Page 1 :
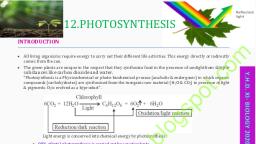
Photosynthesis in higher plants, Products of light reaction : ATP, NADPH, CO2 and H2O. Next stage is the biosynthetic phase. , , In this, ATP and NADPH are used for synthesising the food., , CO2 is fixed from CO2 fixation product., , This stage is also called the dark phase as it is independent of light, but deals with the products of light reaction.
Page 2 :
The reaction involved in the biosynthetic phase takes place in the Stroma of Chloroplast.
Page 3 :
In some plants, the first product of co2 fixation is a 3-carbon compound called 3- phosphoglyceric acid (PGA). These plants are said to adopt the c3 pathway. For example : Rice , Wheat, etc. These plants are the most common and most efficient at photosynthesis in cool, wet climates. , , In other plants, the first co2 fixation product is a 4-carbon compound called oxaloacetic acid . These plants are said to adopt the c4 pathway. For example: Maize , Sugarcane, etc. These plants are most efficient at photosynthesis in hot, sunny climates.
Page 6 :
Calvin cycle occurs in all photosynthetic plants, irrespective of weather they have C3 or C4 pathway., , The primary acceptor of co2 was found to be a 5-carbon ketose sugar called Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). This was surprising as it was believed that the formation of a 3-carbon product, co2 would have to be accepted by a 2-carbon compound., , RuBP is used in cyclic manner(regenerated) and a sugar is synthesised.
Page 9 :
Reduction:, , The 6 molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3c) are phosphorylated to 6 molecules of 1,3 diphosphoglyceric acid by utilising 6 ATP molecules., , The enzyme Kinase catalyses this reaction., , The 6 molecules of 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid (3c) are reduced to 6 molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate (3c) utilising NADPH2 supplied by light reaction (PS- 2)., , The enzyme dehydrogenase catalyses this reaction., , Thus, glycolytic reversal regenerates ADP and NADP required for light reaction.
Page 10 :
Regeneration of RuBP:, , The regeneration of RuBP requires the utilisation of 5 molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate and 3 molecules of ATP., , There is regeneration of RuBP for maintaining the continuity of Calvin cycle., , The one molecule of glyceraldehyde phosphate forms the glucose and other sugars., , This step is essential to maintain the continuity of Calvin cycle for fixation of fresh supply of CO2.
Page 11 :
Thus, to synthesize one molecule of glucose, the 6 turns of dark reaction cycles are required., , For every CO2 molecules entering the Calvin cycle, 3 molecules of ATP and 2 of NADPH are required. So, to make one molecule of glucose, 18 ATP and 12 NADPH are needed.
Page 12 :
C4 pathway (Hatch and slack pathway), Occurs in plants like maize, sugarcane- plants adapted to dry tropical regions., , The leaves of C4 plants have Kranz Anatomy. They have special large cells around their vascular bundles called Bundle Shealth cells. These cells form several layers around the vascular bundles and have large number of chloroplasts, thick walls impermeable to gaseous exchange, and lack intercellular spaces., , First CO2 fixation product is a 4-carbon compound called Oxaloacetic Acid, but C3 cycle is used as the main biosynthetic phase.
Page 13 :
Mesophyll cells: Occur in the C4 cycle., , Bundle Sheath cells: Occur in the C3 cycle., , C4 plants can tolerate high temperature and high light intensity, show greator productivity of biomass, and lack photorespiration.
Page 14 :
Hatch and Slack pathway.
Page 16 :
Pyruvic acid is then exported to the chloroplast of the mesophyll cells where it is phosphorylated to generate PEP by pyruvic dikinase. Here 2 ATP molecules are utilised., , In these plants, the CO2 fixation undergoes through the processes of Calvin cycle as well as by Hatch and Slack pathway. The additional process of CO2 fixation through Hatch and Slack pathway., , The additional amount of CO2 fixation through Hatch and Slack pathway requires extra amount of 12 ATPs., , C3 cycle cannot directly occur in the mesophyll cells of C4 plants because of the lack of the enzyme RuBisCO in these cells., , RuBis CO is found in abundance in the bundle sheath cells of the C4 plants. They lack PEPcase.
Page 17 :
Thanks….