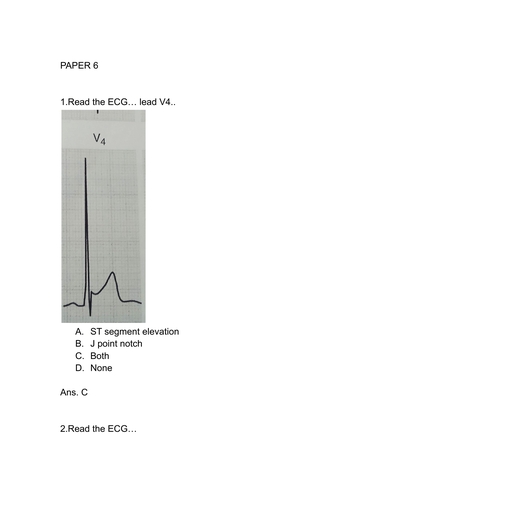
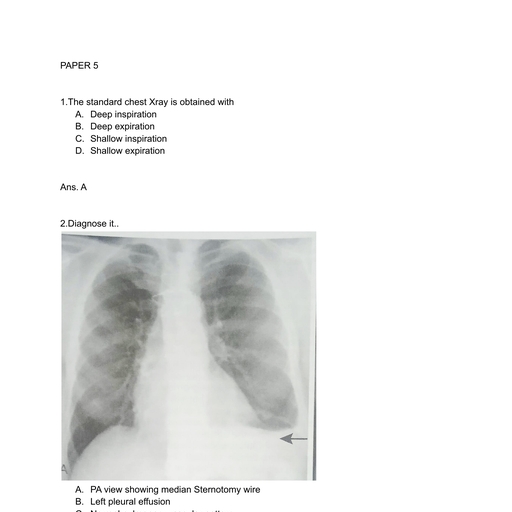
Page 1 :
CARDIAC SURGERY SIMPLIFIED BY DR ABHISHEK, SRIVASTAVA, MODULE 31…..CORONARY ARTERY ANEURYSM, AND FISTULAS…, BULLET POINTS, Coronary artery aneurysm are defined as the local, dilatation of artery greater than 1.5 times that of, the diameter of the adjacent segment and can be, very large termed as giant aneurysm., Coronary angiography is the gold standard for, diagnosis of coronary artery aneurysm and fistula., Treatment of aneurysm consists of medical, therapy, covered Stent and surgical intervention., Large fistula require treatment regardless of, symptoms., For small to moderate fistula, symptoms guide, timing of intervention., Surgical ligation and transcatheter closure are well, established technique for coronary fistula.
Page 2 :
CORONARY ARTERY ANEURYSM, INTRODUCTION, Coronary dilatation can be much more significant, and reach upto four times the adjacent coronary, segment termed giant coronary artery aneurysm., Aneurysm formation is most commonly seen in the, right coronary artery (40 to 87%)., Males are three times more commonly affected, than females., CLASSIFICATION
Page 3 :
Saccular aneurysm occur when the maximal, transverse diameter overcome the longitudinal, diameter., Fusiform aneurysm are defined by the longitudinal, diameter exceeding the transverse diameter., True aneurysm involve all three layers of vessel, wall (tunica intima, tunica media, tunica adventia).
Page 4 :
False aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm only involve, outer layer., RISK FACTORS AND ASSOCIATIONS, Male gender and hyperlipidemia., Obstructive coronary artery disease is common in, patients with coronary artery aneurysm., PATHOGENESIS, , PATHOGENESIS OF CORONARY ANEURYSM...
Page 5 :
CLINICAL PRESENTATION, Anginal symptoms with or without myocardial, infarction as well as Dyspnea are amongst the, most symptoms., Rupture is rare but when it occurs, sudden death,, tamponade and acute heart failure are possible, outcome., Mediastinal mass may also be seen on imaging., Distal embolization has also been observed., Fistula formation between aneurysm and other, cardiac chamber has also been described., DIAGNOSIS, Coronary angiography, Coronary CT angiography, TREATMENT, Aspirin and Statin therapy., Medical therapy is indicated for all aneurysmal, coronary disease.
Page 6 :
Percutaneous and surgical treatment is not, indicated for asymptomatic small or medium sized, aneurysm., Giant aneurysm have greater chance of rupture, and surgery is generally recommended., , Coronary angiography illustrating coronary artery, aneurysm....
Page 7 :
CORONARY ARTERY FISTULA, INTRODUCTION, Coronary artery fistula are abnormal connections, between the coronary arteries and any of the, cardiac chambers or other vessels., They are also known as coronary arteriovenous, fistula., , PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Page 8 :
Most CAF are small and asymptomatic. Pathology, primarily occur through coronary steal and volume, overload from shunt physiology., Coronary steal results from compromised, myocardial perfusion distal to the fistula as blood, will flow through the lower resistance fistula, rather than the smaller and higher resistance, myocardial vessels., Left to right coronary artery fistula flow to the, right heart chambers or venous structure occur, throughout the cardiac cycle similar to patent, ductus arteriosus (PDA) and can result in coronary, steal with complications of volume overload of, both ventricle., Left to left CAF flow into the left atrium or, pulmonary vein will cause continuous flow through, out the cardiac cycle and volume overload of left, chambers only., CLINICAL PRESENTATION, Asymptomatic
Page 9 :
Dyspnea with exertion is most common symptoms., Continuous murmur at lower left sternal border., NATURAL HISTORY, Small CAF in children tend to grow with age., Spontaneous thrombosis and fistula closure is rare., Complications include..., Volume overload of cardiac chambers, Congestive heart failure, Arrhythmia, Dilatation of coronary artery branches proximal to, fistula site, Myocardial infarction, Cardiomyopathy, Valvular regurgitation from papillary dysfunction, Endocarditis, Pulmonary hypertension, DIAGNOSIS, Coronary angiography is the gold standard.
Page 10 :
ECG.. Chamber enlargement, AF, ischemia, X-RAY.... Cardiomegaly and pulmonary congestion, TEE.. Transesophageal Echocardiography, CT, MRI... Noninvasive, IVUS, FFR, MANAGEMENT GUIDELINE, Large CAVF, regardless of symptoms, should be, closed after fistula course is defined., Small to moderate CAVF be closed in the presence, of symptoms including myocardial ischemia., TREATMENT, Treatment options for coronary artery fistula are, either surgical ligation or transcatheter closure., Surgical ligation can occur alone with or without, cardiopulmonary bypass or with coronary artery, bypass grafting.
Page 11 :
TRANSCATHETER DEVICE CLOSURE... Coils,, detachable balloons, stents, double umbrella,, vascular plugs, COMPLICATIONS, Distal embolization, dissection and MI.
Page 12 :
END OF CORONARY ARTERY ANEURYSM AND, FISTULAS...