Page 1 :
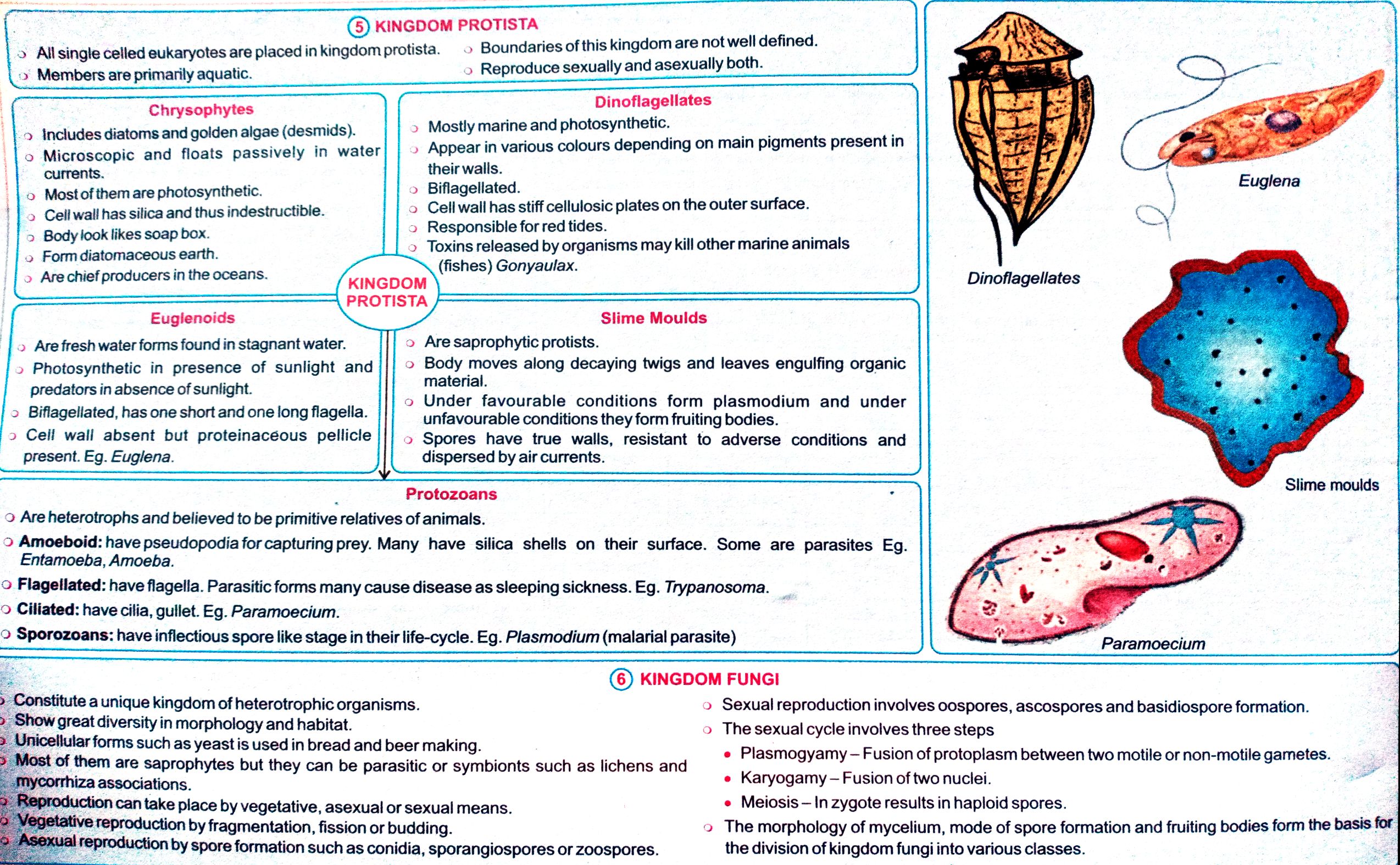
@ KINGDOM PROTISTA, , > Allsingle celled eukaryotes are placed in kingdom protista. © Boundaries of this kingdom are not well defined., -> Members are primarily aquatic. > Reproduce sexually and asexually both., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Dinoflagellates, , > Mostly marine and photosynthetic. :, » Appear in various colours depending on main pigments present in, their walls., , > Biflagellated., © Cell wall has stiff cellulosic plates on the outer surface., , o Responsible for red tides., > Toxins released by organisms may kill other marine animals, , (fishes) Gonyaulax., , , , , , , , , , Chrysophytes, 5 Includes diatoms and golden algae (desmids)., © Microscopic and floats passively in water, currents., © Mostofthem are photosynthetic., > Cell wall has silica and thus indestructible., > Body look likes soap box., o Formdiatomaceous earth., 2 Are chief producers in the oceans., , , , , , , , , , Dinoflagellates, , , , KINGDOM, PROTISTA, , , , , , , Euglenoids Slime Moulds, , , , , , Are saprophytic protists., o Body moves along decaying twigs and leaves engulfing organic, material., , Under favourable conditions form plasmodium and under, unfavourable conditions they form fruiting bodies., , Spores have true walls, resistant to adverse conditions and, dispersed by air currents., , > Are fresh water forms found in stagnant water., » Photosynthetic in presence of sunlight and, predators in absence of sunlight., 2 Biflagellated, has one short and one long flagella., 2 Cell wall absent but proteinaceous pellicle, present. Eg. Euglena., , , , ©, , , , , , °, , , , Protozoans Slime moulds, , 2 Are heterotrophs and believed to be primitive relatives of animals., , ° Amoeboid: have pseudopodia for capturing prey. Many have silica shells on their surface. Some are parasites Eg., Entamoeba, Amoeba., , o Flagellated: have flagella. Parasitic forms many cause disease as sleeping sickness. Eg. Trypanosoma. ;, 2 Ciliated: have cilia, gullet. Eg. Paramoecium., 2 Sporozoans: have inflectious spore like stage in their life-cycle. Eg. Plasmodium (malarial parasite), , , , 2 © KINGDOM FUNGI, Constitute a unique kingdom of heterotrophic organisms. 2 Sexual reproduction involves oospores, ascospores and basidiospore formation., Show great diversity in morphology and habitat. o The sexual cycle involves three steps, , Unicellutar forms su i i i, ch as yeasts used in bread and beer making. e Plasmogyamy — Fusion of protoplasm between two motile or non-motile gametes., , st of them are saprophytes but they can be parasitic or symbionts such as lichens and ; ‘ ,, : e Karyogamy — Fusion of two nuclei. _—, , Juction can take place by vegetative, asexual or sexual means. e Meiosis — In zygote results in haploid spores., © reproduction by fragmentation, fission or budding. 2 The morphology of mycelium, mode of spore formation and fruiting bodies form the basis for, , Peppotuction by spore formation such as conidia, sporangiospores or zoospores. the division of kingdom fungi into various classes.