Page 1 :
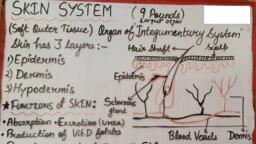
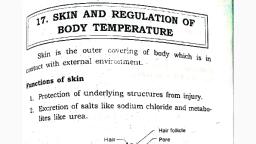
“Integumentary” means a body’s outer covering., Q. Write a detail note on structure of skin, Q. Write about the Structure of Hypodermis, Skin :The skin is the body’s largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals., Your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature., Nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold., Your skin, along with your hair, nails, oil glands and sweat glands, is part of the, integumentary system., , Three layers of tissue make up the skin:, , , Epidermis, the top layer.
Page 2 :
, , , Dermis, the middle layer., Hypodermis, the bottom or fatty layer., , , , 1. Epidermis, , The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides, a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone., , The epidermis is composed of layers; most body parts have four layers, but, those with the thickest skin have five. The layers are:, , , Stratum corneum (horny layer);, , , , Stratum lucidum (only found in thick skin – that is, the palms of the hands, the, soles of the feet and the digits);, , , , Stratum granulosum (granular layer);, , , , Stratum spinosum (prickle cell layer);, , , , Stratum basale (germinative layer).
Page 3 :
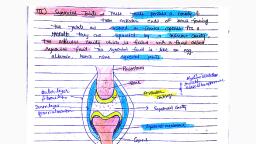
Langerhans cells. These are antigen (micro-organisms and foreign, proteins)-presenting cells found in the stratum spinosum., , Merkel cells. These cells are only present in very small numbers in the, stratum basale. these have a role in sensation, especially in areas of the, body such as palms, soles and genitalia., , 2. Dermis, , The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough, connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands., This is Situated between the basement membrane zone and the, subcutaneous layer, and Size about (1-5mm)., The primary role of the dermis is to sustain and support the epidermis.
Page 4 :
Layers of dermis., The dermis is made up of two layers:, , , The more superficial Papillary dermis;, , , , The deeper Reticular dermis., , 1. Papillary dermis, , The papillary dermis is the thinner layer, consisting of loose, connective tissue containing capillaries, elastic fibres and some, collagen., 2. Reticular dermis, , The reticular dermis consists of a thicker layer of dense connective, tissue containing larger blood vessels, closely interlaced elastic fibres, and thicker bundles of collagen., It also contains fibroblasts, mast cells, nerve endings, lymphatics, and epidermal appendages., , Specialised dermal cells and structures., Fibroblast :, The fibroblast is the major cell type of the dermis and its main, function is to synthesise collagen, elastin and the viscous gel within, the dermis., Collagen: – which gives the skin its toughness and strength – makes, up 70% of the dermis and is continually broken down and replaced;, elastin fibres give the skin its elasticity., Mast cells:- Mast cells contain granules of vasoactive chemicals, (the main one being histamine). They are involved in moderating, immune and inflammatory responses in the skin.
Page 5 :
Hypodermis, The hypodermis is the subcutaneous layer lying below the dermis., it consists largely of fat. It provides the main structural support for the skin,, as well as insulating the body from cold and aiding shock absorption. It is, interlaced with blood vessels and nerves.