Page 1 :
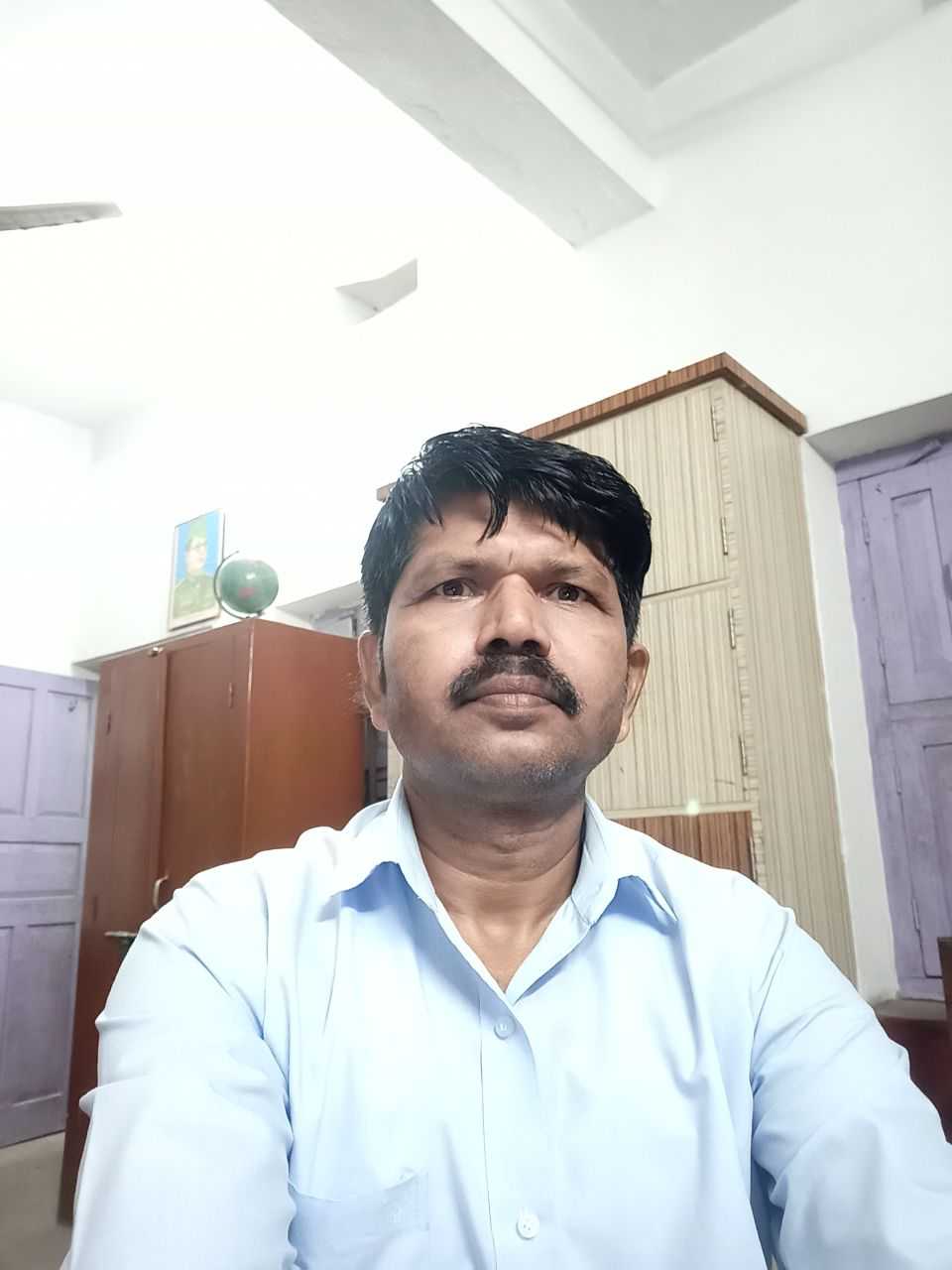
Carbon and its, , , , Chapter - 4, , Introduction :, * The element carbon is non-metal. Its symbol is C., , * Carbon is a versatile element the percentage of carbon present in earth, crust in form of mineral is 0.02% and in atmosphere as CO, is 0.03%., , * All the living things, plants and animals are made up of carbon based, compounds., , Carbon always form covalent bonds :, , The atomic number of carbon is 6,, , Electronic configuration :, K L, C(6) 2 4, , How carbon attain noble gas configuration ?, , (i) Carbon is tetravalent, it does not form ionic bond by either losing four, electrons (C**) or by gaining four electrons (C*>). It is difficult to hold, four extra electron and would require large amount of energy to remove, four electrons. So, carbon can form bond by sharing of its electrons with, the electrons of other carbon atom or with other element and attain noble, gas configuration., , (ii) The atoms of other elements like hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen,, chlorine also form bonds by sharing of electrons,, , (iii) The bond formed by sharing of electrons between same or different, atoms is covalent bond.
Page 2 :
(i) Hy,, , (m) (m) Hydrogen atom, , Hyetrogen atom, , , , , , One shared pair of electron, H- H single bond between hydrogen atoms, , ae _, , Oxygen molecule, , (ii) 0,, , Two shared pair of electron, O =O double bond between oxygen atoms, , @) ) Nitrogen atom, , Nitrogen atom, , (iii) N,, , Three shared pair of electrons, , N =N triple bond between nitrogen atoms, Molecule of water has single covalent bond between one oxygen and two, , hydrogen atoms.
Page 3 :
Physical Properties of Covalent Compounds, , (a) Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points as they have, weak intermolecular force., , (b) They are generally poor conductor of electricity as electrons are shared, between atoms and no charged particles are formed., , Versatile Nature of Carbon, , The two characteristic properties of carbon element which lead to the formation of large number of compounds :, (i) | Catenation : Carbon can link with carbon atoms by means of covalent, bonds to form long chains, branched chains and closed ring compound., Carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds., (ii) Tetravalency : Carbon has 4 valence electrons. Carbon can bond with, four carbon atoms, monovalent atoms, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur., , Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds, Compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon are called hydrocarbon., , , , Hydrocarbon, Y : Y, Saturated Unsaturated, , * Single bond between carbon * Double or triple bond between, , atoms. carbon atoms., °*-¢€-C- * -€=C- -C=C* Alkanes ° Alkenes Alkynes, , General formulae, , C,H, He CH, CyH5, -2, , Electron Dot Structure of Saturated Hydrocarbons, Ethane C,H,, , Qa@ /, QD vein, see, , The names, molecular formulae and saturated formulae of saturated, , hydrocarbons (alkanes) are given below :
Page 4 :
Name of Hydrocarbon, , 1. Methane, , 2. Elhane, , 3. Propane, , 4. Butane, , 5. Pentane, , Mileculas, formula, , CH,, , C,H, , 2 6, , C3Hg, , C,Hjo, , CH,, , Structural Formula, , H, |, H—C—H, |, H, |, H—C—C—H, |, H H, h ua H, 7 | (|, H—C—C—C—H, | |, HoH H, aH iS, | ol, H—C—C—C—C—H, me |, fit. FF, . HH He, | |, H—C—C—C—C—C—H, | | oe, mH HH 2, , Electron Dot Structure of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons, Ethyne C,H,, , Ethene C,H,
Page 5 :
Name of Hydrocarbon, , Alkenes :, , 1. Ethene, , 2. Propene, , 3. Butene, , Alkynes :, 1. Ethyne, , 2. Propyne, , 3. Butyne, , Mileculas, formula, , C,H,, , CH,, , C,H,, , Structural Formula, , Ee, | |, H—C=C—H, pil, H H, eo 8, a: |, H—C=C—C—H, | |, H H, H, |, H—C=C—C—C—H, So |, Him Ho, H—C=C—H, H, |, H—C=C—C—H, |, H, q 2, |, H—C=C—C—C—H, | ail, H H, , Carbon Compounds on the Basis of Structure, , (i) Straight (unbranched) chain, , —C—C—C—C—C— egC,H,, , H—C—, , HH H, , |, H, , | |, C—C—H, |