Page 1 :
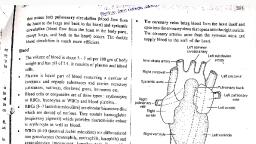
VASCULAR SURGERY… PART 2, During the first three weeks of gestation, simple, diffusion is sufficient to support the embryo, however by the fourth week, a functional, cardiovascular system must be in place to maintain, the rapidly developing embryo., The cardiovascular system in embryo is one of the, first and earliest system to appear and begin to, function., Isolated blood vessels and blood components form, in the yolk sac by day 17., The heart begin to beat by day 22 and pumps, blood by day 24., Vasculogenesis begins first in the yolk sac at day, 17., The hematopoitic stem cells serve as the source of, blood cells to the embryo until day 60., The heart, dorsal aorta, umbilical vessels, vitelline, vessels and cardinal veins are being formed by, Vasculogenesis.
Page 2 :
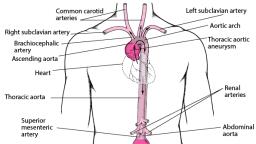
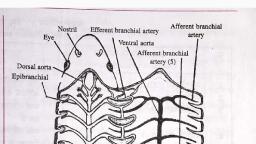
As the developing heart lengthen, a series of, Swelling become visible. Beginning at the inflow, end these include the sinus venosus with its right, and left horns, primitive atrium, primitive left, ventricle, bulbus cordis and Truncus arteriosus., AORTIC ARCH, The right common carotid and right subclavian, arteries arise from the brachiocephalic artery,, where as the left common and left subclavian, arteries originate as separate vessels from the, aortic arch., The first two aortic arches appear and regress, quickly and contribute to very little to adult, structure, whereas fifth aortic arch never develops, in humans.
Page 3 :
The six primitive aortic arches……., The third aortic arches become the common, carotid arteries and proximal segments of the, internal carotid arteries.
Page 4 :
The distal segment of the internal carotid arteries, are derived from the dorsal aorta between the first, and third arches., The external carotid arteries sprout from the, common carotid arteries., The dorsal aorta on each side of the embryo, between the third and fourth arches disappear., The fourth aortic arches are asymmetrical with, regard to their fate., The left aortic arch forms the part of the adult, aortic arch between the left common carotid and, left subclavian arteries, whereas the right aortic, arch becomes the proximal segment of the right, subclavian artery., The right horn of aortic sac, connected to the right, third and fourth aortic arches, elongate to become, the brachiocephalic artery and left horn becomes, initial portion of aortic arch., The proximal portion of the both six arches, becomes the right and left pulmonary arteries.
Page 5 :
The distal segment of the right sixth arch, disappear., But the distal segment of the left six arch becomes, the ductus arteriosus during fetal life., And a trophies after birth to become the, Ligamentum arteriosum., AORTIC ARCH ANOMALIES, In 22% of the population, the left common carotid, artery originates from the brachiocephalic trunk, rather than the aortic arch, in what is termed as, bovine arch., In this case, the brachiocephalic truk give rise to, right subclavian, right common carotid and left, common carotid arteries, where as the left, subclavian artery originates from aortic arch., This varient account for the 73% of all arch, anomalies., PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS, The ductus arteriosus develops from the distal, portion of the left sixth aortic arch and is
Page 6 :
responsible for shunting blood from the immature,, developing fetal lungs to the systemic circulation., A patent ductus arteriosus is the most common, vascular anomaly., By the age of 1 month, ductus normally obliterates, to become Ligamentum arteriosum., If the ductus arteriosus does not constrict and, remain patent, blood is shunted from high pressure, thoracic aorta to low pressure pulmonary system,, eventually resulting in significant pulmonary, hypertension.
Page 7 :
Right sided aorta with patent ductus arteriosus., Arrow points to right side aorta A. A patent ductus, arteriosus B is filling pulmonary artery C., , To be continued….