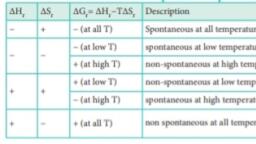
Page 1 : 7.5 Enthalpy (H), , , , The enthalpy (H), is, thermodynamic property of a syst., defined as the sum of the internal e1, (U) ofa system and the product of pres, and volume of the system. That is,, , , , H=U+PV- (7.8), , It reflects the capacity to do, mechanical work and the capacity to, release heat by the system. When a process, occurs at constant pressure, the heat, involved (either released or absorbed) is, ‘equal to the change in enthalpy., , Enthalpy is a state function which, depends entirely on the state functions T,, P and U. Enthalpy is usually expressed as, the change in enthalpy (AH) for a process, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , between enthalpy “H’ and, internal energy “U’, , When the system at constant, jure undergoes changes from an, state with H,, U, and V, to a final, state with H,, U, and V, the change in, enthalpy AH, can be calculated as follows:, , H=U+PV, , In the initial state, , , , H,=U, + PV,-----(7.10), , In the final state, , , , H, =U, + PV,----(7.11), change in enthalpy is (7.11) - (7.10), , (Hy-H,) = (U,-U,) + P(V;-V,), , , , , , , , , , , , , , ® between initial and final states at constant @, peneees. Al \U + PAV --- (7.12), AH = AU + PAV ~~ (7.9) As per first law of thermodynamics,, ‘The change in enthalpy (AH) is AU=qtw, ‘equal to the heat supplied at the constant, pressure toa system (aslong asthe system Equation 7.12 becomes, does no additional work)., AH =q+w+PAV, AH=q,, w= -PAV, In an endothermic reaction heat, is absorbed by the system from the AH =q,- PAV + PAV, surroundings that is q>0 (positive)., ‘Therefore, AH is also positive. In an AH= qs Om), exothermic reaction Pee seedy the e che aea a eo, system to the surroundings that is, q<0 ee cede cies aed, (negative). If q is negative, then AH will Pressure and’is considered!as heat content., also be negative. Consider a closed system of gases, which are chemically reacting to form, gaseous products at constant temperature, 197, [| meet mn e cosas cai], | e ||, = www intextbooks in =, and pressure with V, and V,as the total _Fe(s)+ S(s) > FeS(s), volumes of the reactant and product gases, respectively, and n, and nas the number of AH, = - 100.42 kJ mol", moles of gaseous reactants and products,, tas: 2C(s)+H,(g)> CH,(g), For reactants (initial state) : AH P= + 222.33 kj mol!, PY,=n,RT- (7.14) $4, @+3H, @) +HA®, For products (final state) AH? =~ 924k} molt, ener 789), ‘The standard heats of formation of, 745)
[email protected]) some compounds are given in Table 7.4., ‘Table: 7.4 standard heat of formation of, P(Vp-V) = (npn) RT aa, PAV= Ang RT ~~ Substituting in 7.16 in 7.12 2, 2, ® AH = = ®, 8