Page 1 :
1
Page 2 :
SHS General Biology 2, Activity Sheet No.4 – Mechanisms of Evolutionary Changes, First Edition, 2021, Published in the Philippines, By the Department of Education, Region 6 – Western Visayas, Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of, the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office, wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such, agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties., This Learning Activity Sheet is developed by DepEd Region 6 – Western Visayas., ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this learning resource may be reproduced or, transmitted in any form or by any means electronic or mechanical without written permission, from the DepEd Regional Office 6 – Western Visayas., , 2
Page 3 :
Introductory Message, Welcome to General Biology 2, The Learning Activity Sheet is a product of the collaborative efforts of the, Schools Division of Aklan and DepEd Regional Office VI - Western Visayas through, the Curriculum and Learning Management Division (CLMD). This is developed to, guide the learning facilitators (teachers, parents and responsible adults) in helping, the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum., The Learning Activity Sheet is self-directed instructional materials aimed to, guide the learners in accomplishing activities at their own pace and time using the, contextualized resources in the community. This will also assist the learners in, acquiring the lifelong learning skills, knowledge and attitudes for productivity and, employment., , For learning facilitator:, The General Biology 2 Activity Sheet will help you facilitate the leachinglearning activities specified in each Most Essential Learning Competency (MELC), with minimal or no face-to-face encounter between you and learner. This will be, made available to the learners with the references/links to ease the independent, learning., , For the learner:, The General Biology 2 Activity Sheet is developed to help you continue, learning even if you are not in school. This learning material provides you with, meaningful and engaging activities for independent learning. Being an active learner,, carefully read and understand the instructions then perform the activities and answer, the assessments. This will be returned to your facilitator, on, the, agreed, schedule., , 3
Page 4 :
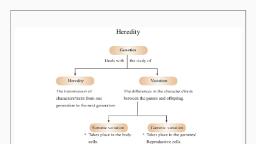
Learning Activity Sheets in General Biology II, Name of Learner:, School:, , Grade Level/ Section:, Teacher:, , Date:, , Mechanism of Evolutionary Change, I. Competency with Code, Explain the mechanism that produce change in population from generation to, generation (eg artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and, recombination), , II. Background Information for Learners, There are millions of other organisms by which we directly and indirectly interact, with. The number and the kinds of organisms living on Earth at a particular time is called, biological diversity. The evolutionary theory is the scientific explanation of the diversity, of life. Evolution, or change over time, is the process of how present- day organisms have, descended from ancient ones., Four (4) forces or mechanisms of evolution are said to have caused disruptions in the, equilibrium. These are: artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and, recombination, 1. Artificial Selection, The nature provides the variation among different organisms so that humans can, select the variations that are useful to, them. This can be done through, selective breeding. This technique is, usually done by farmers and breeders., Individuals with desirable traits or, characteristics are bred to increase the, chances of having offspring with the, same desirable traits. Breeders are able, to produce wide range of plants and, animals that look very different from the, ancestors., Figure 1 shows an enormous, amount of variety of the dog breeds due, to the targeted selection of particular traits by man., Figure 1. Dog Breeding, Source: https://bit.ly/39CtvmL, , 4
Page 5 :
2. Natural Selection, Natural selection is the process through which species adapt to their environments. It, is the engine that drives evolution. Furthermore, it can only takes place if there is variation,, or differences among individuals in population. Importantly, these differences must have, some genetic basis; otherwise, selection will not lead to change in the next generation., There are three types of natural selection such as (1) directional selection, it, happens when a change in the environment causes a change in the observable spectrum of, phenotypes; (2)stabilizing selection, it occurs when intermediate phenotypes are more, likely to survive in the environment; and (3)disruptive or diversifying selection, it occurs, when extreme phenotypes are more likely to adapt to the environment., 3. Genetic Drift, Genetic drift is a mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population, change over generations due to chance (sampling error). Genetic drift occurs in all, populations of non-infinite size, but its effects are strongest in small populations. There were, two examples of genetic drifts that can have significant effects in small populations, namely:, Population bottleneck, it occurs when a sudden sharp decline in the population and, founder effect, it happens when there is a loss of genetic variation because of migration of, a small subgroup in population., 4. Mutation, It is the change in the structure if a gene caused by alterations in the DNA sequence, of an organism. There were different types of mutations such as; (1) substitution, it occurs, when the genetic codon has one altered nitrogenous base; (2) insertion, which, characterized by the addition of an extra set of base pairs to the genetic material, and (3), deletion, occurs when a set of base pair in the genetic material is omitted., 5. Recombination, It simply a rearrangement of genes. This process naturally occurs during the crossing, over stage in meiosis, where there is an exchange of DNA between homologies, chromosomes., , III. Activity Proper, Activity 1. Cross Word Puzzle. Complete the crossword puzzle., ACROSS, 2. It is the change in the structure if a gene caused by alterations in the DNA sequence of an, organism., 3. A type of mutation that occurs when a set of base pair in the genetic material is omitted., 4. A type of natural selection that happens when a change in the environment causes a, change in the observable spectrum of phenotypes., 5. It is the process of how present- day organisms have descended from ancient ones., DOWN, 1. It is the process creates genetic diversity at the level of genes that reflects differences in, the DNA sequences of different organisms., 4. A type of natural selection that occurs when extreme phenotypes are more likely to adapt, to the environment., 5
Page 6 :
Activity 2., Direction: Answer the following questions comprehensively., 1. Which process would be faster, natural or artificial selection? Why?, , 2. How does artificial selection, natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and recombination, beneficial to the different organisms?, 6
Page 7 :
3. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN),, has declared 418 animal species in the Philippines to be threatened: meaning they are, either vulnerable, endangered, or critically endangered. As a learner, what small steps that, you can do to save these animals?, , Reflection, Complete the statements below., I understand, _, _, I don’t understand, _, _, I need more information about, _, , _, _, , Reference for Learners:, Mirabete, G.S., Javier, M.A.O. (2020). General Biology 2 (2nd Edition). Diwa Learning, System, Inc. Makati City, Philippines., Tiamson, M.E. (2016). General Biology (Philippine Edition). Vibal Group., https://ib.bioninja.com.au/standard-level/topic-5-evolution-and-biodi/51-evidence-for-evolutio, n/selective-breeding.html, https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/phenylketonuria, https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/natural-selection/, 7
Page 9 :
9