Page 1 :
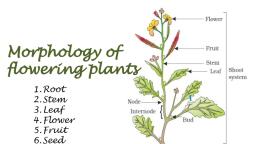
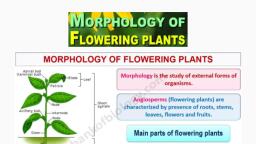
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS:, ROOTS AND STEM, PLANT MORPHOLOGY, Study of the physical form and external structure of plants, Studies the diversity in forms, with the naked cye or slight optical magnification, Also termed as phytomorphology, Observes both the vegetative (somatic) as well as the reproductive structures of plants, Vegetative structures of vascular plants: study of the shoot system as well as the root system, Reproductive structures: flowers, fruits and seeds, BASIC PLANT PARTS, Root - absorbing/anchoring organ (sometimes storage), Stem - supportive, conductive organ (sometimes storage), Leaf-photosynthetic organ (sometimes modified), Apical bud, (terminal bud)., -Blade, Lecf, Petiolc, Sroct, Node, Axillary bud,, Internode, Node, Stem, Lateral root, kcct, System, Primary root, ROOT, Radicle forms the root, Functions:, Absorption of water and minerals from the soil, Providing a proper anchorage to the plant parts, Storing reserve food material, Synthesis of plant growth regulators, TYPES OF ROOT SYSTEMS, Tap root system: In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of, primary root which grows inside the soil, It bears lateral roots of several orders that are referred to as secondary, tertiary roots, Fibrous root system: In monocotyledons, the primary root is short lived and is replaced by a large number of roots, These roots originate from the base of the stem, Adventitious Root system:, In some plants, like grass, Monstera and the banyan tree (Ficus), roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle, These are called adventitious roots, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 3 :
THREE TYPES OF ROOT SYSTEMS, Fibrous root, Taproot, Adventitious root, REGIONS OF THE ROOT, Reglon of, maturation, Roo: hair., Reglon of, elongation, 7 Region of, meristematic, activity, Root cap-, REGIONS OF THE ROOT, Root cap: cup-like structure that protects the tender apex of the root as it makes its way through the soil, Region of meristematic activity: a few mm away from the root cap; very small, thin-walled cells with dense protoplasm, Region of elongation: cells proximal to the above region undergo rapid elongation and enlargement; responsible for the, growth of the root in length, Region of maturation: cells of the elongation zone gradually differentiate and mature; give out root hairs, MODIFICATIONS OF THE ROOT, MODIFIED TAP ROOT FOR STORAGE, Primary root swollen for storage of food and secondary roots remain thin, Sometimes, hypocotyl also joins in to store food, The stem in this case is reduced and discoid; bears leaves called as the radical leaves, Fusiform roots, Conical roots, Napiform roots, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 4 :
MODIFIED TAP ROOT FOR STORAGE: FUSIFORM ROOTS, Tuberous roots, Nodulated roots, These roots are thicker in the middle and tapering on both ends, Spindle-shaped appearance, In this type of roots both hypocotyl and root help in storage of food, Fine secondary roots arise from the apical, part, E.g. radish, MODIFIED TAP ROOT FOR STORAGE: CONICAL ROOTS, These roots are thicker at their upper side and tapering at basal end, Conical in shape, Thread-like secondary roots present throughout, Fleshy basal part is derived from the hypocotyl, E.g. carrot, MODIFIED TẬP ROOT FOR STORAGE: NAPIFORM ROOTS, These roots become swollen and spherical at upper end and tapering like a thread at their lower end, Top-shaped, Beet root: swollen part is hypocotyl and the root; turnip: swollen part is hypocotyl and narrow part is root, E.g. beetroot, turnip, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 5 :
MODIEIEDTAP ROOT FOR STORAGE: TUBEROUS I OOTS, Such roots do not have regular shape and get swollen and fleshy at any portion of roots, E.g. Mirabilis jalapa, MODIFIED TAP ROOT FOR STORAGE: NODULATED ROOTS, Secondary, tertiary or primary roots bear small nodule-like swellings, Swellings called as tubercles, Contain nitrogen fixing bacteria, Also called tuberculated roots, Relationship: mutualistic symbiosis, E.g. leguminous plants, MODIFIED TAP ROOT FOR RESPIRATION: RESPIRATORY ROOTS, Found in plants growing in the mangroves or swamps; deficient in, Possess horizontal cable roots which give rise to vertically upward aerial roots at short intervals, Possess minute pores called pneumathodes or lenticels, Also called pneumatophores or aerophores, E.g. Rhizophora, Ceriops, Heritiera, охygen, Simplified diagram of the mature mangrove root system., 1. Main trunk, 3. Nutntive roots, 5. Cable rcots, 2. Pneumatophors, 4, Support roots, Scanned by TapScanner