Page 1 :
S.N.T. PUBLIC SCHOOL, Subject : English Grammar, Chapter: The Verb, Verb:, A verb is a doing word that shows some action, feeling or, existence., It tells us something about the subject in a sentence., Examples:, i), ii), iii), , Ankit eats sweets., I feel cold., Ashoka was a great king., , Classification of Verb:, , (action), (feeling), (existence)
Page 2 :
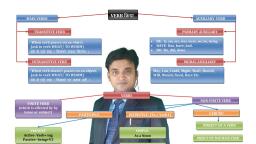
Verb can be classified into two classes., 1. Main Verb, 2. Auxiliary Verbs, , 1. Main Verbs:, The words expressing something being done , state or quality, of subject are termed as main verbs., Main Verbs are of two types., A) Finite Verb, B) Non finite verb, , (A) Finite Verb:, A finite verb is that which is limited to the number, person and, tense of its subject., OR, A finite verb is that which changes according to the number, person and tense of its subject., Examples:, 1. I am a teacher., 2. They are teachers., 3. He is a teacher., 4. You are a teacher.
Page 3 :
Finite verbs are of two types., a) Transitive verb, b) Intransitive verb, , a) Transitive Verbs:, A verb that requires an object to complete Its meaning is called, a transitive verb., Examples:, 1. Boys fly their kites., 2. Priya laughs at the joker., 3. Look into the book., 4. He is talking about the movie., , b) Intransitive Verbs:, A verb that does not require an object to complete its meaning,, but makes sense by itself is called an intransitive verb., Examples:, 1. Birds fly., 2. Priya laughs., 3. Look forward., 4. He is talking.
Page 4 :
(B) Non-finite Verb:, A non-finite Verb is that which is not limited to the number,, person and tense of its subject., OR, A non-finite Verb is that which does not change according to, the number, person and tense of its subject., • A non-finite verb is a verb form that does not show tense., Examples:, 1. I like a blooming flower., 2. He likes a blooming flower., 3. They like a blooming flower., 4. She likes a blooming flower., , There are three types of non-finite verb:, (1) Gerunds, (2) Infinitives, (3) Participles
Page 5 :
1. Gerunds, Gerunds is that form of verb which end in -ing: and act like, nouns and can serve as subjects or objects of sentences., *Gerund = ‘Verb +ing’ and act like Noun., Examples:, •, •, •, , I like swimming., Smoking is injurious to health., I like reading story books., , 2. Infinitives, The base Form of a verb not limited by number and person is, called an infinitive., • An infinitive is usually formed by writing ‘to’ before the, root verb., • It can be used as subject or object., Examples:, 1. I have to go to school., 2. Children love to go out., 3. I was about to leave., , 4. Participles, •, A Participle is a verb usually added -ing or -ed. It, works as an adjective.
Page 6 :
•, There are two types of Participle. –, Present Participles and past participle., Present Participles = ‘Verb +ing’ and works as an adjective., Past Participles = ‘Verb +ed’ and works as an adjective., Examples:, •, The sun was shining so I went for a walk., •, The man speaking English is our teacher., •, He has flown to Chicago twice., •, The house was decorated with lights., , 2.Auxiliary Verbs:, , Auxiliary are those that help the main verbs in the formation of, tenses., It is also called helping verb., Examples:, 1. Aditi is eating an apple., 2. I have written a letter., 3. You are going to school., , Auxiliary Verbs are of two types., a) Primary Auxiliary (Helping verb), b) Model Auxiliary
Page 7 :
(a) Primary Auxiliaries : It includes three types of verb-, , • Verb 'to be'............is, are, am, was , were, , • Verb 'to do'................do, does , did, , • Verb 'to have'.................have , has , had, , (b) Modal Auxiliaries :, These arecan, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought, to, need, used and dare.