Page 1 :
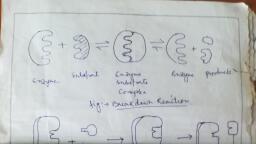
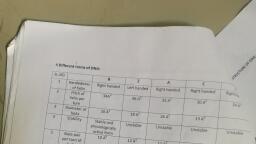
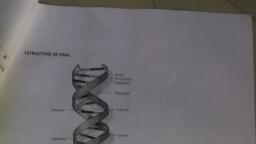
WDNA replication: |i, 18, he process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule, , , , SUL, , , , , Loading stand | i., ‘, NINA primar s ths nn, rea, DNA : AL, RNA primase ue y — fA OULU ,, | @. f Cmacaks agenant, ‘ DWApoll + ’, Lagging strand eriPEER YR, iy ., , Fig: DNA replication,, , !, , There are three main steps which involved in replication, They are:, a) Initiation: Initiator protein known as helicase enzyme binds to the origin site (ori C) and, , helps to unwind the double stranded DNA strand by breaking the hydrogen bonds between, complementary bases, Then single stranded binding proteins (SSBP) attached to the, , separated strands prevents from reannealing,, b) Elongation: DNA polymerase formed newly discontinuous strands called lagging strands and, , synthesized continuous strands but cannot formed without RNA primer, RNA primer, synthesize at the 5’end of new DNA strand with the help of RNA polymerase enzyme called, primase, The lagging strands unwind in small sections resulting to form okazaki fragments., , c) Termination: RNA primers are removed from the end of lagging strand and the gap is filled, , by DNA synthesis. The okazaki fragments are sealed by DNA ligase enzyme., , SL.NO, Leading strand ee Lagging Strand, , FI ecoyeiieatieneeealseeensond einedeieesiiee ;, DNA ligase is not required. DNA ligase is required for joining okazaki, , fragments,, , , , , , , , oof, , Formation of leading strand is quite | Formation of leading strand is quite slower., , rapid,, Its template opens in 3 —> D | Its template opens in 5’ ———3 ‘direction., direction,