Page 1 :
SHS, , General Biology 2 Activity, Sheet QUARTER 3 MELC 7, Week 4, Evidences of Evolution, , REGION VI-WESTERN, VISAYAS
Page 2 :
General Biology 2, Activity Sheet No. 7- Evidences of Evolution, First Edition, 2021, Published in the Philippines, By the Department of Education, Region 6 – Western Visayas, Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work, of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or, office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit., Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of, royalties., This Learning Activity Sheet is developed by DepEd Region 6 – Western Visayas., ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this learning resource may be reproduced or, transmitted in any form or by any means electronic or mechanical without written permission, from the DepEd Regional Office 6 – Western Visayas., , Development Team of Science Activity Sheet, Writer:, , BUENA MAJAH VANESSA T. BONUS, , Content and Language Editing:, Dr. MARY CHERRY LYNN M. DALIPE, Division of Aklan Management Team:, Dr. MIGUEL MAC D. APOSIN, CESOV, Mr. SAMUEL J. MALAYO, Dr. DOBIE P. PAROHINOG, Dr. MARY CHERRY LYNN M. DALIPE, Mr. MAHNNIE Q. TOLENTINO, Regional Management Team, RAMIR B. UYTICO, PEDRO T. ESCOBARTE, JR., ELENA P. GONZAGA, DONALD T. GENINE, ROVEL R. SALCEDO, MOONYEEN C. RIVERA, ANITA S. GUBALANE, MINDA L. SOLDEVILLA, DAISY L. LOPEZ, JOSEPH M. PAGALARAN, , ii
Page 3 :
Introductory Message, Welcome to SHS General Biology 2!, The Learning Activity Sheet is a product of the collaborative efforts of the Schools, Division of Aklan and DepEd Regional Office VI - Western Visayas through the Curriculum, and Learning Management Division (CLMD). This is developed to guide the learning, facilitators (teachers, parents and responsible adults) in helping the learners meet the, standards set by the K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum., The Learning Activity Sheet is self-directed instructional materials aimed to guide, the learners in accomplishing activities at their own pace and time using the contextualized, resources in the community. This will also assist the learners in acquiring the lifelong, learning skills, knowledge and attitudes for productivity and employment., , For learning facilitator:, The SHS General Biology I Activity Sheet will help you facilitate the teachinglearning activities specified in each Most Essential Learning Competency (MELC) with, minimal or no face-to-face encounter between you and learner. This will be made available, to the learners with the references/links to ease the independent learning., , For the learner:, The SHS General Biology 2 Activity Sheet is developed to help you continue, learning even if you are not in school. This learning material provides you with meaningful, and engaging activities for independent learning. Being an active learner, carefully read and, understand the instructions then perform the activities and answer the assessments. This, will be returned to your facilitator on the agreed schedule., , iii
Page 4 :
Name of Learner:, Grade and Section:, , Date:, , GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 ACTIVITY SHEET No. 7, Evidences of Evolution, , I. Learning Competency with Code, Explain evidence of evolution (e.g., biogeography, fossil record, DNA/protein, sequences, homology and embryology) (STEM_BIO11/12-IIIc-g-12), , II. Background Information for Learners, SOURCES OF EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION, Evidence from biogeography, Biogeography is the study of the past and present geographic distribution of, organisms. Evolutionary patterns arise among organisms in the same area. Similar, organisms that are found in different locations could mean that these places where once, connected., Evidence from fossil records, Fossils are remains, impression, or trace of organisms of past geologic age that has, been preserved in the Earth’s crust., Evidence from molecular biology, Similarities shared by many organisms in their DNA and RNA structure suggest, common ancestry with modification. The near universality of the genetic code provides, evidence of relatedness between and among organisms., Evidence from structures, Homologous structures are physical structures shared by different organisms such, as set of bones or body form that may have been inherited from a common ancestor,, although it may appear different and have varied functions. These structures are believed, to have the same origin but functions differently., Analogous structures are structures that perform the same function but have, emerge from different origin., Vestigial structures are structures that exist in organisms that have no known, function which is believed to be remaining parts from the ancestor., Evidence from embryology, Embryology is the study of the development of an organism from embryo to its, adult form. Organisms that are related shows similarity in embryonic development., , 1
Page 5 :
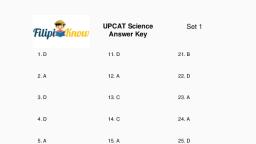
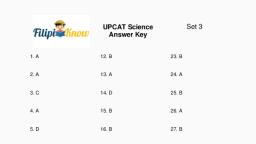
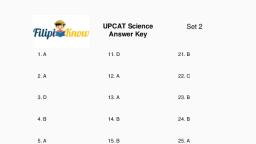
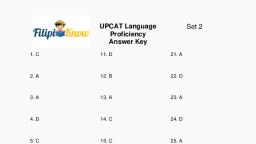
III. Activity Proper, A. Figure 1 below shows corresponding portions of hemoglobin molecules in humans, and five other vertebrates. The numbers indicate the position of a particular amino, acid (abbreviated name) in the chain., , Figure 1: Portion of hemoglobin molecules in vertebrates, , Directions: Study figure 1 and complete the table below by comparing the amino acid, sequence of each organism with that of a human and count the number of differences., Answer the guide questions that follow., Organisms being compared, , Amino acid difference, , Human & Chimpanzee, Human & Gorilla, Human & Rhesus monkey, Human & Horse, Human & Kangaroo, , Questions:, 1. Based on your answer in the table, which organisms do you think are the least related?, Explain your answer., , 2. Which organisms do you think are closely related? Explain your answer., , 3. How does similarity in the biochemical level can be used as evidence of evolution?, , 2
Page 6 :
B. Directions: Examine the following statements and then decide which evidence of, , evolution does it supports. Choose whether biogeography, fossil records, molecular, biology, structure, or embryology., 1. Wolves and dogs share approximately 99.8% similarities in their genes., 2. Most mammals have five toes or fingers which have changed through time, for different usage., 3. Vertebrates have tails at some point in their early development., 4. Footprints of prehistoric organisms found in rocks., 5. Remnants of ancient ferns that are found in the continents of Africa and, South America., 6. Diversification of marsupials and the absence of other mammals in, Australia., 7. Difference in the beaks of finches found in Galapagos Island compared to, those that are found in mainland., 8. Human and chimpanzee have the highest number of similarities in the, amino acid sequence found in hemoglobin molecules., 9. Pharyngeal arches are structures in embryonic stage of fishes and humans, that are differentiated in the later stages of development., 10. Forelimbs of mammals, reptiles and birds show similarities in anatomical, patterns., , C., , Directions: Given the following sources of evidence, explain how it supports, evolution., Biogeography, , https://www.ck12.org/c/biology/biogeography/l, esson/Biogeography-BIO/, , Fossil, , https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/fossil-words, , Homologous Structure, , https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopenbiology1/chapter/outcome-evidence-for-evolution/
Page 8 :
Reflection:, Complete the statements below., I understand, I don’t understand, I need more information about