Page 1 :
Prokaryotic cells, The prokaryoticcells are represented by bacteria, blue-green algae, Mycoplasma and, PPLO. They are generally smaller and multiply more rapidly than the eukaryotic cells., , They vary greatly in shape and size. The four, , basic, , shapes of bacteria are, , bacillus, , (rod like), coccus (spherical), vibrio (comma shape) and spirillum (spiral)., All prokaryotes have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane except in, , mycoplasma. There is no well-defined nucleus. The genetic material is basically, naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane. In addition to the genomic DNA,, many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the, , genomic DNA. These smaller DNA
Page 2 :
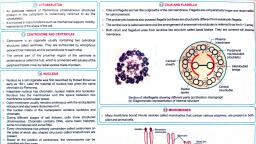
are called plasmids. No organelles are found in prokaryotic cells except ribosomes. A, , specialised differentiated form of cell membrane called mesosome is the, characteristic of prokaryotes. They are essentially infolding of cell membrane., Mesosome, GycopenLpid, , Respiratory enzymes, , RNA, , mona), , Filament, Ribosome, Polyrbosome, , Nucleor body, , ageyoplasm, , (ucleoio) Plasma, membrane, , Fg.03 Diagremmetic representetion of, a typical bectérial ce, , Cell Envelope and its Modifications, Most prokaryotic cells have a chemically complex cell envelope. The cell envelope, consists of a tightly bound three layered structure glycocalyx cell wall and the, plasma membrane. Bacteria can be classified into two groups on the basis of the, , differences in the cell envelopes and the manner in which they respond to the, staining procedure developed by Gram viz., those that take up the gram stain are, Gram positive and the others that do not are Gram negative bacteria. Glycocalyx, differs in composition and thickness among different bacteria. It could be a loose, sheath called the slime layer in some, it may be thick and tough, called the capsule., The cell wall determines the shape of the cell and provides a strong structural, support to prevent the bacterium from bursting or collapsing. The plasma membrane, , is selectively permeable in nature., A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed bythe extensions, of plasma membrane into the cel. These extensions are in the form of vesicles,, tubules and lamellae. They help in cell wall formation, DNA replication and, , distribution to daughter cells. They also help in respiration, secretion processes, to, increase the surface area of the plasma membrane and enzymatic content. In, cyanobacteria, there are other membranous extensions into the cytoplasm called, chromatophores which contain pigments., Bacteria cells may be motile or non-motile. If motile, they have thin filamentous, , extensions from their cell wall called flagella. Bacterial flagellum is composed of, three parts-filament, hook and basal body., , Pili and fimbriae are also surface structures present in bacteria. The pili are, elongated tubular structures made of a special protein. The fimbriae are small bristle, like fibres sprouting out of the cell. In some bacteria, they are known to help attach, , the bacteria to rocks in streams and also to the host tissues.