Page 1 :
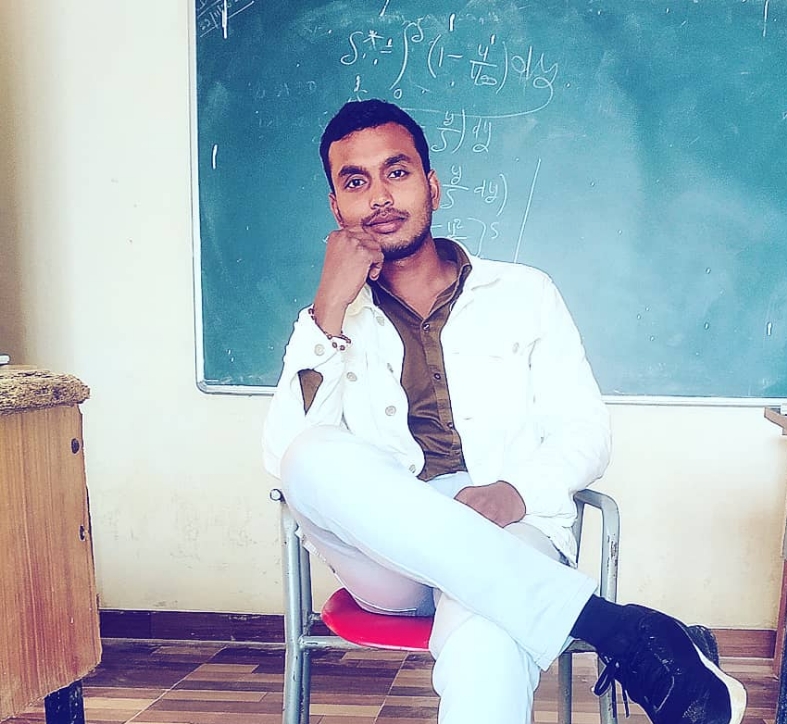
UNIT-IV, Interview: An Interview is a two-way process. It provides an opportunity to employer and the, applicant to sit face-to-face and interact on certain points related to job. L. brown defines, interview and writes, “it is a conversation between two people. It is a conversation, yet, but, directed to a purpose other than personal, social satisfaction”., Purposes of an Interview, The dual purposes of interviews are:, 1. First to find out the best person available for the job., 2. The applicant’s objective is to find the job best suited to his goal., Sequence of Interviews, The three-tier process to interview a potential or deserving interviewee whom the company is, going to offer job is:, 1. Screening Stage, 2. Selection Stage, 3. Final Stage, Types of Interviews, Organizations use various types of interviews to discover of an applicant. Some such types of, interviews are:, 1. Structured Interview: A Structured Interview is generally used in the screening stage., The purpose of the structured interviews is to screen out the candidates so that they can, be passed on to the next stage., 2. Open-ended Interview: Open-ended interviews are used in the selection stage. The, interviewer poses open ended questions and wants the applicant to answer them freely., The employer knows about the qualifications of the applicant beforehand but he wants to, judge the applicant’s personality and to test professional judgment and his ability to get, along with co-worker., 3. Stress Interview: Stress Interviews are set up to judge the interviewee’s capacity to, handle the stressful situations. The interviewer creates artificial stressful situations to, judge the applicant’s ability., 4. Group Interviews: Now-a-days group interviews have been in practice in which, candidates of a group are interviewed at the same time by the panel of interviewers. This, type of interview is useful for judging the inter-personal skills., 5. Panel Interview: Some companies set up panel interviews in which an applicant is, interviewed by several interviewers at once., 6. Situational Interview: The purpose of the situational interviews is to find out how well, the applicant performs on the job., 7. Video-Interview: Some organizations use video-conferencing systems to screen out, potential candidates. The sole purpose of video interview is to cut the travel cost., Enumerate the factors to be emphasized upon while preparing for an interview., An interview is usually called a formal meeting. It provides an opportunity to the participants to, exchange views and also to evaluate others. Bovee et al defines an employment interview “as a, formal meeting during which both employer and applicant ask questions and exchange
Page 2 :
information”. In the word of L. Brown, “it is a conversation between two people. It is a, conversation, yet, but directed to a purpose other than personal, social satis, satisfaction”., faction”., Preparations for Interview:, Adequate preparation and practice is necessary to enhance the skill appearing in interviews. The, applicant has to know about the basic questions and their answers for specific jobs. The main, tasks for a successful interview, erview are as follows:, 1. Learn about the organization: The first thing which an interviewee should learn is, about the organization- its products or services, its personnel, its latest business activities, and other details of the like nature. One’s understanding of the operations of the company, might give a competitive advantage to the interviewee., 2. Think about questions: The applicant should be able to anticipate some of the questions, of interviewer will ask. It will help him/her to control the nervo, nervousness, usness and he/she will be, able to answer quite confidently., 3. Bolster Confidence: The most important thing for the interviewee is to build their, confidence. For this, first of all they must try to build rapport with the interviewer and, also be fully prepared, d for the interview. They must be able to know their flaws and merits, as this knowledge of themselves will raise them confident. They will be bold enough to, face interview confidently., 4. Polish Interview Style: For success in an interview, how to say is as important as what, to say. They should do good practice and learn proper way/style of speaking. Often the, coaching institutes organize mock interviews so that the interviewee can learn the right, style of answering the interviewer’s questions., Besides the above, bove preparations, Physical preparation is also important. The interviewee, should dress up themselves formally and have good posture and manners., Group Discussion:, A group discussion is a meeting of eight to ten persons for discussing a given topic. The group, has a problem or a topic to discuss and find a solution or come to the conclusion within the, allotted time. It is a joint effort of the group. While it is not a very formal situation, the, communication has to be controlled and focused on the task. Th, There, ere is no appointed leader, but a, leader may emerge during the discussion. Often, several persons show leadership qualities, and, control and guide the group to a conclusion. All participants need discussion skills., The abilities which are checked in GD ar, are as follows:Communication skills, Ability to work in a team, Logical ability, Leadership skills, Initiative ability, Boldness, Flexibility, Creativity, Ability to think; etc.
Page 3 :
Importance of GD:The reason for conducting group discussion in institutes put the candidates through a Group, discussion and an interview, after testing their technical and conceptual skills in an exam, is to, know them as a person and gauge how well they will fit in their institute. The Group discussion, tests how the candidates function as a part of a team. As a manager, they will always be working, in teams, as a member or as a leader. Therefore how they interact in a team becomes an, important criterion for their selection. Managers have to work in a team and get best results out, of teamwork. That is the reason why management institutes include GD as a component of the, selection procedure., GDs can be topic-based or case-based., Topic based Gds can be classified into three types :1. Factual Topics, 2. Controversial Topics, 3. Case Based GD, Factual Topics:Factual topics are about practical things related to some facts, which an ordinary person is aware, of in his day-to-day life. These are about socio-economic topics. These can be current, i.e. they, may have been in the news lately, or could be unbound by time. A factual topic for discussion, gives a candidate a chance to prove that he/she is aware of and sensitive to his/her environment., E.g. The Mercy Killing, Tourism in India; etc., Controversial Topics:Controversial topics are the ones that are argumentative in nature. They are meant to generate, controversy. Some people can be agreeing but the others are not. In GDs where these topics are, given for discussion, the noise level is usually high. The idea behind giving a topic like this is to, see how much maturity, leadership quality, patience, handling situation etc, the candidates are, displaying by keeping their temper cool, by rationally and logically arguing their point of view, without getting personal and emotional., E.g. Reservations for women is important, Science as boon or bane., Case-based GDs:Another variation is the use of a case instead of a topic. The real or fake incident is narrated to, the candidates and some problems are exposed to them. Their suggestions to solve the problems, are invited. The objective in the case study is to get you to think about the situation from various, angles., Reasons for conducting a GD, It helps you to understand a subject more deeply., It improves your ability to think critically., It helps in solving a particular problem., It helps the group to make a particular decision., It gives you the chance to hear other students' ideas., It improves your listening skills., It increases your confidence in speaking., It can change your attitudes., Strategies for Improving GD Skills:, Asking questions and joining in discussions are important skills for university study. If you find, it difficult to speak or ask questions in tutorials, try the following strategies.
Page 4 :
Observe:, Attend as many seminars and lectures as possible and notice what other students do. Analysis, following things in you:, How do other students make critical comments?, How do they ask questions?, How do they disagree with or support arguments?, What special phrases do they use to show politeness even when they are voicing, disagreement?, How do they signal to interrupt, ask a question or make a point?, How they face the people?, How confidently do they answer the questions?, Rehearse:, Start practicing your discussion skills in an informal setting or with a small group. Start with, asking questions of fellow students. Ask them about the course material. Ask for their opinions., Ask for information or ask for help., Participate:, Take every opportunity to take part in social/informal discussions as well as more, structured/formal discussion. Start by making small contributions to tutorial discussions; prepare, a question to ask, or agree with another speaker's remarks., Dos for GD:, Speak pleasantly and politely to the group., Don’t be irritated at any issue., Respect the contribution of every speaker., Put your view confidently and logically to the others., Remember that a discussion is not an argument. Learn to disagree politely., Think about your contribution before you speak. How best can you answer the question/, contribute to the topic?, Try to stick to the discussion topic. Don't introduce irrelevant information. Don’t jumble, here and there be fix to prove your view., Be aware of your body language, facial expression, eye contact etc. when you speak., Agree with and acknowledge what you find interesting., Don'ts for GD, , , , , , Lose your temper. Keep always in mind that discussion is not an argument., Don’t ever shout. Use a moderate tone and medium pitch., Use too many gestures when you speak. Gestures like finger pointing and table thumping, can appear aggressive., The gestures should support your expression and speech., Dominate the discussion. Confident speakers should allow quieter students a chance to, contribute., Draw too much on personal experience or anecdote. Although some tutors encourage, students to reflect on their own experience, remember not to generalize too much., Don’t interrupt anyone while he/she speaks. Wait for speakers to finish what they are, saying before you speak., Different techniques to initiate a GD and make a good first impression:, i. Quotes, ii. Definition, iii. Question, iv. Shock statement, v. Facts, figures and statistics, vi. Short story, vii. General statement, , ,
Page 5 :
i. Quotes: Quotes are an effective way of initiating a GD., If the topic of a GD is: Should the Censor Board be abolished?, you could start with a quote, like, 'Hidden apples are always sweet'., For a GD topic like, Customer is King, you could quote Sam (Wall-mart) Walton's famous, saying, 'There is only one boss: the customer. And he can fire everybody in the company -from the chairman on down, simply by spending his money somewhere else.', ii. Definition: Start a GD by defining the topic or an important term in the topic. For, example, if the topic of the GD is Advertising is a Diplomatic Way of Telling a Lie, why not, start the GD by defining advertising as, 'Any paid form of non-personal presentation and, promotion of ideas, goods or services through mass media like newspapers, magazines,, television or radio by an identified sponsor'?, iii. Question: Asking a question is an impact way of starting a GD. It does not signify asking, a question to any of the candidates in a GD so as to hamper the flow. It implies asking a, question, and answering it yourself., Any question that might hamper the flow of a GD or insult a participant or play devil's, advocate must be discouraged., iv. Shock statement: Initiating a GD with a shocking statement is the best way to grab, immediate attention and put forth your point. If a GD topic is, The Impact of Population on, the Indian Economy, you could start with, 'At the centre of the Indian capital stands a, population clock that ticks away relentlessly. It tracks 33 births a minute, 2,000 an hour,, 48,000 a day. Which calculates to about 12 million every year. That is roughly the size of, Australia. As a current political slogan puts it, 'Nothing's impossible when 1 billion Indians, work together'.', v. Facts, figures and statistics: If you decide to initiate your GD with facts, figure and statistics,, make sure to quote them accurately. Approximation is allowed in macro level figures, but micro, level figures need to be correct and accurate. For example, you can say, approximately 70 per, cent of the Indian population stays in rural areas (macro figures, approximation allowed). But, you cannot say 30 states of India instead of 28 (micro figures, no approximations). Stating wrong, facts works to your disadvantage. For a GD topic like, China, a Rising Tiger, you could start, with, 'In 1983, when China was still in its initial stages of reform and opening up, China's real, use of Foreign Direct Investment only stood at $636 million. China actually utilized $60 billion, of FID in 2004, which is almost 100 times that of its 1983 statistics.", vi. Short story: Use a short story in a GD topic like, motivation is all about satisfaction., vii. General statement: Use a general statement to put the GD in proper perspective., Summarization/ Conclusion, , , , Most GD does not really have conclusions. A conclusion is where the whole group, decides in favor or against the topic., But every GD is summarized. You can summaries what the group has discussed in the, GD in a nutshell., Keep the following points in mind while summarizing a discussion:, , 1. Avoid raising new points., 2. Avoid stating only your viewpoint.
Page 6 :
3., 4., 5., 6., 7., , Avoid dwelling only on one aspect of the GD., Keep it brief and concise., It must incorporate all the important points that came out during the GD., If the examiner asks you to summaries a GD, it means the GD has come to an end., Do not add anything once the GD has been summarized., , Preparing for a Group Discussion:, While GD reflects the intrinsic qualities of an individual, appearing for it unprepared may not, predict well for you. These tips would help you prepare for GDs:, Reading:, This is the first and the most important aspect in preparation. This is a never ending process and, the more you read, the better you will be in your thoughts. While you may read anything to, everything, you must ensure that you are in good touch with current affairs. Chances are the, topics would be around these. Read both for the thoughts as well as for data. Also read multiple, view points on the same topic and then create your point of view with rationale. Also create, answers for counter arguments for your point of view. The electronic media also will be of good, use here., Mocks: Create an informal GD group and meet regularly to discuss and exchange feedback and, think it as a real one. This is the best way to prepare. This would give you a good idea about your, thoughts and how well can you convince. Remember, it is important that you are able to express, your thoughts well., SEMINAR:, A seminar is a form of academic instruction, either at an academic institution or offered by a, commercial or professional organization. It has the function of bringing together small groups for, recurring meetings, focusing each time on some particular subject, in which everyone present is, requested to participate., CONFERENCE, A conference is generally understood as a meeting of several people to discuss a particular topic., It is often confused with a convention, colloquia or symposium. While a conference differs from, the others in terms of size and purpose, the term can be used to cover the general concept. A, convention is larger than a conference; it is a gathering of delegates representing several groups., At a conference, innovative ideas are thrown about and new information is exchanged among, experts. Its purpose could be one of the following:, , , , , , , An academic conference is a gathering of scientists or academicians, where research findings, are presented or a workshop is conducted., A business conference is held for people working in the same company or industry. They, come together to discuss new trends and opportunities pertaining to the business, A trade conference takes place on a larger scale. Besides businessmen, there are members of, the public who come to network with vendors and made new connections. Such a conference, consists of workshops and white paper presentations., An unconference differs from the traditional conference, since it avoids the high costs, topdown organizational hierarchy and sponsored presentations. All attendees are equally
Page 7 :
knowledgeable about the topic and the discussion follows an open mode; usually without a, single speaker addressing the gathering., Most conferences have one or more keynote speakers who will deliver the keynote speech., These are common at academic and business conferences. The speakers chosen are eminent, personalities in the related field and their presence is meant to attract more people to attend the, conference. There are various types of conferences:, A symposium is a casual gathering and includes refreshments and entertainment., A seminar is organized to discuss a particular topic. They are usually educational in nature, and attendees are expected to gain new knowledge or skills at the end of the seminar, A workshop is more of a hands-on experience for the participants with demonstrations and, activities; the amount of time one speaker addresses the group is limited, A round-table conference is a get-together of peers to exchange thoughts and opinions on a, certain topic, usually political or commercial. There are a limited number of participants who, sit at a round table, so that each one can face all the others., UNIT-V, Kinesics: Kinesics is the interpretation of body motion communication such as facial, expressions and gestures, nonverbal behavior related to movement of any part of the body or the, body as a whole., Importance of Kinesics:, In face to face interaction, body language plays an important role. We began to form an, impression about a speaker as soon as we see him. The way he is dressed, the way he walks, the, way he smiles, the way he stands,-all these things show his personality, his skills…. kinesics is, the study of the movement of human body in the process of communication., Kinesics (the language of body) contains below points, , , , , , , Personal appearance, Facial expressions, Eye contact, Movement, Postures, Gestures, , Kinesics helps in effective communication as it helps to improve our body language and, interaction quality. It helps in maintaining eye contact, proper posture, and effective gesture, throughout the whole communication process. ., Thus these little things make our communication or interaction effective and efficient. And hence, of course kinesics is helpful for advancing our communication skills., Q. What is body language? How do the physical movements of the body help in, communication?, Ans. There are two modes of communication- Verbal and Non-verbal. Whenever we, communicate through non-verbal means of communication, Kinesics i.e. the body, movements or body language plays a vital role. For self control, the speaker should pay, attention to some of the following things…
Page 8 :
i., ii., iii., iv., v., , Maintain proper eye-contact, Expressions of face and eye should appear, Gestures, Postures, Physical appearances etc., , Q. What is space language/ propximics? Discuss, Ans. Non-verbal communication includes kinesics as well as proxemics (space language), which means the space between speaker and listener or the physical surroundings or, environment. The spatial dimension or distance between us and different people tells us, about our relations with others and the nature of our communication with them. Edward T., Hall has given four types of space languages, depending on the distance, those are:, 1. Intimate Space Language- Where the speaker and the listener are within the circle or, about 18inchs distance., 2. Personal Space Language- Where the speaker and the listener are in the personal space, i.e. from 18 inches to 4 feet., 3. Social Space Language- Where the circle extends from 4 feet to 12 feet., 4. Public Space Language- Where it extends from 12 feet to audible., Q. How can nuances of voice dynamics help the speaker to make the oral presentation, impressive?, Ans. In order to control the audience, the speaker has to adopt certain strategies, primary, among them is the use of language. The speaker should speak a language which is close to, the participants. The speaker should speak a language which is close to the participants., Clearity is the key-word in oral presentation. Below are given few important points which a, presenter should keep in mind:, i., , ii., a., b., c., , Pronunciation- Words should be pronounced clearly, with proper stress and, intonation. Mispronunciation sometimes, leads to confusion and spoils all, presentation howsoever well planned it is., Voice ModulationVoice should be vibrant and well- modulated., Pauses should be at the right place., Rate of delivery should be normal., , What is Linguistics?, Linguistics is the study of language. The word Linguistics is derived from the Latin words, Lingua and istics- meaning tongue and knowledge respectively. Thus, linguistics may be known, as the scientific study of Language., Phonetics: Phonetics is the science of human speech sounds. It deals with the pronunciation and, representation of the sounds of speech. T. Balasubramanian writes, “Linguistics is a systematic, study of language. Phonetics is a branch of linguistics and it is the branch dealing with the
Page 9 :
medium of speech. It deals with the production, transmission and reception of the sounds of, human speech.”, Phoneme: Every language has a large number of different sound segments, both vowels and, consonants. These sound segments of a language are known as phonemes., Allophone: There may be certain variants of one and the same phoneme. For example, in the, word pin and spin, the phoneme /p/ has two different sounds /ph/ and /p/ respectively. The, situationally determined variants of a phoneme are called its allophones., Syllable: The syllable is a unit adopted for the analysis of speech. It can be defined in terms of, the pulmonic air stream mechanism. When we make use of this mechanism in speech, the air, from the lungs does not come out in a regular and continuous flow. The muscles of the chestcontract and relax alternately and thus the air is pushed out in small puffs at the rate of, approximately five times per second. Each such movement of the muscles, called a chest-pulse,, corresponds to a syllable. A syllable may be defined as a unit of pronunciation consisting of a, vowel alone or a vowel with one or more consonants. On the basis of the number of syllable, the, words are classified into monosyllabic, disyllabic and polysyllabic. As pen-cil, po-pu-lation etc., Phonetic Transcription: Phonetic transcription means turning the sounds into written form. It is, a written record of sounds made by a speaker. Phonetic transcription is a device by which the, correct pronunciation can be conveyed by the help of certain symbols., Word Accent/Stress in Speech:, In the words of more than one syllable, not all the syllables are equally important. Some syllables, in polysyllabic words are strongly stressed while some are weakly stressed. The syllable that is, more prominent than others is said to receive stress or the accent., The word stress means force or pressure. In terms of spoken language, stress means a greater, breath force, greater muscular effort and greater vibration of the vocal cords in producing certain, sounds. Paul Christophersen explains, “When we say that a certain syllable is strongly stressed,, we mean that it is altered with great energy. The air is ejected from the lungs with more effort, and the other speech organs perform their actions with more vigour than for a weakly stressed, syllable. The effect is that the stressed syllable seems louder than the others.” Like Iagent,, I, always,Idamage,Icarry,Ieffort, employIee, conItinue. Etc., Types of Stress and Accent: The accent or stresses are of two types:, 1. Primary Stress or Tonic Accent, 2. Secondary Stress or Non-tonic Accent, There are several polysyllabic words in which two syllables may be prominent or strong. The, syllable which is more prominent (as it is articulated with greater breath) may receive a pitch, change. In a polysyllabic word the syllable on which a pitch movement takes place is said to, receive Primary Stress or Tonic Accent. The syllable that has the next degree of prominence in, the same word is said to receive Secondary stress or non-tonic accent. Primary stress is marked, with a vertical bar above and in front of the syllable to which it refers. As IConstiItution,, I, IDepo sition
Page 10 :
Intonation: When somebody speaks then continual variations in pitch can easily be noticed., There are continuous rise and fall in one’s speech. S. K. Bansal says, “The term intonation refers, to pitch patterns that are part of the structure of sentences.”, Kinds of Intonations:, There are mainly the following types of Intonations:, The Falling Tone: When the speaker begins a sentence at a high note but gradually shifts to a, lower as he reach to the end of a sentence, it is known as a falling tone. A falling tone will be, marked with a symbol \ in front of the syllable to which it refers. The symbol will be above the, line for a high falling tone and below the line for a low falling tone. As \Then, \ Look, \Do \Tell, The Rising Tone: When the speaker begins at a lower note, but gradually shifts to a higher note, as he reaches to the end of a sentence, it is known as a rising tone. A rising tone will be marked, with a symbol./in front of the syllable to which it refers. As What’s the matter? Are you calling, me?, The Falling-Rising Tone: This tone is sometimes referred to as the dive. It consists of a fall, from high to low and then a rise to the middle of the voice. It can be used either on one syllable, of different syllables of a word or sentence. This tone is often used to indicate wish, warning etc., As: Don’t go out in winter. I am waiting. Please be careful, Voice Modulation:, Modulation is when you control or adjust something, like when you lower your voice to a loud, whisper in order to make what you're saying more dramatic and mysterious. The, noun modulation has several meanings, including a change of key in music or of the sound of a, person's voice., Pitch: Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related, scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher", and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies., Rhythm: Rhythm generally means a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong, , and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions., Vowel and Consonant Sounds