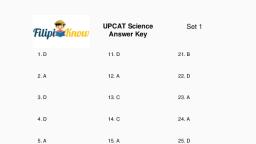
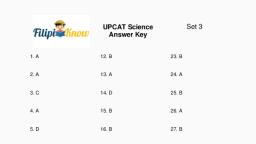
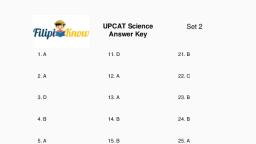
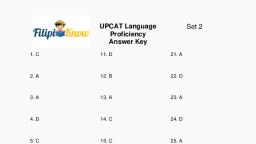
Page 1 :
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1, Quarter 1- Module 2:, Qualitative Research and Its Importance, In Daily Life, , Department of Education ● Republic of the Phili
Page 2 :
Lesson, , The Value of Qualitative Research, , 1, , Its Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses and Kinds, , The general purpose of qualitative research is to develop concepts that help you to understand, social phenomena in, wherever possible, natural rather than experimental settings, to gain an, understanding of the experiences, perceptions, and/or behaviors of individuals, and the meanings, attached to them. The effective applications of qualitative methods to other disciplines, including health, and education research have expanded. This module outlines the nature and potential value of, qualitative research features its various parameters., , What’s in?, (, In the previous module, you learned the nature of inquiry and research. Inquiry and research, encourage high levels of critical thinking in order to attain appropriate methods and resources. As a, researcher you have to follow the different processes in research equipped with the etiquettes in, conducting your study. Those samples of research in areas of interest will help you guide to choose, you topic or research problem., , What’s New?, , I. Definition of Qualitative Research, Qualitative Research is a scientific method of observation to gather non-numerical data. It refers to the, meanings, concepts, characteristics, metaphors, symbols and description of phenomena, and not to, their counts or measures., II.Purpose of Qualitative Research, Qualitative Research promotes a deep, holistic understanding of a particular phenomenon., III.Characteristics of Qualitative Research, 1. Human understanding and interpretation in data analysis, 2. Active, powerful and forceful in data gathering and rephrasing interview questions, 3. Multiple research approaches and methods that allows you to plan your study and, being multi-method research, 4. Specificity to generalization on specific ideas will lead to generalizations or, conclusions., , 1
Page 3 :
5. Contextualization - context or situation of individual’s life, 6. Diversified data in real-life situations on collecting data in a natural setting, 7. Abounds with words and visuals that presents people’s view in a picture, video,, drawing or graphs., 8. Internal analysis on examining the data yielded by the internal traits of the subject, persons., IV. Strengths of Qualitative Research, 1. It adopts a naturalistic approach to its subject matter., 2. Promotes a full understanding of human behavior/personality traits in their natural, setting., 3. It is instrumental for positive societal changes., 4. It engenders respect for people’s individuality., 5. it’s a way of understanding & interpreting social interactions., 6. Increases researcher’s interests in the study., 7. Offers multiple ways of acquiring and examining knowledge about something., V.Weaknesses of Qualitative Research, 1. It involves a lot of researcher’s subjectivity in data analysis., 2. It is hard to know the validity/reliability of the data., 3. It is open-ended questions yield “data overload” that requires long-time analysis., 4. It is time-consuming., 5. It involves several processes, whose results greatly depend on the researcher’s, views or interpretations., , VI. Kinds of Qualitative Research2, 1. Case Study - Long time study of a person, group, organization or situation and an empirical, inquiry that investigates current phenomenon., Example: “Teenage Pregnancy in the Public High Schools”, 2. Ethnography- a study of a particular cultural group., Example: “Cultural Awareness and Integration of Peace Education in the Indigenous Peoples, (IP) Communities”, ., 3. Phenomenology- “live-experienced” of a phenomenon., Example: “Life without Gadget”, , 2
Page 4 :
4. Content and Discourse Analysis• Content Analysis- is a research technique that analyzes the modes of communication, such as letters, e-mails, etc., •, , Discourse Analysis- is the study of social life, understood through an analysis of, language it includes face-to-face talk, non-verbal interaction, images, and symbols., , Materials for Discourse Analysis include books, newspapers, periodicals, brochures, and, advertisements., Example: “A Discourse Analysis on the Impact of Modern Technologies on Communication”, 5. Historical Analysis- is a qualitative method where there is an examination of past events to draw, conclusions and make predictions about the future., Example: “The Impact of Ferdinand Marcos’ Speech”, , 6. Grounded Theory- takes place when there is a discovery of a new theory which underlies your, study at the time of data collection and analysis., Example: “The Story Behind the Migration of Christians from Visayas and Luzon to Mindanao”, 7. Narrative Report - designed to present things or events that have happened in the past through, a logical progression of the relevant information. The main purpose of a narrative report is to, present a factual depiction of what has occurred., Example: “Vocabulary Building of Students through Proper Solid Waste Management”, 8. Biography- is the study of an individual’s life and struggles and how they reflect cultural themes, of the society. It deals with an interesting story found in documents and archival materials. It is, concerned with the reconstruction of life histories and the constitution of meaning based on, biographical narratives and documents., ❖ Five common types of biography are, (1) Scholarly Chronicles -focus on the historical portrayal of an individual life., e.g. “Biography of Gloria M. Arroyo, the First Woman President of the Philippines”, (2) Intellectual Biography- narrative of life through the conceptual analysis of the subject’s, motives and beliefs within the world of ideas., e.g. “Life and Works of Dr. Jose Rizal”, (3) Life History Writing- recording of life memories, experiences, whether one’s or another’s., e.g. “The Hardships of Overseas Filipino Workers (OFW’s)”., (4) Memoir Biography- stylistic presentation of the biographer’s reflections and insights in, relation to the factual account of life., e.g. “The Experiences of Stranded Students in the COVID-19 Pandemic”, (5) Narrative Biography-a nonfiction account of the life experiences of a person., 9. Action Research- is classroom-based or school-based research that seeks transformative, change through the process of taking action and doing research, which is linked together by, critical reflection. This type of research is commonly conducted by the teachers to give solutions, to the existing problems to improve students’ academic performance and positive attitudes., , 3
Page 5 :
Activity 1: Question and Answer, Directions: Answer the questions briefly. Write your answers in the space provided., 1. How will you use qualitative research in real life?, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, 2. What are the kinds of qualitative research?, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, , What is it?, Discussion of Activity 1, You just learned the valuable aspects of qualitative research., 1. Can you recognize the nature of qualitative research; its kinds, characteristics, strengths, and, weaknesses? Kindly provide a brief explanation., , 2., , How do the strengths and weaknesses help us in writing the research proposal?, , What’s more?, On the table below, draft your proposed topics for a research paper. The first column is for the, topic, second for the purpose and third for the type of qualitative research to be used. Give five topics., Topic, Example:, Post Traumatic Experiences, of the COVID-19 Survivors, , Purpose, , To, determine, the, experiences, of, those, survivors in the COVID-19, phenomena., , 1., , 2., , 3., , 4., , 5., 4, , Type of Qualitative Reserach, , Phenomenological
Page 6 :
What I have learned, , Explain the concepts you have learned by answering the following questions., 1. What comes to your mind when you hear qualitative research?, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, 2. Pretend you are the subject of a phenomenological study, how will the researcher obtain data, from you?, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, __________________________________________________________________________, 3. Name the type of qualitative research best suited for the following topics., a. Grade 11 Science Textbook_____________________________, b. Filipino COVID-19 Front liners in Europe____________________, c. Travails of SHS Graduates in Public Schools_________________, d. The Ifugao Wedding Practices____________________________, e. Relatives of COVID-19 Victims____________________________, , What I can do, , Contemplate on the matters you see in your surroundings, your house, appliances and gadgets,, school, your friends, etc. Ponder over these things, think of a good topic you can research on, qualitatively. Write a short descriptive paragraph on your chosen topic applying what you have learned, about qualitative research. Write in a separate sheet of paper., , 5
Page 7 :
Lesson, 2, , The Importance of Qualitative Research Across Fields, of Inquiry, , Qualitative research is an emerging area of inquiry that graces through disciplines and subject, matter. However, it's also essential to recognize that qualitative research is a method generally used in, the social sciences searching social interactions, schemes, and processes. It delivers a detailed, appreciation of the ways people come to understand and achieve their daily life in particular situations., , What’s in?, (, In the previous lesson, you learned to describe the nature and characteristics of qualitative, research with its kinds, strength, and weaknesses. Qualitative research is capable to give rich, information about the respondents, be it humans or animals. Despite having such strength, its weakness, is perceived on its approach is not applicable to some research objectives. The kinds of qualitative, research will help you discover facts and information about the object of your interest and work with, others. The lessons you had learned will guide you to appreciate the importance of qualitative research, across fields of inquiry., , What’s New?, , Research in Different Areas of Knowledge, Research studies happen in any field of knowledge:, Communication, Education, Engineering, Law, and Nursing., , Anthropology, Business,, , A. Basic Research Approaches in a Specific Area of Discipline, 1. Scientific or Positive Approach, Deals with empirical data instead of personal views, feelings or attitudes., Allows control of variables or factors affecting the study (Laursen 2010)., Express and records findings quantitatively., Presents structured interviews, questionnaires, and observational checklists., 2. Naturalistic Approach, • A people-oriented approach focusing on discovering the real concept or meaning, behind people’s lifestyles and social relations., • Present things qualitatively through verbal language. Using words as a unit of analysis., • Bases determining universal social values to define ethical and unethical that society, ought to know, not only for the benefit of individual and community but also for the, satisfaction of man’s quest for knowledge.” (Sarandakos 2013; Ransome 2013), Example: Talking to ethnic groups or people with other cultures in a natural setting. In this case,, the researcher uses unstructured interviews, and the participants’ answer/response is not, scripted, 6
Page 8 :
3. Triangulation/ Mixed Method, • Allows a combination or a mixture of research designs, data collection, and data, analysis techniques., • Enhance the validity and reliability of qualitative research design., • Enhances accuracy of interpretation., • Has an opportunity to view every angle of the research from different perspectives., (3) Main Methods of Data Collection, a. Interactive interviewing- people asked to verbally describe their experiences of the, phenomenon., b. Written descriptions by the participant-people asked to write descriptions of their experiences, of the phenomenon., c. Observation- descriptive observations of verbal and non-verbal behavior., In the field of Humanities, researchers ought to focus not on man’s social life but instead, studies the meanings, significance, and visualizations of man’s experiences in the field of Fine, Arts, Literature, Music, Drama, Dance, and other artistically inclined subjects., Humanistic Categories, 1. Literature and Art Criticism, Focus on language depends on interpretative and reflective thinking., 2. Philosophical Research, The focus of the inquiry is on knowledge and principles of being and on the manner human, beings conduct themselves on Earth., 3. Historical Research, The investigation centers on events and ideas that took place in man’s life at a particular, period., II. Hard Sciences versus Soft Sciences 3, , •, •, •, , Quantitative Research, , Qualitative Research, , Hard Sciences, Studies natural data-driven phenomenon., Objective, Tests Theory, Numbers, Cause and Effect Relationship, Statistical Analysis and Generalizations, Examples:, , Soft Sciences, Studies human behavior in a scientific, manner., Subjective, Develops Theory, Words, Knowing meaning & discovery, Researcher’s interpretation, Examples:, , Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Astronomy,, Earth Science, , Sociology, Psychology, Political Science,, Economics, Anthropology, History, , Qualitative and Quantitative Research can go together in a research approach., There is a symbiotic relationship between these two research methods, in which they, reinforce or strengthen each other., Moreover, any form of knowledge, factual or opinionated and any statistical or verbal, expression of this knowledge are deduced from human experience that is subjective., (Hollway 2013; Letherby 2013), 7
Page 9 :
Activity 1: Question and Answer, Directions: Answer the questions in 3-5 sentences. Write your answers in the space provided., 1. What are the three types of approaches to basic research? Describe each type., , 2., , How do you differentiate soft sciences from hard sciences?, , What is it?, , You just learned the importance of qualitative research across fields of inquiry., 1. Can you figure out the importance of qualitative research? Organize your ideas by presenting, three important functions of qualitative research., , 2. How do you inquire data in a certain field of study? Write your top three methods when collecting, data and describe each., , What’s more?, , As a continuation on Lesson 1 of this Module from the table, you have drawn which listed your, own three topics for qualitative research, purpose, and type to use, add a fourth column as what, approach of research you will use, and the fifth column your choice of data collection. Copy your, answers from the previous table to complete columns 1 to 3., Topic, , Sample:, Post Traumatic, Experiences, of, , Purpose, , To determine the, experiences, of, those survivors in, , Type of Qualitative, Research, , Research, Approach, , Data Collection, Choice, , Phenomenological, , Triangulation or, mixed, , Written, description/, Interview, , 8
Page 10 :
the, COVID-19, Survivors, , the, COVID-19, phenomena., , 1., , 2., , 3., , What I have learned, Given the following Research topics, name the specific subject on each topic and give the, importance on researching such topic in a person’s day to day life. The first one is done for you., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., Topics, 1, , Nutrient Contents of Spices and Herbs, Juan dela Cruz: A Filipino Inventor, Parents Views About The New Normal Education, Body Parts of a Korean Car, Bacteria in a Food, SHS Learners Study Habits, Medicinal Elements of Lemon Leaves, History Development of Asian Novels, Higa-onon Wedding Rites, The Nature of Corona Virus Disease, Subject, Spices and Herbs, , Importance of the Research, To know its nutrient content use as medicine, , 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, , 9
Page 11 :
What I can do, , What are your views on qualitative research across fields of inquiry? Is research important?, Why? Present your answers in various viewpoints in terms of:, Sample: Health issues: Through qualitative research, we understand how HIV patients, go through bodily changes, etc., , 1. Social:________________________________________________, , 2. Economical____________________________________________, , 3. Political:______________________________________________, , Additional Activities, , Ask somebody whom you know has already done a research work or is currently conducting a, research study. Ask him the details of his study and tabulate the results from your interview with him., 1. Title, 2. Method of Research ( data gathering and data analysis), , 3. Subject Area or areas of interest where the study belongs, , 4. The importance of the research work, , 10