York, 1967., 8.Advanced Organic Chemistry by Jerry March, 9.Mechanism and Structure in Organic Chemistry S. Mukerjee, , Paper CH 103 ( PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY), PC-01: Thermodynamics-I, PC-02: Electrochemistry-I, PC-03: Quantum Chemistry-I, PC-04: Chemical Kinetics-I, PC-01: Thermodynamics-I, 15 hrs, Concept of Entropy, Entropy as a function of V and T, Entropy as a function of P and T., Entropy change in isolated systems- Clausius inequality. Entropy change as criterion for, spontaneity and equilibrium., Third law of thermodynamics. Evaluation of absolute entropies from heat capacity data for, solids, liquids and gases. Standard entropies and entropy changes of chemical reactions., Thermodynamic relations. Gibbs equations. Maxwell relations., Gibbs equations for non-equilibrium systems. Material equilibrium. Phase equilibium., Clausius-Clapeyron equation .Conditions for equilibrium in a closed system., Chemical potential of ideal gases. Ideal-gas reaction equlibrium-derivation of equilibrium, constant. Temperature dependence of equilibrium constant-the van’t Hoff equation., Solutions: Specifiying the Solution composition. Partial molar poperties-significance., Relation between solution volume and partial molar volume. Measurement of partial molar, volumes- slope and intercept methods. The chemical potential. Variation of chemical potential, with T and P. Gibbs-Duhem equation-derivation and significance., PC-02: Electrochemistry- I, 15 hrs, Electrochemical Cells: Derivation of Nernst equation – problems. Chemical and, concentration cells (with and without transference). Liquid junction potential (LJP) –, derivation of the expression for LJP – its determination and elimination. Types of electrodes., Applications of EMF measurements: Solubility product, potentiometric titrations,, determination of pH using glass electrode, equilibrium constant measurements., Decomposition potential and its significance. Electrode polarization – its causes and, elimination. Concentration over-potential., Concept of activity and activity coefficients in electrolytic solutions. The mean ionic activity, coefficient. Debye-Huckel theory of electrolytic solutions. Debye-Huckel limiting law, (derivation not required). Calculation of mean ionic activity coefficient. Limitations of, Debye-Huckel theory. Extended Debye-Huckel law., Theory of electrolytic conductance. Derivation of Debye-Huckel-Onsager equation – its, validity and limitations., Concept of ion association – Bjerrum theory of ion association (elementary treatment)-ion, association constant – Debye-Huckel-Bjerrum equation., 5
Page 6 :
6, PC-03: Quantum Chemistry- I, 15 hrs, A brief review of Black body radiation-Planck’s concept of quantization-Planck’s equation,, average energy of an oscillator (derivation not required), Wave particle duality and uncertain, principle-significance of these for microscopic entities. Emergence of quantum mechanics., Wave mechanics and Schrödinger wave equation., Operators- Operator algebra. Commutation of operators, linear operators. Complex functions., Hermitian operators. Operators and 2 .Eigenfunctions and eigenvalues. Degeneracy., Linear combination of eigenfunctions of an operator. Well behaved functions. Normalized and, orthogonal functions., Postulates of quantum mechanics: Physical interpretation of wave function. Observables and, Operators. Measurability of operators. Average values of observables. The time dependent, Schrodinger equation. Separation of variables and the time-independent Schrodinger equation., Theorems of quantum mechanics. Real nature of the eigen values of a Hermitian operatorsignificance. Orthogonal nature of the eigen values of a Hermitian operator-significance of, orthogonality. Expansion of a function in terms of eigenvalues. Eigen functions of commuting, operators-significance. Simultaneous measurement of properties and the uncertainty principle., Particle in a box- one dimensional and three dimensional. Plots of and 2-discussion., Degeneracy of energy levels. Calculations using wave functions of the particle in a boxorthoganality, measurability of energy, position and momentum, average values and, probabilities. Application to the spectra of conjugated molecules., PC-04: Chemical Kinetics- I, Theories of reaction rates: Collision theory, steric factor. Transition state theory., Thermodynamic formulation of transition state theory. Potential energy surface diagram,, Reaction coordinate, Activated complex. Activation parameters and their significance. The, Eyring equation. Unimolecular reactions and Lindamann’s theory., Complex reactions- Opposing reactions, parallel reactions and consecutive reactions (all first, order type). Chain reactions-general characteristics, steady state treatment. Example- H2-Br2, reaction. Derivation of rate law., Effect of structure on reactivity- Linear free energy relationships. Hammett and Taft, equations-substituent ( and *) and reaction constant (ρ and ρ*) with examples. Deviations, from Hammett correlations, reasons- Change of mechanism, resonance interaction. Taft four, parameter equation. Correlations for nucleophillic reactions. The Swain – Scott equation and, the Edward equation. Reactions in solutions: Primary and secondary salt effects., The reactivity-selectivity principle – Isokinetic temperature -Isoselectivty rule, Intrinsic, barrier and Hammond’s postulate., References:, 1. Atkin’s Physical Chemistry, Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, Oxford University press, 2. Physical Chemistry, Ira N. Levine, McGraw Hill, 3. Physical Chemistry-A Molecular approach, D.A. McQuarrie and J.D. Simon, Viva Books, Pvt. Ltd, 4. Molecular Thermodynamics, D.A. McQuarrie and J.D. Simon, University Science Books, 5. Quantum Chemistry, Ira N. Levine, Prentice Hall, 6. Introduction to Quantum Chemistry, A.K. Chandra, Tata McGraw Hill, 7. Chemical Kinetics, K.J. Laidler, McGraw Hill, 6
Page 8 :
8, ASP 03: Rotational, Vibrational and Raman spectroscopy, 15 hrs, a). Microwave Spectroscopy: Classification of molecules based on moment of inertia., Diatomic molecule as rigid rotator and its rotational energy levels. Selection rules (derivation, not required). Calculation of bond lengths from rotational spectra of diatomic molecules., Isotope effect on rotational spectra. Calculation of atomic mass from rotational spectra. Brief, description of microwave spectrometer., b). Vibrational Spectroscopy. Vibrational energy levels of diatomic molecules, selection, rules (derivation not required). Calculation force constant from vibrational frequency., Anharmonic nature of vibrations. Fundamental bands, overtones and hot bands, Fermi, Resonance. Vibrationrotation spectra diatomic molecules. Vibrations of poly atomic, molecules. Normal modes of vibration, concept of group frequencies. Characteristics of, vibrational frequencies of functional groups; Stereochemical effects on the absorption pattern, in carbonyl group, cis-trans isomerism and hydrogen bonding. Isotopic effect on group, frequency. IR spectra of metal coordinated NO3-, SO42- and CO32- ions., c) Raman Spectroscopy- Classical and Quantum theories of Raman effect. Rotational Raman, and Vibrational Raman spectra, Stokes and anti- Stokes lines. Complementary nature of IR, and Raman spectra., ASP 04:Electronic spectroscopy, 15 hrs, Electronic spectroscopy: Electronic spectra: Elementary energy levels of molecules-selection, rules for electronic spectra; types of electronic transitions in molecules. Chromophores:, Congugated dienes, trienes and polyenes, unsaturated carbonyl compounds, Benzene, mono, substituted derivative (Ph-R), di substituted derivative (R-C6H4-Rʹ) and substituted benzene, derivatives (R-C6H4-CORʹ), Woodward-Fieser rules. Polynuclear aromatic compounds, (Biphenyl, stilbene, naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene). Heterocyclic, systems. Absorption spectra of charge transfer complexes. Solvent and structural influences, on absorption maxima, stereochemical factors. Cis-trans isomers, and cross conjugation., Beer’s law application to mixture analysis and dissociation constant of a weak acid., References:, 1. Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy, Banwell and McCash., 2. Introduction to Molecular Spectroscopy, G.M. Barrow., 3. Absorption Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds, J.R. Dyer., 4. Biochemistry: Hames and Hooper., 5. Introduction to Spectroscopy, Pavia Lampman Kriz., 6. Pharmaceutical analysis, Watson, 7. NMR in Chemistry- A multinuclear introduction, William Kemp., 8. Organic Spectroscopy, William Kemp., 9. Spectroscopy of organic compounds, P.S. Kalsi., 10. Structural methods n Inorganic chemistry, E.A.V Ebsworth., 11. Organic Spectroscopy, LDS Yadav, 12. Organic Spectroscopy, Y.R. Sharma, 13. Molecular Spectroscopy – Arhuldas, 14. Vibrational spectroscopy – D.N. Satyanarayana, , 8
Page 10 :
10, Conductometry:, Titration of strong acid vs strong base, Titration of weak acid vs strong base, Determination of cell constant, Determination of dissociation constant of a weak acid, Potentiometry:, Titration of strong acid vs strong base, Titration of weak acid vs strong base, Determination of dissociation constant of a weak acid, Determination of single electrode potential, Polarimetry:, Determination of specific rotation of sucrose, Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of sucrose (inversion of sucrose), Adsorption and others:, Adsorption of acetic acid on animal charcoal or silica gel, Determination of critical solution temperature of phenol-water system, Effect of added electrolyte on the CST of phenol-water system, Determination of molecular weight o f a polymer by viscometry., , References:, 1. Senior Practical Physical Chemistry: B.D. Khosla, V.C. Garg and A. Khosla, 2. Experimental Physical Chemistry: V. Athawale and P. Mathur., 3. Practical Physical Chemistry: B. Vishwanathan and P.S. Raghavan., 4. Practical in Physical Chemistry: P.S. Sindhu, 5. Advanced Practical Physical chemistr: J.B.Yadav, 6. Vogel Text book of Quantitative Analysis, 6th edition, Pearson education Ltd. 2002., , 10
Page 11 :
11, SEMESTER –II, (Semester-I and Semester-II syllabus is common for all specializations i.e., InorganicAnalytical, Organic, Physical, Chemistry (Pharmacoinformatics) and Physical- Organic.), Paper CH 201 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY, IC 05: Reaction mechanisms of transition metalcomplexes, IC 06: Bonding in metal complexes-II, IC 07: Metal clusters, IC 08: Biocoordination chemistry, Teaching hours/week-4, , Marks-80, , IC-05: Reaction mechanisms of transition metal complexes:, 15 hrs, Ligand substitution reactions:, Energy profile of a reaction – Transition state or Activated Complex. Types of substitution, reactions (SE, SN, SN1, SN2). Langford and Grey classification – A mechanism, DMechanism, Ia, Id, and Intimate mechanism., Ligand substitution reactions in octahedral complexes:, Aquation or Acid hydrolysis reactions, Factors effecting Acid Hydrolysis , Base Hydrolysis,, Conjugate Base Mechanism, Evidences in favour of SN1CB Mechanism., Substitution reactions with out Breaking Metal-Ligand bond. Anation reaction, Ligand Substitution reactions in Square-Planar complexes: Mechanism of Substitution in, Square-Planar complexes- Trans-effect, Trans-influence, Grienberg’s Polarization theory and, Π - bonding theory – Applications of Trans-effect in synthesis of Pt (II) complexes., Electron Transfer Reactions (or Oxidation-Reduction Reactions) in Coordination compounds:, Mechanism of One-electron Transfer Reactions: Atom (or group) Transfer or Inner Sphere, Mechanism, Direct electron Transfer or Outer Sphere Mechanism. Factrors affecting direct, electron transfer reactions, Cross reactions and Marcus-Hush theory., IC-06: Bonding in Metal Complexes – II:, 15 hrs, Free ion terms and Energy levels: Configurations, Terms, States and Microstates – Formula, for the calculation of Microstates pn and dn configurations – L-S (Russel-Saunders) coupling, scheme – j-j coupling scheme – Determination of terms for various pn and dn configurations of, metal ions. Hole formalism – Energy ordering of terms ( Hund’s rules) Inter – electron, repulsion Parameters ( Racah parameters) – Spin-Orbital coupling parameters. Effect of weak, cubic crystal fields on S,P,D and F terms- Orgel Diagrams., IC-07: Metal Clusters:, 15 hrs, Carbonyl clusters: Factors favouring Metal-Metal bonding – Classification of Clusters –, Low Nuclearity Clusters : M3 and M4 clusters , structural patterns in M3(CO)12 (M=Fe,Ru,Os), and M4(CO)12 (M=Co,Rh,Ir) Clusters. Metal carbonyl scrambling – High Nuclearity clusters, M5, M6, M7, M8 and M10 Clusters-, Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory and Total Electron, Count theory – Capping rule – Structural patterns in, [Os6(CO)18]2- , [Rh6(CO)16], {Os7(CO)21] , {Rh7(CO)16]3-, [Os8(CO)22]2- , [Os10C(CO)24]2- and, [Ni5(CO)12]2-., , 11
Page 12 :
12, Metal Halide clusters: Major structural types in Dinuclear Metal-Metal systems – Edge, sharing Bioctahedra, Face sharing Bioctahedra, Tetragonal prismatic and Trigonal, antiprismatic structures -. Structure and bonding in [Re2Cl8]2- and Octahedral halides of, [Mo6(Cl)8]4+ and [Nb6(Cl)12]2+. Trinuclear halides of Re(III). Hoffman’s Isolobal analogy and, its Structural implications. Boranes, carboranes, STYX Rule. Stereo chemical non-rigidity in, [Rh4(CO)12] and [Fe2(Cp)2(CO)4]., IC-08: Bio coordination chemistry:, 15 hrs, Metal ions in Biological systems: Brief survey of metal ions in biological systems. Effect of, metal ion concentration and its physiological effects. Basic principles in the biological, selection of elements., Oxygen transport and storage: Hemoglobin (Hb) and Myoglobin (Mb) primary, secondary,, tertiary and quarternary structures and non-covalent bonds present in them. Oxygenation, equilibria for Mb and Hb. Factor effecting oxygenation equilibria. Cooperativity and its, mechanism. Spin state of iron. Spatial and electronic aspects of dioxygen binding. Allosteric, models (T and R states). Role of globin. Transport of NO and CO2. Hemocynin (Hc) and, Hemerythrin (Hr): Introduction-structure of active sites with oxygen and without oxygen., Comparison of Hemerythrin and Hemocyanin with hemoglobin., Photosynthesis: Structural aspects of Chlorophyll. Photo system I and Photo system II., Vitamin B6 model systems: Forms of vitamin B6 with structures. Reaction mechanisms of (1), Transamination (2) Decarboxylation and (3) Dealdolation in presence of metal ions., References:, 1. Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms. M.L.Tobe and John Burgess, Addison Wesley Longman, (1999)., 2. Metal ions in Reaction Mechanisms. K.Veera Reddy. Golgotia Publications (P) Ltd, 3. Mechanisms of Reactions in Transition Metal Sites. Richard A Henderson, Oxford Science, Publications, London (1993)., 4. Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms, F.Basolo and R.G.Pearson, New York (1967)., 5. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. F.A.Cotton, G.Wilkinson, C.A.Murillo and M.Bochmann, 6, Th Edition, Wiley Interscience, N.Y (1999, 6. Inorganic Chemistry, J.E.Huheey , K.A.Keiter and R.L.Keiter 4 th Edition Harper Cottens, College Publications (1993)., 7. Inorganic Biochemistry Edited by G.L.Eichorn, Volume 1 Elsevier ( 1982)., 8. The Chemistry of Metal Cluster Complexes. D.F.Shriver, H.D.Kaerz and R.D.Adams (Eds),, VCH, NY (1990)., 9. Inorganic Chemistry, Keith F.Purcell and John C.Kotz, Holt-Saunders International Editions,, London (1977)., 10. Bioinorganic Chemistry, I.Bertini, H.B.Gray, S.J.Lippard and S.J.Valentine, Viva Low-Priced, Student Edition, New Delhi (1998)., 11. Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life, W.Kain and, B.Schwederski, John Wiley and Sons, NY (1999)., , 12
Page 14 :
14, Photochemistry of (n-π*) transitions: Excited states of carbonyl compounds, homolytic, cleavage of α- bond, Norrish type I reactions in acyclic and cyclic ketones and strained, cycloalkane diones., Intermolecular abstraction of hydrogen: photoreduction-influence of temperature, solvent,, nature of hydrogen donor and structure of the substrate., Intramolecular abstraction of hydrogen: Norrish type II reactions in ketones, esters and 1,2, diketones, Addition to carbon-carbon multiple bonds, Paterno-Buchi reaction,, Photochemistry of nitrites-Barton reaction., OC-08: Reactive intermediates and Molecular rearrangements 15 hrs, Reactive Intermediates: Generation, detection, structure, stability and reactions of, carbocations, carbanions, carbenes, nitrenes and free radicals., Molecular rearrangements: Definition and classification. Molecular rearrangements, involving 1) electron deficient carbon: Wagner- Meerwein, Pinacol-Pinacolone, Allylic and, Wolf rearrangement. 2) electron deficient Nitrogen: Hofmann, Lossen, Curtius, Schmidt and, Beckmann rearrangements 3) electron deficient Oxygen: Baeyer-Villiger oxidation. 4) Base, catalysed rearrangements: Benzilic acid, Favourski , Transannular , Sommlett-Hauser and, Smiles rearrangement, References :, 1. Stereochemistry of Carbon compounds by Ernest L Eliel / Samuel H. Wilen, 2. Stereochemistry of organic compounds – Principles and Applications by D Nasipuri, 3. The third dimension in organic chemistry, by Alan Bassindale, 4. Stereochemistry: Conformation and Mechanism by P S Kalsi, 5. Stereochemistry by V M Potapov, 6. Advanced Organic Chemistry by Jerry March, 7. Mechanism and Structure in Organic Chemistry S. Mukerjee, 8. Organic chemistry Vol.I and II by I.L.Finar, 9. Comprehensive organic chemistry Vol.5 D.H.R.Barton and W.D..Ollis, , Paper CH 203 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY, PC-05: Thermodynamics-II & Statistical Thermodynamics, PC-06: Photochemistry-I, PC-07: Quantum Chemistry-II, PC-08: Solid state chemistry, PC-05:Thermodynamics-II & Statistical Thermodynamics, 15 hrs, Ideal solutions. Thermodynamic properties of ideal solutions. Mixing quantities. Vapour, pressure -Raoult’s law. Thermodynamic properties of ideally dilute solutions. Vapour, pressure- Henry’s law., Nonideal systems. Concept of fugacity, fugacity coefficeient. Determination of fugacity. Non, ideal solutions. Activities and activity coefficients. Standard-state conventions for non ideal, solutions. Determination of activity coefficients from vapour pressure measurements. Activity, coefficients of nonvolatile solutes using Gibbs-Duhem equation., Multicomponent phase equilibrium: Vapour pressure lowering, freezing point depression and, boiling point elevation, , 14
Page 15 :
15, Statistical Thermodynamics:, Partition Functions: Concepts of distribution and probability, Boltzmann distribution law., Interpretation of partition functions- translational, rotational, vibrational and electronic, partition functions. Relationship between partition functions and thermodynamic functions, (only S & G)., PC-06: Photochemistry –I, 15 hrs, Electronic transitions in molecules. The Franck Condon principle. Electronically excited, molecules- singlet and triplet states. Radiative life times of excited states-theoretical, treatment. Measured life times. Quantum yield and its determination. Experimental set up of a, photochemical reaction. Actinometry-ferrioxalate and uranyl oxalate actinometers – problems., Derivation of fluorescence and phosphorescence quantum yields. E-type delayed, fluorescence- evaluation of triplet energy splitting(∆EST). Photophysical processesphotophysical kinetics of unimolecular reactions. Calculation of rate constants of various, photophysical processes-problems, State diagrams, Photochemical primary processes. Types of photochemical reactions- electron transfer,, photodissociation, addition, abstraction, oxidation and isomerization reactions with examples., Effect of light intensity on the rates of photochemical reactions. Photosensitization., Quenching-Stern-Volmer equation. Introduction to fast reactions- Principle of flash, photolysis., PC-07: Quantum chemistry-II, Cartesian, Polar and spherical polar coordinates and their interrelations., , 15 hrs, , Schrodinger equation for the hydrogen atom- separation into three equations. Hydrogen like, wave functions. Radial and angular functions. Quantum numbers n, l and m and their, importance. The radial distribution functions. Hydrogen like orbitals and their representation., Polar plots, contour pots and boundary diagrams., Many electron systems. Approximate methods. The variation method-variation theorem and, its proof. Trial variation function and variation integral. Examples of variational calculations., Paricle in a box. Construction of trial function by the method of linear combinations., Variation parameters. Secular equations and secular determinant., Bonding in molecules. Molecular orbital theory-basic ideas. Construction of MOs by LCAO,, H2+ ion. The variationan integral for H2+ ion. Detailed calculation of Wave functions and, energies for the bonding and antibonding MOs. Physical picture of bonding and antibonding, wave functions. Energy diagram. The MO wave function and the energy of H2 molecule MO, by LCAO method and Valence bond method (detailed calculations not required)-comparison, of MO and VB models., PC-08: Solid state chemistry, 15 Hrs, Electronic properties of metals, insulators and semi-conductors: Electronic structure of, solids, Band theory, band structure of metals, insulators and semi-conductors. Electrons, holes, and Excitons. The temperature dependence of conductivity of extrinsic semi-conductors., Photo conductivity and photovoltaic effect – p-n junctions., Superconductivity: Occurrence of superconductivity. Destruction of superconductivity by, magnetic fields – Meissner effect. Types of superconductors. Theories of super conductivity –, BCS theory., , 15
Page 16 :
16, High temperature superconductors: Structure of defect perovskites. High Tc, superconductivity in cuprates. Phase diagram of Y-Ba-Cu-O system. Crystal structure of, YBa2Cu3O7-x. Prepartion of 1-2-3 materials. Origin of high Tc superconductivity., Nanoparticles and their applications:, Introduction to nanoparticles. Reduced dimensionality in solids – zero dimensional systems,, fullerenes, quantum dots. One dimensional systems, carbon nano tubes, preparation of nano, particles –top down and bottom up methods. Preparation of nanomaterials- – sol gel methods,, and chemical vapour deposition method; thermolysis. Characterization of nanoparticles –, experimental methods – powder X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy (TEM),, and atomic force microscopy (AFM) ( detailed theory and instrumentation are not required)., Optical properties of nanoparticles, Applications of nanoparticles., References:, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27., , Atkin’s Physical Chemistry, Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, Oxford University press, Physical Chemistry, Ira N. Levine, McGraw Hill, Physical Chemistry-A Molecular approach, D.A. McQuarrie and J.D. Simon, Viva, Books Pvt Ltd, Molecular Thermodynamics, D.A. McQuarrie and J.D. Simon, University Science, Books, Quantum Chemistry, Ira N. Levine, Prentice Hall, Introduction to Quantum Chemistry, A.K. Chandra, Tata McGraw Hill, Introduction to Solids, Leonid V. Azaroff, Tata McGraw Hill, Solid state Chemistry, D.K. Chakrabarthy, New Age International, Solid state Chemistry and its aplications, A.R. West, Plenum., Fundamentals of Photochemistry, K.K.Rohtagi-Mukherji, Wiley-Eastern, Molecular Photochemistry, N.J. Turro, Benjamin, Photochemistry, R.P.Kundall and A. Gilbert, Thomson Nelson, Essentials of Molecular Photochemistry by A. Gilbert and J. Baggott, Blackwell, Scientific Publications., Organic Photochemistry by J.M.Coxon and B.Halton, Cambridge University press., Introductory Photochemistry by A.Cox and T.J.Kemp. McGraw-Hill, London., Principles of the Solid State, H. V. Keer, New Age International, Elements of Physical Chemistry by Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, Oxford University, Press, Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics, L. K. Nash, Addison – Wesley, Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics, T. L. Hill, Addison Wiley, Statistical Thermodynamics, M. C. Gupta, New Age International, Quantum Chemistry, D.A. McQuarrie, Prentice Hall, Elementary Quantum Chemistry, F. L. Pilar, McGraw Hill., Nanostructured Materials and Nanotechnology, edited by Hari Singh Nalwa,, Academic Press, Self-Assembled Nanostructures, Jin Zhang, Zhong-lin Wang, Jun Liu, Shaowei Chen, & Gan-Yu-Liu, Kluwer Academic/Plenum, Introduction to Nanotechnology, Charles P. Poole Jr, F. J. Owens, Wiley India Pvt., Ltd., The physics and chemistry of solids by Stephen Elliott, Wiley Publishers., Introductory Photochemistry by A.Cox and T.J.Kemp. McGraw-Hill, London., 16
Page 18 :
18, Origin of mass spectrum, principles of EI mass spectrometer. Types of fragments: odd, electron and even electron containing neutral and charged species (even electron rule),, Nitrogen rule, isotopic peaks, determination of molecular formula, metastable ion peaks. High, resolution mass spectrometry. Salient features of fragmentation pattern of organic compounds, including β-cleavage, Mclafferty rearrangement, retro Diels – Alder fragmentation and ortho, effect. Principle of EI, CI, Fast Atom Bombardment (FAB), Secondary Ion Mass, Spectrometry (SIMS), Electrospray (ESI) ionization and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption, Ionization (MALDI) methods. Introduction to principle and applications of Gas, Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and Liquid chromatography-Mass, Spectrometry (LC-MS) techniques., ASP-08: Photoelectron & ESR sprectroscopy, 15 hrs, Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Principle and Instrumentation, Types of Photoelectron Spectroscopy – UPS & XPS. Binding, Energies, Koopman's Theorem, Chemical Shifts. Photoelectron Spectra of Simple Molecules:, N2, O2, F2, - Vibrational Structure of PES Bands, Potential energy curves, Interpretation of, Vibrational spectral data for ionized (M+) species, Prediction of Nature of Molecular Orbitals., ESCA in qualitative analysis, Principles of Auger electron spectroscopy., Electron Spin Resonance, Introduction, principle, instrumentation, selection rules, interpretation of Lande’s factor ‘g’., Hyperfine and super hyperfine Coupling. Anisotropy in ‘g’ values and hyperfine coupling, constants. Zero field splitting, Kramer’s degeneracy and quadrupolar interactions., Study of free radicals and transition metal complexes. Evidence for covalency in complexes,, ex. Cu(II) Bissalcylaldimine, Bis-acetylacetanatovanadyl(II) and hexachloroiridium(IV), complexes., References:, 1. Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds by R.M. Silverstein and F.X. Webster., 2. Organic spectroscopy by William Kemp, 3. Mass Spectrometry for Chemists and biochemists by M. Rose and R.A. W. Johnstone, 4. Spectroscopic methods in organic chemistry by D.H. Williams and I. Fleming, 5. Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry by A. H. Beckett and J.B. Stenlake, 6. Biological Mass Spectrometry by A.L. Burlingame, 7. Principles and Practice of Biological Mass Spectrometry by Chhabil Das, 8. Spectrscopic identification of organic compounds by R.M.Silverstein. G.C.Bassler and, T.E.Morrill, 9. NMR-A multinuclear introduction by William Kemp, 10. Stereochemistry of Carbon compounds by Ernest L Eliel / Samuel H. Wilen, 11. Principles of Polarography, Heyrovsky., 12. Principles of Polarography, Kapoor., 13. Modern Electroanalytical methods, edited by C.Charlot, Elsevier Company., 14. Principles of Instyrumental analysis, Skoog, Holler and Nieman, Harcourt Asia PTE Ltd., 15. Analytical Chemistry-An Introduction, Skoog, West, Holler and Crouch, Saunders, College Publishing., 16. Prinicples of Instrumental Analysis, Skoog and Leary, Saunders College Publishing., 17. International series of Monographs, Vol. 53: Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Edited by, D. Beckerand D. Betteridge 1972., 18. Sructural methods in inorganic chemistry, E.A.V. Ebsworth, 18
Page 19 :
19, Practicals:, Paper CH 251 : Inorganic chemistry practicals, I. Analysis of Two component mixtures:, (i). Separation of Ni2+ and Cu2+ in a mixture and estimation of Ni2+ (gravimetric) and Cu2+, (volumetric)., (ii). Separartion of Fe2+ and Al3+ in a mixture and estimation of Fe2+ volumetrically and Al3+, gravimetrically., (iii). Separartion of Ag+ and Ca2+ in a mixture and estimation of Ag+ volumetrically and Ca2+, volumetrically, II. Analysis of three component mixtures:, (i). Separation of (Ni2+ and Cu2+) from Mg2+ in the given mixture and estimation of Mg2+, (Gravi)., III Applied titrimetric analysis, (i) Determination of Iron and calcium in Cement, (ii) Determination of Calcium in calcium tablets, (iii) Determination of alkali content in antacid, IV. Ion exchange methods of analysis:, (i). Determination of capacity of an ion exchange resin., (ii). Separation of Zinc and Magnesium on an anion exchange resin and estimation of Mg2+, and Zn2+., Suggested Books: (For both semesters)., 1. (i). Text book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis by A.I.Vogel, 3rd edition, ELBS 1969., (ii). Vogel’s text book of Quantitative Inorganic analysis. Jeffery etal, 4th edition, ELBS 1988., (iii). Vogel’s text book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis. 6th edition, Pearson education ltd, 2002., 2. Practical Inorganic chemistry By G.Marr and R.W.Rockett 1972., 3. Experimental Inorganic/Physical Chemistry – An Investigative integrated approach to, Practical Project work. By Mounir A.Malati, 1999., 4. Advanced experimental Inorganic chemistry by. Ayodhya Singh., 5. Practical Inorganic Chemistry by G. Pass & H. Sutchiffe, 2nd edn John Wiley & sons, Paper CH 252 Organic Chemistry Lab 6 hours/ week, Identification of organic compounds systematic qualitative analysis:, Physical data BP / MP, Ignition test, solubility classification, Extra elements-N,S & Halogens,, (Lassagnine sodium fusion test, Beilstein test), Functional groups tests, Preparation of crystalline derivative and determination of their m.p.s, and reference to literature to identify the compounds, A minimum of 8 following compounds to be studied as unknown covering atleast one from, each of the solubility classes, Glucose, benzoic acid, 2-chloro benzoic Acid, Anisic acid, p-Nitrobenzoic acid; p-Cresol, pChlorophenol, -Naphthol; Aniline, o/m/p-Chloroanilines; N-Methyl aniline/N-Ethylaniline,, N,N-Dimethylaniline,Benzamide, Benzaldehyde, Anisaldehyde,, Acetophenone,benzophenone,Ethylbenzoate,methylbenzoate,Nitrobenzene, chlorobenzene,, bromobenzene , naphthalene, biphenyl anthracene., Identification of unknown organic compounds from their IR, UV, 1H nmr and MS:, 19
Page 20 :
20, Analysis of recorded spectra of 6 compounds belonging to i) aromatic carboxylic acid ii), alcohols and phenols iii) aldehydes and ketones iv) amides v) esters vi) alkenes and alkynes, References, 1. Text book of practical organic chemistry, Vogel, 2. Text book of practical organic chemistry, Mann and Saunders., 3. Spectral identification of organic compounds Bassler, Silverstein 5th Edition, Paper CH 253: Physical Chemistry Lab: 6 hrs /week, Data analysis II: Mean and standard deviation; absolute and relative errors; linear regression;, covariance and correlation coefficient., Distribution:, 1) Distribution of I2 between hexanes / cyclo hexanes / CCl4 and aq.KI solution- calculation of, equilibrium constant., 2) Study of complex formation between ammonia and metal ion, Chemical Kinetics, 1) Stoichiometry of peroxydisulphide- iodide reaction, 2) Peroxydisulphide- iodide reaction: order w.r.t [I-] by isolation method, 3) Peroxydisulphide- iodide reaction: order w.r.t [S2O82-] by initial rate method, Condutometry:, 1) Titration of a mixture of strong and weak acids vs strong base, 2) Determination of the hydrolysis constant of aniline hydrochloride, 3) Determination of solubility product, Potentiometry:, 1) Titration of Fe+2 vs Cr2O72- (redox titration), 2) Titration of Cl- vs Ag+ (precipitation titration), 3) Determination of solubility product, Polarimetry:, 1) Determination of specific rotation of glucose and fructose, 2) Enzyme catalysed inversion of sucrose, Colorimetry:, 1) Verification of Beer’s law and calculation of molar absorption coefficient using, CuSO4 and KMnO4 solutions, pH metry:, 1) Calibration of a pH meter and measurement of pH of different solutions, 2) Preparation of phosphate buffers, 3) Titration of strong acid vs strong base, References:, 1. Senior Practical Physical Chemistry: B.D. Khosla, V.C. Garg and A. Khosla, 2. Experimental Physical Chemistry: V. Athawale and P. Mathur., 3. Practical Physical Chemistry: B. Vishwanathan and P.S. Raghavan., 4. Practical in Physical Chemistry: P.S. Sindhu, 5. Advanced Practical Physical chemistr: J.B.Yadav, 6. Vogel Text book of Quantitative Analysis, 6th edition, Pearson education Ltd. 2002, , 20