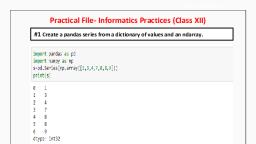
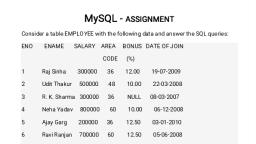
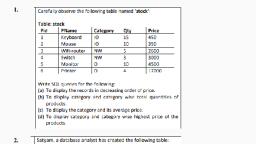
Page 1 :
E-content:, Emerging Trends., (Based on NCERT), , It includes, Lesson Plan,, Reading Material, and, Hyperlink of YouTube, video explanation of econtent,, Question, /, Answer and Activity, Exercise based on this, topic., , EMERGING, TRENDS, INFORMATION PRACTICES, CLASS XI, , Designed By:, SHILPI RANI, PGT IT, JNV GUNTUR
Page 2 :
Lesson Plan Table, Emerging Trends, , Overview & Purpose:, , Education, Computers have been around for quite some time now. New technologies Standard, and initiatives emerge with each passing day. In order to understand the Addressed:, existing technologies and have a better view of the developments around, us, we must keep an eye on the emerging trends. Many new technologies, Senior, are introduced almost every day. Some of these do not succeed and fade, Secondary, away over time. Some of these new technologies prosper and persist over, time, gaining attention from users. Emerging trends are the state-of-the-art, technologies, which gain popularity and set a new trend among users. In, this topic, we will learn about some emerging trends that will make a huge, impact (in the future) on digital economy and interaction in digital societies., , Objectives, (Skills &, information to, be taught), Information, (Demonstrate, necessary, information), , Verification, (Steps to, Check for, student, understanding), Activity, (Independent, Activity to, reinforce the, Lesson), Summary, , Teacher Guide, , Student Guide, , Material Needed, , Aware the students of, new technological, developments that are, succeeding in each, field., Artificial Intelligence,, Machine learning,, Natural language, processing, Immersive, experience , Robotics,, Big Data, Internet of, Things, Web of Things,, Sensors, Smart Cities,, Cloud Computing,, Blockchain, Technology., Give, e-content, exercise as Homework, and take class test, based on it., , Know, about, different, technology, and, how it is working,, their usage., To be involve with, lesson, with, curiosity and try to, find out latest trend, related to each, topic from Internet, and try to find out, what new you can, add, to, technological, development., Attend all Exercise, and, class, test, based on the topic., , E-content, reading, material,, Reference, book by Preeti Arora /, Sumita Arora, Internet, & Newspaper., , E-content, exercise,, previous year CBSE, question, papers,, Model, question, papers., , Conduct, e-content Attempt, class E-content, ‘Activity, ‘Activity corner’ in based, ‘Activity Corner’, &, latest, classroom in oral- corner’, program technological, exam mode to check with, enthusiasm developments, from, student, and try to answer all internet / newspaper., understanding., oral-questions., The topic is very informative and its prime objective is to aware, students about different technology growing day by day and have, been increasing its essence in every field of life.
Page 3 :
Artificial Intelligence (AI), ▪ Artificial Intelligence endeavors to simulate the natural intelligence of, human beings into machines, thus making them behave intelligently., ▪ An intelligent machine is supposed to imitate some of the cognitive, functions of humans like learning, decision-making and problem solving., ▪ In order to make machines perform tasks with minimum human, intervention, they are programmed to create a knowledge base (a, knowledge base is a store of information consisting of facts,, assumptions and rules which an AI system can use for decision making), and make decisions based on it. AI system can also learn from past, experiences or outcomes to make new decisions., , Machine Learning, ▪ Machine Learning is a subsystem of Artificial Intelligence, wherein, computers have the ability to learn from data using statistical, techniques, without being explicitly programmed by a human being., ▪ It comprises algorithms that use data to learn on their own and make, predictions. These algorithms, called models, are first trained and tested, using a training data and testing data, respectively., ▪ After successive trainings, once these models are able to give results to, an acceptable level of accuracy, they are used to make predictions about, new and unknown data., , Natural Language Processing (NLP), ▪ Natural Language Processing (NLP) system deals with the interaction, between human and computers using human spoken languages, such as, Hindi, English, etc., ▪ An NLP system can perform text-to-speech and speech-to-text, conversion., ▪ The predictive typing feature of search engine that helps us by, suggesting the next word in the sentence while typing keywords and the, spell checking features are examples of Natural Language Processing, (NLP).
Page 4 :
▪ Machine translation is a rapidly emerging field where machines are able, to translate texts from one language to another with fair amount of, correctness. Another emerging application area is automated customer, service where a computer software can interact with customers to serve, their queries or complaints., , Figure 1: Use of natural language processing, , Immersive Experiences, ▪ Immersive experiences allow us to visualize, feel and react by, stimulating our senses. It enhances our interaction and involvement,, making them more realistic and engaging., ▪ Immersive experiences have, been used in the field of training,, such as driving simulators, flight, simulator and so on., ▪ Immersive experience can be, achieved using virtual reality, and augmented reality., , Figure 2: Driving Simulator, Virtual Reality:, ▪ Virtual Reality (VR) is a three-dimensional, computer-generated situation, that simulates the real world. The user can interact with and explore that, environment by getting immersed in it while interacting with the objects, and other actions of the user.
Page 5 :
▪ *** Everything that we experience in our reality is perceived through our, senses. From this came the idea that if we can present our senses with, made-up or non-real information, our perception of reality would also, alter in response to that., ▪ At present, it is achieved with the help of VR Headsets. In order to make, the experience of VR more realistic, it promotes other sensory, information like sound, smell, motion, temperature, etc., ▪ It is a comparatively new field and has, found its applications in gaming,, military training, medical procedures,, entertainment, social science and, psychology, engineering and other, areas where simulation is needed for, a better understanding and learning., , Figure 3: VR Headset, Augmented Reality:, ▪ The superimposition of computer generated perceptual information over, the existing physical surroundings is called as Augmented Reality (AR)., It adds components of the digital world to the physical world, along with, the associated tactile and other sensory requirements, thereby making, the environment interactive and digitally manipulable., ▪ With the help of location-based AR App, travelers can access real-time, information of historical places just by pointing their camera viewfinder, to subjects. Users can access information about the nearest places with, reference to their current location., ▪ Unlike, Virtual, Reality,, the, Augmented Reality does not create, something new, it just alters or, augments the perception of the, underlying physical world through, additional information., Figure 4: Location based
Page 6 :
Robotics, ▪ A robot is basically a machine capable of carrying out one or more tasks, automatically with accuracy and precision. A robot is programmable,, which means it can follow the instructions given through computer, programs. Sensors are one of the prime components of a robot., ▪ Robots were initially conceptualized for doing repetitive industrial tasks, that are boring or stressful for humans or were labor-intensive., ▪ Robot can be of many types, such as wheeled robots, legged robots,, manipulators and humanoids. Robots that resemble humans are known, as humanoids. Some examples are:, a. NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission is a robotic space mission, to study about the planet Mars., b. Sophia is a humanoid that uses artificial intelligence, visual data, processing, and facial recognition and also imitates human gestures and, facial expressions., c. A drone is an unmanned aircraft which can be remotely controlled or can, fly autonomously through software-controlled flight plans in their, embedded systems, working in conjunction with onboard sensors and, GPS. Drones are being used in many fields, such as journalism, filming, and aerial photography, shipping or delivery at short distances, disaster, management, search and rescue operations, healthcare, geographic, mapping and structural safety inspections, agriculture, wildlife, monitoring or pooching, besides law-enforcement and border patrolling., , Figure 5: NASA’s Mars, , Figure 6: Sophia: Humanoid, , Figure 7: an, Unmanned aircraft, , ▪ Robotics is primarily concerned with the design, fabrication, operation,, and application of robots.
Page 7 :
Big Data, ▪ Today, there are over a billion Internet users, and a majority of the, world’s web traffic is coming from smartphones. Figure below shows, that at the current pace, around 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are created, each day, and the pace is increasing with the continuous evolution of the, Internet of Things (IoT)., ▪ This results in the generation of data sets of enormous volume and, complexity called Big Data., , Figure 6: Sources of big data (numbers are approximate), ▪ Such data cannot be processed and analyzed using traditional data, processing tools as the data is not only voluminous, but also, unstructured. Big data not only represents voluminous data, it also, involves various challenges like integration, storage, analysis,, searching, processing, transfer, querying and visualization of such data, ▪ Big data hold rich information and knowledge which is of high business, value, and therefore there is a keen effort in developing software and, methods to process and analyze big data.
Page 8 :
Characteristics of Big Data:, (A) Volume:, The most prominent characteristic of big data is its enormous size. If a, particular data set is of such large size that it is difficult to process it with, traditional DBMS tools, it can be termed as big data., (B) Velocity:, It represents the rate at which the data under consideration is being, generated and stored. Big data has an exponentially higher rate of generation, than traditional data sets., (C) Variety:, It asserts that a data set has varied data, such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Some examples are text, images, videos, web pages, and so on., (D) Veracity:, Big data can be sometimes inconsistent, biased, and noisy or there can be, abnormality in the data or issues with the data collection methods. Veracity, refers to the trustworthiness of the data because processing such incorrect, data can give wrong results or mislead the interpretations., (E) Value:, Big data is not only just a big pile of data, but also possess to have hidden, patterns and useful knowledge which can be of high business value. But as, there is cost of investment of resources in processing big data, we should, make a preliminary enquiry to see the potential of the big data in terms of value, discovery., , Figure 7: Characteristics of Big Data, Data Analytics, ▪ Data analytics is the process of examining data sets in order to draw, conclusions about the information they contain, with the aid of, specialized systems and software.
Page 9 :
▪ Data analytics are used in commercial industries to enable organizations, to make more informed business decisions. In the field of science and, technology, it can be useful for researchers to verify or disprove, scientific models, theories and hypotheses., , Internet of Things (IoT), ▪ The ‘Internet of Things’ is a network of devices that have an embedded, hardware and software to communicate (connect and exchange data), with other devices on the same network., ▪ At present, in a typical household, many devices have advanced, hardware (microcontrollers) and software. These devices are used in, isolation from each other, with maximum human intervention needed for, operational directions and input data. IoT tends to bring together these, devices to work in collaboration and assist each other in creating an, intelligent network of things., ▪ For example, if a microwave oven, an air conditioner, door lock, CCTV, camera or other such devices are enabled to connect to the Internet, we, can access and remotely control them on-the-go using our smartphone., , Figure 8: Internet of Things (IoT), , Web of Things (WoT), ▪ Web of Things (WoT) allows the use of web services to connect anything, in the physical world, besides human identities on web. It will pave way, for creating smart homes, smart offices, and smart cities and so on.
Page 10 :
Sensors:, ▪ A smart sensor is a device that takes input from the physical environment, and uses built-in computing resources to perform predefined functions, upon detection of specific input and then process data before passing it, on., ▪ For example, what happens when we hold our mobile vertically or, horizontally? The display also changes to vertical or horizontal with, respect to the way we hold our mobile. This is possible with the help of, two sensors, namely accelerometer and gyroscope (gyro). The, accelerometer sensor in the mobile phones detects the orientation of the, phone. The gyroscope sensors tracks rotation or twist of our hand and, add to the information supplied by the accelerometer., ▪ The evolution of smart electronic sensors is contributing in a large way, to the evolution of IoT. It will lead to creation of new sensor-based,, intelligent systems., Smart Cities:, ▪ With rapid urbanization, the load on our cities is increasing day-by-day,, and there are challenges in management of resources like land water,, waste, air pollution, health and sanitation, traffic congestions, public, safety and security, besides the overall city infrastructures including, road, rail, bridge, electricity, subways, disaster management, sports, facilities, etc., ▪ These challenges are forcing many city planners around the world to, look for smarter ways to manage them and make cities sustainable and, livable., ▪, , The idea of a smart city as shown in Figure, makes, use, of, computer, and, communication technology along with IoT,, WoT to manage and distribute resources, efficiently. The smart building shown here, uses sensors to detect earthquake tremors, and then warn nearby buildings so that, they can prepare themselves accordingly., The smart bridge uses wireless sensors to, detect any loose bolt, cable or crack. It, alerts concerned authorities through SMS., The smart tunnel also uses wireless, sensors to detect any leakage or, congestion in the tunnel. This information, can be sent as wireless signals across the, network of sensor nodes to a centralized, computer for further analysis., , Figure 9: Smart City
Page 11 :
Cloud Computing, ▪ Cloud computing is an emerging trend in the field of information, technology, where computer-based services are delivered over the, Internet or the cloud, for the case of their accessibility form anywhere, using any smart device., ▪ The services comprise software, hardware (servers), databases,, storage, etc. These resources are provided by companies called cloud, service providers and usually charge on pay per use basis., Cloud Services:, ▪ A service corresponds to any facility provided by the cloud. There are, three standard models to categorize different computing services, delivered through cloud. These are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS),, Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)., , Figure 10: Cloud Computing Services, (A) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):, ▪ The IaaS providers can offer different kinds of computing infrastructure,, such as servers, virtual machines (VM), storage and backup facility,, network components, operating systems or any other hardware or, software., ▪ Using IaaS from the cloud, a user can use the hardware infrastructure, located at a remote location to configure, deploy and execute any
Page 12 :
software application on that cloud infrastructure, thereby they can save, the cost of software, hardware and other infrastructures as well as the, cost of setting up, maintenance and security., (B) Platform as a Service (PaaS):, ▪ PaaS provides a platform or environment to develop, test, and deliver, software applications., ▪ In PaaS, the user has complete control over the deployed application and, its configuration. It provides a deployment environment for developers, at a much reduced cost lessening the complexity of buying and managing, the underlying hardware and software., ▪ For example, we have developed a web application using MySQL and, Python. To run this application online, we can avail a pre-configured, Apache server from cloud having MySQL and Python preinstalled. Thus,, we are not required to install MySQL and Python on the cloud, nor do we, need to configure the web server (Apache, nginx)., (C) Software as a Service (SaaS):, ▪ SaaS provides on-demand access to application software, usually, requiring a licensing or subscription by the user., ▪ For example, while using Google doc, Microsoft Office 365, Drop Box,, etc., to edit a document online, we use SaaS from cloud., ▪ A user is not concerned about installation or configuration of the, software application as long as the required software is accessible. Like, PaaS, a user is provided access to the required configuration settings of, the application software that they are using at present., , In order to utilize and harness the benefits of cloud computing, Government, of India has embarked upon an ambitious initiative —‘GI Cloud’ which has, been named as ‘MeghRaj’ (https://cloud.gov.in).
Page 13 :
Grid Computing, ▪ A grid is a computer network of geographically dispersed and, heterogeneous computational resources. Unlike cloud, whose primary, focus is to provide services, a grid is more application specific and, creates a sense of a virtual supercomputer with an enormous processing, power and storage. The constituent resources are called nodes. These, different nodes temporarily come together to solve a single large task, and to reach a common goal., ▪ Grid can be of two types — (i) Data grid, used to manage large and, distributed data having the required multi-user access, and (ii) CPU or, Processor grid, where processing is moved from one PC to another as, needed or a large task is divided into subtasks, and allotted to various, nodes for parallel processing., ▪ Grid computing is different from IaaS cloud service. In case of IaaS cloud, service, there is a service provider who rents the required infrastructure, to the users. Whereas in grid computing, multiple computing nodes join, together to solve a common computational problem., ▪ The grid provides an opportunity to solve computationally intense, scientific and research problems without actually procuring a costly, hardware., , ▪ To set up a grid, by connecting, numerous nodes in terms of data, as well as CPU, a middleware is, required, to, implement, the, distributed, processor, architecture. The Globus toolkit, (http://toolkit.globus.org/toolkit) is, one such software toolkit used for, building grids, and it is as open, source. It includes software for, security, resource management,, data, management,, communication, fault detection,, etc., , Figure 11: Grid computing
Page 14 :
Blockchains, ▪ Digital transactions are performed by storing data in a centralized, database and the transactions performed are updated one by one on the, database. However, since all the data is stored on a central location,, there are chances of data being hacked or lost. So, rescue is blockchain, technology., ▪ The blockchain technology works on the concept of decentralized and, shared database where each computer has a copy of the database., ▪ A block can be thought as a secured chunk of data or valid transaction., Each block has some data called its header, which is visible to every, other node, while only the owner has access to the private data of the, block., ▪ Blockchain can define as a system that allows a group of connected, computers to maintain a single updated and secure ledger. Each, computer or node that participates in the blockchain receives a full copy, of the database. It maintains an ‘append only’ open ledger which is, updated only after all the nodes within the network authenticate the, transaction., ▪ Safety and security of the transactions are ensured because all the, members in the network keep a copy of the blockchain and so it is not, possible for a single member of the network to make changes or alter, data., , Figure 12: Block chain technology
Page 15 :
Applications of Blockchain Technology:, ▪ The most popular application of block chains technology is in digital, currency., ▪ In healthcare, better data sharing between healthcare providers would, result in a higher probability of accurate diagnosis, more effective, treatments, and the overall increased ability of healthcare organizations, to deliver cost-effective care., ▪ Another potential application can be for land registration records, to, avoid various disputes arising out of land ownership claims and, encroachments., ▪ A blockchain based voting system can solve the problem of vote, alterations and other issues. Since everything gets stored in the ledger,, voting can become more transparent and authentic., ▪ The blockchain technology can be used in diverse sectors, such as, banking, media, telecom, travel and hospitality and other areas., , For video explanation of the topic, click the link:, https://youtu.be/gnMpg21FhEo
Page 16 :
EXERCISE -------------------------------------------1. List some of the cloud-based services that you are using at present., 2. What do you understand by the Internet of Things? List some of its potential, applications., 3. Write a short note on the following:, a) Cloud computing, b) Big data and its characteristics, 4. Explain the following along with their applications., a) Artificial Intelligence, b) Machine Learning, 5. Differentiate between cloud computing and grid computing with suitable, examples., 6. Justify the following statement- ‘Storage of data is cost effective and time, saving in cloud computing.’, 7. What is on-demand service? How it is provided in cloud computing?, 8. Write examples of the following:, a) Government provided cloud computing platform, b) Large scale private cloud service providers and the services they, provide., 9. A company interested in cloud computing is looking for a provider who, offers a set of basic services such as virtual server provisioning and ondemand storage that can be combined into a platform for deploying and, running customized applications. What type of cloud computing model fits, these requirements?, a) Platform as a Service, b) Software as a Service, c) Infrastructure as a Service, 10. Which is not one of the features of IoT devices?
Page 17 :
a) Remotely controllable, c) Can turn themselves off if necessary, , b) Programmable, d) All of the above, , 11. If Government plans to make a smart school by applying IoT concepts, how, can each of the following be implemented in order to transform a school into, IoT enabled smart school?, a) e-textbooks, b) Smart boards, c) Online tests, d) Wifi sensors on classrooms doors, e) Sensors in buses to monitor their location, f) Wearable’s (watches or smart belts) for attendance monitoring, 12. Five friends plan to try a startup. However, they have a limited budget and, limited computer infrastructure. How can they avail the benefits of cloud, services to launch their startup?, 13. Governments provide various scholarships to students of different, classes. Prepare a report on how blockchain technology can be used to, promote accountability, transparency and efficiency in distribution of, scholarships?, 14. How IoT and WoT are related?, 15. Match the following:, Column A, , Column B, , You got a reminder to take medication, You got a sms alert that you forgot to lock the door, , Smart Parking, Smart Wearable, , You got the sms alert that parking space is available Home Automation, near your block, You turned off your LED TV from your wrist watch, Smart Health
Page 18 :
ACTIVITY CORNER, Activity 1: Find out how NLP is helping differently-abled persons?, Activity 2: Find out what role are robots playing in the medical field?, Activity 3: Explore and list a few IoT devices available in the market., Activity 4: We use GPS to navigate outdoors. VPS is another emerging trend, that uses Augmented Reality. Explore and find its other utilities., Activity 5: Name a few data centers in India along with the major services that, they provide., Activity 6: Identify the pictures given below and give one suitable word to it., , a. ________________________________, , b. ____________________________________, , c. ________________________________, , d. __________________________________