Page 1 :
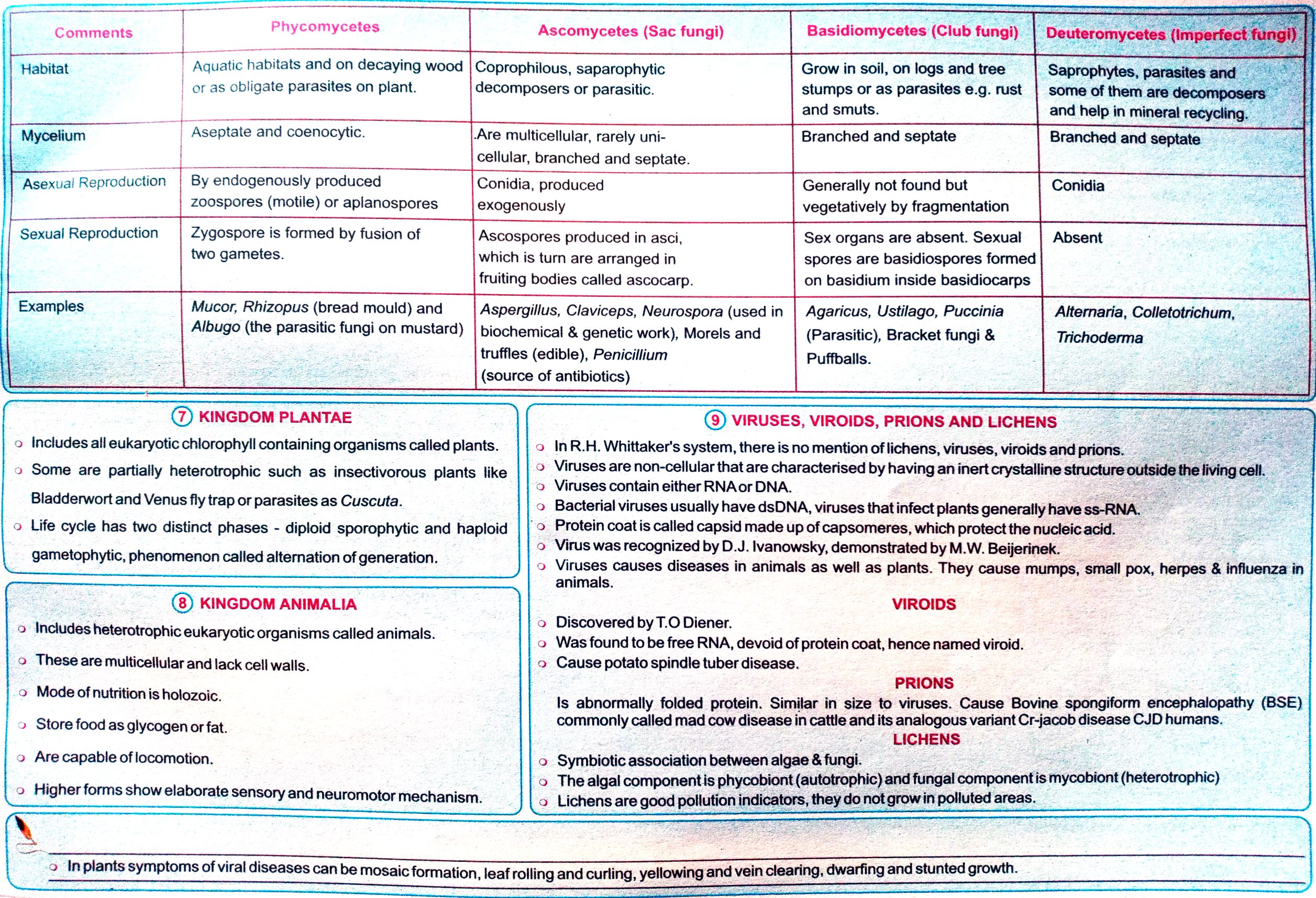
a aa, }, , | Z ~ f, i Commuants Phycomycetes, H, , , , jabitat "Aquatic habitats and on decaying wood Coprophilous, saparophytic, , or as obligate parasites on plant., ~~ | Aseptate and coenocytic., |, , By endogenously produced, zoospores (motile) or aplanospores, , “Asexual Reproduction, , Sexual Reproduction Zygospore is formed by fusion of, , two gametes., , Mucor, Rhizopus (bread mould) and, Albugo (the parasitic fungi on mustard), , Ascomycetes (Sac fungi), , decomposers or parasitic., , Are multicellular, rarely unicellular, branched and septate., , Conidia, produced, exogenously, , Ascospores produced in asci,, which is turn are arranged in, fruiting bodies called ascocarp., , Aspergillus, Claviceps, Neurospora (used in, biochemical & genetic work), Morels and, truffles (edible), Penicillium, , Basidiomycetes (Club fungi), , Grow in soil, on logs and tree, stumps or as parasites e.g. rust, and smuts., , Branched and septate, , Generally not found but, vegetatively by fragmentation, , Sex organs are absent. Sexual, spores are basidiospores formed, on basidium inside basidiocarps, , Agaricus, Ustilago, Puccinia, , (Parasitic), Bracket fungi &, Puffballs., , Alternaria, Colletotrichum,, Trichoderma, , (source of antibiotics), , @) KINGDOM PLANTAE, 2 Includes all eukaryotic chlorophyll containing organisms called plants., 2 Some are partially heterotrophic such as insectivorous plants like, Bladderwort and Venus fly trap or parasites as Cuscuta., 2 Life cycle has two distinct phases - diploid sporophytic and haploid, , gametophytic, phenomenon called alternation of generation., , KINGDOM ANIMALIA, 9 Includes heterotrophic eukaryotic organisms called animals., 2. These are multicellular and lack cell walls., 2 Mode ofnutritionis holozoic., 2 Store food as glycogen or fat., , 2 Are capable of locomotion., , 2 Higher forms show elaborate sensory and neuromotor mechanism., , @ VIRUSES, VIROIDS, PRIONS AND LICHENS, In R.H. Whittaker's system, there is no mention of lichens, viruses, viroids and priors., , Viruses are non-cellular that are characterised by having an inert crystalline structure outside thelvingcol., Viruses contain either RNAor DNA., , Bacterial viruses usually have dsDNA, viruses that infect plants generally have ss- RNA., Protein coat is called capsid made up of capsomeres, which protect the nucleicacid., Virus was recognized by D.J. lvanowsky, demonstrated by M.W. Beijerinek. _, , Viruses causes diseases in animals as well as plants. They cause mumps, small pox, herpes & influenza in, animals., , VIROIDS Z, Discovered by T.O Diener., Was found to be free RNA, devoid of protein coat, hence named viroid., Cause potato spindle tuber disease., PRIONS :, ls abnormally folded protein. Similar in size to viruses. Cause Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly called mad cow disease in cattle and its analogous variant Cr-jacob disease CJD humans., LICHENS :, Symbiotic association between algae & fungi., The algal componentis phycobiont (autotrophic) and fungal componentis mnycoblont (heterotrophic), Lichens are good pollution indicators, they do not growin polluted areas., , , , 2_Inplants symptoms of viral diseases can be mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing and stunted growth.