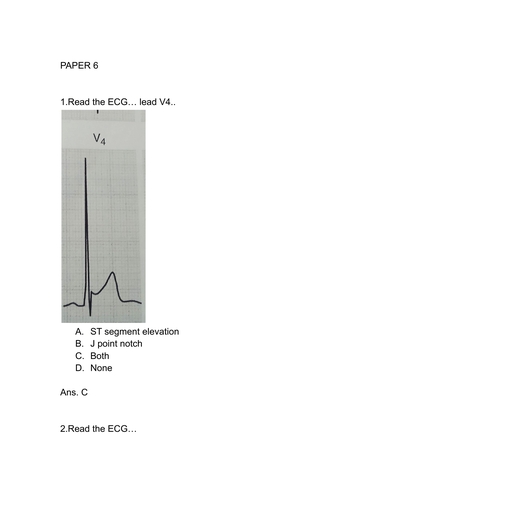
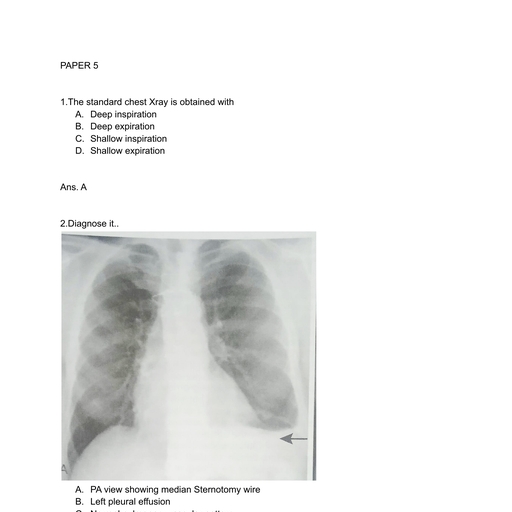
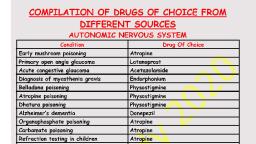
Page 1 :
CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE PART 2..., ADRENERGIC ANTAGONIST...., This include alpha 1 receptor antagonist, beta, receptor antagonist and non Selective alpha/beta, antagonist., ALPHA 1 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST, Selective alpha 1 antagonist, Doxazosin(Cardura), Prazocin(Minipress), Terazocin, MECHANISM OF ACTION, Selective alpha 1 receptors antagonist act, peripherally and lead to arterial and venous, vasodilation., SIDE EFFECTS, Side effects of alpha 1 receptors antagonist include, ORTHOSTATIC hypotension, Dizziness, light headed, Ness, drowsiness, headache, dry mouth and, malaise.
Page 2 :
The first dose should be given at bed time to limit, the effect associated with ORTHOSTATIC, hypotension., Tachyphylaxis may develop with long term, administration in patients with heart failure., INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS, Used in hypertension and BPH, NON Selective ALPHA ANTAGONIST, Phentolamine, MECHANISM OF ACTION, Nonselective alpha adrenergic antagonist with, similar affinities for alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors, producing vasodilation and increase in heart rate., SIDE EFFECTS, Side effects of these drugs include Hypotension,, tachycardia, arrhythmia, angina, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
Page 3 :
They may exacerbate peptic ulcer disease and, produce nasal congestion., INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS, Phentolamine is labelled for use in hypertensive, crisis in patients with Pheochromocytoma and for, treatment in skin necrosis in patients with, norepinephrine, Dopamine and epinephrine., BETA RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST, Beta blockers were first discovered in 1958., The effects produced depends on the degree of, endogenous Sympathetic activity., Beta blocker are classified as Selective or non, Selective as well as having alpha 1 blocking, properties., MECHANISM OF ACTION, Non Selective beta blockers antagonise both beta 1, and beta 2 receptors, inhibiting the effects of, catecholamines on these receptors. Cardiovascular, effect includes decrease in contractility and heart, rate.
Page 4 :
Non cardiovascular effects mediated through beta, 2 blockade include increased peripheral vascular, resistance and bronchospasm., Selective beta blockers antagonise beta one, receptors to a greater extent than beta 2, receptors., Cardiovascular effects are the same as with non, Selective beta blockers., Both classes generally lead to decrease in blood, pressure, sinus node automaticity, conduction, through the Atrioventricular node and increased, AV nodal refractories., It has intrinsic sympathomimetic activity ., Beta blocker without intrinsic sympathomimetic, activity have been shown to decrease recurrent, myocardial infarction and sudden death., Reduce mortality and hospitalization secondary to, heart failure., SIDE EFFECTS
Page 5 :
Side effects of these drugs include fatigue,, Bradycardia, heart block, bronchospasm,, depression, lipid abnormality, masking the, symptoms of hypoglycaemia, rebound effect with, Abrupt discontinuation, precipitation of heart, failure and impotence., INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS, Indications for beta blockers include hypertension,, ischemic heart disease, acute myocardial, infaraction, stable and Unstable angina, heart, failure, arrhythmia., ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS, Include hypersensitivity to beta blockers, asthma,, heart block greater than first degree, insulin, dependent diabetes with frequent hypoglycemic, episodes and overt heart failure., COMBINED ALPHA AND BETA RECEPTOR, ANTAGONIST, MECHANISM OF ACTION
Page 6 :
The combination preparation are specific alpha 1, receptor antagonist but non Selective beta, receptor antagonist. Labetalol is 7:1 Selective beta, to alpha receptor in IV preparation and 3:1 in oral, preparation., INDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS, The labelled indications of labetalol is, hypertension., Carvedilol has labelled indications for hypertension, as well as LV dysfunction following MI and mild to, severe chronic heart failure.., , Thanks... To be continued..