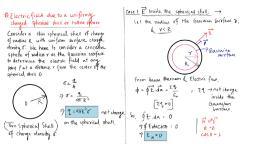
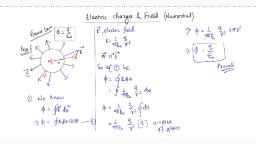
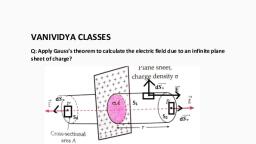
Page 1 :
Physics, 11. The electric field due to a charge configuration with total charge zero, is not zero; but for distances large compared to the size of, the configuration, its field falls off faster than 1/r 2, typical of field, due to a single charge. An electric dipole is the simplest example of, this fact., , EXERCISES, 1.1, 1.2, , 1.3, , 1.4, , 1.5, , 1.6, , 1.7, , 1.8, , 1.9, , 1.10, , 1.11, , 46, , 1.12, , What is the force between two small charged spheres having, charges of 2 × 10–7C and 3 × 10–7C placed 30 cm apart in air?, The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge 0.4 µC due to, another small sphere of charge – 0.8 µC in air is 0.2 N. (a) What is, the distance between the two spheres? (b) What is the force on the, second sphere due to the first?, Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table, of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What, does the ratio signify?, (a) Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body, is quantised’., (b) Why can one ignore quantisation of electric charge when dealing, with macroscopic i.e., large scale charges?, When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on, both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of, bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of, conservation of charge., Four point charges qA = 2 µC, qB = –5 µC, qC = 2 µC, and qD = –5 µC are, located at the corners of a square ABCD of side 10 cm. What is the, force on a charge of 1 µC placed at the centre of the square?, (a) An electrostatic field line is a continuous curve. That is, a field, line cannot have sudden breaks. Why not?, (b) Explain why two field lines never cross each other at any point?, Two point charges qA = 3 µC and qB = –3 µC are located 20 cm apart, in vacuum., (a) What is the electric field at the midpoint O of the line AB joining, the two charges?, (b) If a negative test charge of magnitude 1.5 × 10–9 C is placed at, this point, what is the force experienced by the test charge?, A system has two charges qA = 2.5 × 10–7 C and qB = –2.5 × 10–7 C, located at points A: (0, 0, –15 cm) and B: (0,0, +15 cm), respectively., What are the total charge and electric dipole moment of the system?, An electric dipole with dipole moment 4 × 10–9 C m is aligned at 30°, with the direction of a uniform electric field of magnitude 5 × 104 NC–1., Calculate the magnitude of the torque acting on the dipole., A polythene piece rubbed with wool is found to have a negative, charge of 3 × 10–7 C., (a) Estimate the number of electrons transferred (from which to, which?), (b) Is there a transfer of mass from wool to polythene?, (a) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centres, separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of, 2021–22
Page 2 :
Electric Charges, and Fields, , 1.13, , 1.14, , electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 × 10–7 C? The, radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of, separation., (b) What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double, the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?, Suppose the spheres A and B in Exercise 1.12 have identical sizes., A third sphere of the same size but uncharged is brought in contact, with the first, then brought in contact with the second, and finally, removed from both. What is the new force of repulsion between A, and B?, Figure 1.33 shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform, electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle, has the highest charge to mass ratio?, , FIGURE 1.33, , 1.15, , 1.16, , 1.17, , 1.18, , Consider a uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 î N/C. (a) What is the, flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is, parallel to the yz plane? (b) What is the flux through the same, square if the normal to its plane makes a 60° angle with the x-axis?, What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of Exercise 1.15, through a cube of side 20 cm oriented so that its faces are parallel, to the coordinate planes?, Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black, box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the, box is 8.0 × 103 Nm2/C. (a) What is the net charge inside the box?, (b) If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero,, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why, or Why not?, A point charge +10 µC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre, of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in Fig. 1.34. What is the, magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of, the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.), , 47, , FIGURE 1.34, 2021–22
Page 3 :
Physics, 1.19, , A point charge of 2.0 µC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian, surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the, surface?, , 1.20, , A point charge causes an electric flux of –1.0 × 103 Nm2/C to pass, through a spherical Gaussian surface of 10.0 cm radius centred on, the charge. (a) If the radius of the Gaussian surface were doubled,, how much flux would pass through the surface? (b) What is the, value of the point charge?, , 1.21, , A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If, the electric field 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 × 103 N/C, and points radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere?, , 1.22, , A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.4 m diameter has a, surface charge density of 80.0 µC/m2. (a) Find the charge on the, sphere. (b) What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the, sphere?, , 1.23, , An infinite line charge produces a field of 9 × 104 N/C at a distance, of 2 cm. Calculate the linear charge density., , 1.24, , Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On, their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite, signs and of magnitude 17.0 × 10–22 C/m2. What is E: (a) in the outer, region of the first plate, (b) in the outer region of the second plate,, and (c) between the plates?, , ADDITIONAL EXERCISES, 1.25, , An oil drop of 12 excess electrons is held stationary under a constant, electric field of 2.55 × 104 NC–1 (Millikan’s oil drop experiment). The, density of the oil is 1.26 g cm–3. Estimate the radius of the drop., (g = 9.81 m s–2; e = 1.60 × 10–19 C)., , 1.26, , Which among the curves shown in Fig. 1.35 cannot possibly, represent electrostatic field lines?, , 48, 2021–22
Page 4 :
Electric Charges, and Fields, , FIGURE 1.35, , 1.27, , 1.28, , In a certain region of space, electric field is along the z-direction, throughout. The magnitude of electric field is, however, not constant, but increases uniformly along the positive z-direction, at the rate of, 105 NC–1 per metre. What are the force and torque experienced by a, system having a total dipole moment equal to 10–7 Cm in the negative, z-direction ?, (a) A conductor A with a cavity as shown in Fig. 1.36(a) is given a, charge Q. Show that the entire charge must appear on the outer, surface of the conductor. (b) Another conductor B with charge q is, inserted into the cavity keeping B insulated from A. Show that the, total charge on the outside surface of A is Q + q [Fig. 1.36(b)]. (c) A, sensitive instrument is to be shielded from the strong electrostatic, fields in its environment. Suggest a possible way., , FIGURE 1.36, , 1.29, , 1.30, , 1.31, , A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface., Show that the electric field in the hole is (σ/2ε0) n̂ , where n̂ is the, unit vector in the outward normal direction, and σ is the surface, charge density near the hole., Obtain the formula for the electric field due to a long thin wire of, uniform linear charge density E without using Gauss’s law. [Hint:, Use Coulomb’s law directly and evaluate the necessary integral.], It is now established that protons and neutrons (which constitute, nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more, elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of, three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so called ‘up’ quark, (denoted by u) of charge + (2/3) e, and the ‘down’ quark (denoted by, d) of charge (–1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary, matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise, to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark, composition of a proton and neutron., 2021–22, , 49
Page 5 :
Physics, 1.32, , 1.33, , 1.34, , (a) Consider an arbitrary electrostatic field configuration. A small, test charge is placed at a null point (i.e., where E = 0) of the, configuration. Show that the equilibrium of the test charge is, necessarily unstable., (b) Verify this result for the simple configuration of two charges of, the same magnitude and sign placed a certain distance apart., A particle of mass m and charge (–q) enters the region between the, two charged plates initially moving along x-axis with speed vx (like, particle 1 in Fig. 1.33). The length of plate is L and an uniform, electric field E is maintained between the plates. Show that the, vertical deflection of the particle at the far edge of the plate is, qEL2/(2m vx2)., Compare this motion with motion of a projectile in gravitational field, discussed in Section 4.10 of Class XI Textbook of Physics., Suppose that the particle in Exercise in 1.33 is an electron projected, with velocity vx = 2.0 × 106 m s–1. If E between the plates separated, by 0.5 cm is 9.1 × 102 N/C, where will the electron strike the upper, plate? (|e|=1.6 × 10–19 C, me = 9.1 × 10–31 kg.), , 50, 2021–22