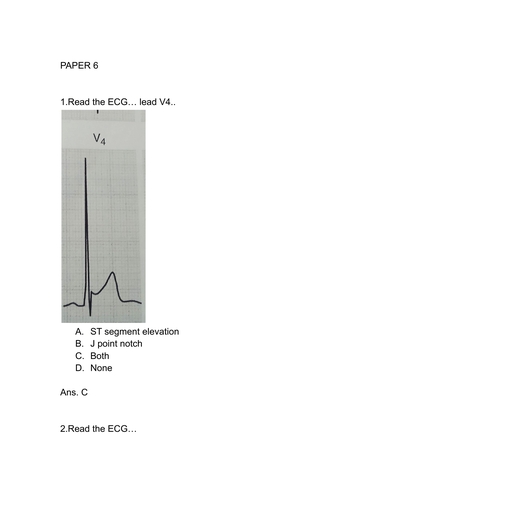
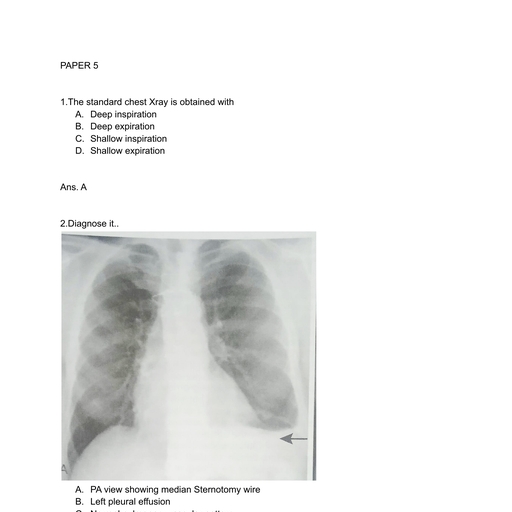
Page 1 :
CARDIAC SURGERY SIMPLIFIED…., BENTALL AND MINI BENTALL PROCEDURE…, MODULE 34….PART.. 1, BULLET POINTS…, The BENTALL procedure and its modification are, the gold standard for treating aortic root, pathology., The modified BENTALL procedure has evolved over, 50 years and involves replacement of entire aortic, root and valve with a composite valve graft and, reimplantation of coronary buttons., The early and long term results of modified, BENTALL procedure are excellent., The mini BENTALL procedure is performed through, an upper mini Sternotomy., MINI Sternotomy is a safe feasible alternative, option to full Sternotomy in aortic root, replacement., INTRODUCTION
Page 2 :
The BENTALL procedure was originally described in, 1968 by BENTALL and de Bono for treatment of, dilated aortic root with aortic incompetence and, involves replacement of the aortic valve, root and, ascending aorta., , EVOLUTION OF BENTALL PROCEDURE..., CABROL PROCEDURE..., Where a separate graft is used to perfuse the, coronaries., BUTTON BENTALL.....
Page 3 :
Where the coronary buttons are excised from the, native aorta, mobilizer and re implanted, appropriately on the graft., VALVE SPARING ROOT REPLACEMENT, PROCEDURE.., David and Yacoub, , Figure... The classical BENTALL procedure and its, modification
Page 4 :
A., Classical BENTALL procedure, B. CABROL PROCEDURE, C. Yacoub’s remodeling valve sparing root, replacement procedure, D., David reimplantation valve sparing root, replacement, INDICATIONS OF PROCEDURE AND ITS, VARIENTS INCLUDE.., PROXIMAL aortic dilatation with involvement, of aortic valve., PROXIMAL aortic dissection., Aortic rupture, Intramural hematoma, Destruction of aortic valve and root by, endocarditis or calcification., The Minimally invasive BENTALL procedure, offers less requirement for blood transfusion,, reduced postoperative pain, reduced, respiratory complications, earlier extubation, and shorter hospital length of stay.
Page 5 :
MINI BENTALL PROCEDURE..., The mini BENTALL procedure follows the, principles of traditional aortic root, replacement surgery., Smaller incision., MINI access hemi arch replacement is for cases, involving distal ascending aortic pathology., MINI STERNOTOMY, The skin incision and caudal extent of mini, Sternotomy is planned by examining contrast, enhanced Computed tomography images., The position of aortic annulus and the, corresponding intercostal space above should, be identified., This is typically fourth or fifth intercostal, space., Patient is exposed and the location of the, Suprasternal notch, Manubriosternal junction,, xiphisternum and intercostal space above and, below the aortic annulus demarcated with a, marking pen.
Page 6 :
The femoral arteries are identified and marked, and patient washed with antiseptic solution, and draped to leave precordium and groin, area exposed., An approximately 5 cm midline skin incision is, made from the Manubriosternal junction to, the third intercostal space., Diathermy is used to extend the incision down, onto the body of sternum, to the supra sternal, notch superiorly and to the sternal edge, laterally., The bridging vein atop the manubrium is, clipped and resected., A subcutaneous drain is inserted Parasternal, lay one intercostal space below inferior limit of, skin incision and passed along the length of, the midline incision., A pneumatic or electric bone saw is used to, develop a mini Sternotomy starting from, Suprasternal notch and moves inferiorly to, terminate at the left Parasternal space.
Page 7 :
Surface landmark for mini access... BENTALL, procedure.
Page 8 :
Bone wax is approximately applied and thymic, fat pad mobilizer superiorly to the level of, innominate vein and resected., The pericardium is incised as an inverted T, from the pericardial reflection to the fourth, intercostal space., Three pericardial traction sutures are placed, on each side and and secured to the skin, incision., A Minimally invasive sternal retractor is then, inserted between the hitched pericardium and, opened to expose ascending aorta., , Thanks.. To be continued...