Page 1 :
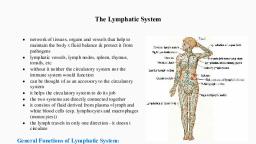
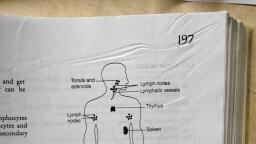
Lymphatic system, This system is present in the body of vertebrates and is composed of vessels,, tissues, and organs. The human lymphatic system helps in maintaining fluid, balance. It does so by collecting the excess fluid from tissues and then deposits, it into the bloodstream. The lymph circulatory system also generates, lymphocytes that help in fighting against the diseases. The fluid that runs, through the lymphatic system is known as lymphatic fluid., Lymphatic System Structure, The lymphatic system in the human body is made up of lymph, lymphatic, vessels, lymphatic nodes, and lymphoid tissue. Lymph is a colourless, watery, fluid that mainly consists of white blood cells and is carried by the lymphatic, system. The lymph vessels are the site of fluid drainage. They pump the lymph, fluid with the help of skeletal and smooth muscles. To prevent the backflow, the larger lymph vessels are present with valves. A lymph node is nothing but, a mere collection of lymphoid tissue. They are located at regular intervals in, the lymphatic system. Lymphoid tissue is composed of lymphocytes along with, other specialized cells and tissues that help in maintaining the immune system, functions. The lymphatic system diagram is shown below.
Page 2 :
Lymphatic, Circulation, The lymphatic system, can be thought of as a, drainage system that, is needed by the body, because, blood, circulates, and, its, plasma is leaked into, the thin walls of the, capillaries., Extracellular fluid is, the portion of the, blood plasma that, escapes, and, it, contains, oxygen,, amino acid, and other, useful nutrients that, are needed by the, body and tissue cells., Almost all of the fluid, gets back into the, bloodstream but a, small percentage of it, along with the particulate matter is left behind. Here then comes the role of, the lymphatic system which helps in removing these fluids and materials from, tissues which thus prevents the fluid imbalance in the body. This imbalance, can lead to the death of the organism. This lymph gets drained into larger, vessels that are known as lymphatic vessels and these vessels converge to, form the lymphatic trunk. These lymphatic trunks are connected to the veins, and thus the excess materials or the infectious microorganisms are removed, via this pathway. These lymphatic vessels are punctuated at intervals by small, masses of lymph tissue which are known as lymph nodes.
Page 3 :
Lymphoid Organs, The body lymph system is divided into primary lymphoid organs and, secondary lymphoid organs. The primary lymphoid organs are the sites of B, and T cells maturation sites and the secondary lymphoid organs are where, these cells are further differentiated and perform their functions. Thymus,, bone marrow, fetal liver are the primary lymphoid organs. Thymus and bone, marrow are the major key players in immune function. The cells that mature, in the bone marrow are termed B cells and the cells that migrate from bone, marrow to thymus are called T cells. When these B and T cells mature they are, migrated to the secondary lymphoid organs via the bloodstream where they, are activated by coming in contact with the foreign materials which are termed, as antigen. Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils are termed secondary lymphoid, organs. This is where these matured cells perform their function.