Page 1 :
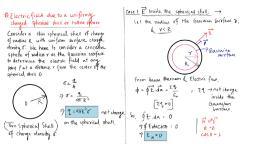
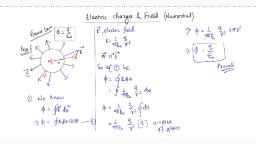
Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance, , ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL, & CAPACITANCE, I. Answer in one word / one, sentence / statel define:, 1., , 2., , 3., , 4., , 5., , 6., , 7., , 8., , Define capacity of a conductor., Ans. The capacity of a conduetor is the, charge given to the conductor to raise its, potential by one unit., What is a capacitor ?, Ans. A capacitor is an electrical device that, stores electric charge and hence electric, energy., Define 1 farad capacity of a conductor., Ans. 1 farad is the capacity of a conductor, to which a charge of 1 coulomb is given to, raise its potential by 1 volt., Define 1 farad capacity of a capacitor., Ans. The capacity of a capacitor is 1 farad, when a charge of 1 coulomb is given to its, positive plate to raise the potential, difference between the capacitor plates by, 1 volt., What are dielectrics ?, Ans. Dielectrics are basically insulators that, are used between the capacitor plates to, reduce the electric field intensity and, potential difference between the plates, and hence to increase the capacitance of, the capacitor., What happens when a dielectric medium is, introduced between the capacitor plates ?, Ans. The p.d between the capacitor plates, decreases due to which capacitance of the, capacitor increases., What is the difference between Insulators, and Dielectrics ?, Ans. Dielectricsare basically insulators but, all insulators are not dielectrics., Dielectricsare used in capacitors to, increase the capacitance but not the, insulators., What are polar molecules ?, Ans. In polar molecules the centres of, positive and negative charge are separated, by a fixed distance., or, If the centers of positive and negative, charges do not coincide because of the, asymmetric shape of the molecules, then, these are called polar molecules., , Yayati Keshari, , Simple Physics, , 9., , What is relative permittivity ?, Ans. It is the ratio of the permittivity (Ɛ0) of, the dielectric medium to the permittivity, of vacuum (or air) (Ɛ0)., Mathematically, Ɛ� =, , Ɛ, Ɛ0, , ; Ɛ� >1, , 10. Name the two SI units of permittivity., �2, , Ans. �.�2 and Farad/m., 11. How the two units of permittivity (Ɛ0) are, derived ?, Ans., (a) From Coulomb's law,, 1 � �, F=4πϵ 1�2 2, ϵ0 =, , 0, , 1 Q1 Q2, , 4π Fr2, , �2, , So the SI unit of ϵ0 is �.�2, (b) From the expression for the, capacity of a parallel plate capacitor, ϵ A, C= 0, �, ��, , ϵ0 =, , �, , =, , ����� × �, �2, , =, , �����, , 12. What is dielectric constant ?, �, Ans. Dielectric constant, K =, , �, , �0, , 13., , 14., 15., , 16., , 17., , Where C & C0 are capacitances with, and without the dielectric respectively., What is Dielectrie strength?, Ans. It is a measure of the maximum, potential gradient that can develop across, the dielectric before the dielectric ruptures,, permitting conduction through it., What type of energy is stored in a, capacitor ?, Ans. Electrostaticpotential energy., How the capacity (C) of a capacitor change, with the change in the separation (S), between the plates ?, Ans. The capacity varies inversely as the, separation between the plates, 1, Cα, d, What happens to the capacity of air, capacitor change when a sheet of mica is, introduced., Ans. Capacity increases by K times where K, is dielectric constant of mica., The space between the capacitor plates is, filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant, K. How will the capacity change?, Ans. C = KC0,, i.e. capacity of the capacitor increases, by K times., 1
Page 2 :
Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance, , 18. Name the CGS electrostatic and SI units of, electric potential., Ans. Statvolt and Volt., 19. Convert 1 volt to statvolt., 1 �����, Ans. 1 volt = 1 �������, 20., , 21., , 22., , 23., , 24., 25., , 26., , 27., , 28., , 107���, , = 3×109�����������, 1, , = 300 statvolt, Write the relation between Joule, volt and, coulomb., 1 Joule, Ans. 1 coulomb = 1volt, How electrie potential and electric, potential energy are related ?, Ans. V= � �, where, V = Electric Potential, U = Electric Potential energy., Define equipotential surface., Ans. It is a closed surface (of the same, shape as the charged body) drawn through, the points having the same potential., Define equipotential line., Ans. It is an imaginary line drawn in an, electric field such that all points on the line, are at the same potential., What is the angle between a equipotential, surface and a line of force ?, Ans. 90°, What is the work done in movinga test, charge over the surface of an isolated, charged metal sphere ?, Ans. Zero, Why the surface of an isolated charged, conductor is an equipotential surface ?, Ans. Charges will move from one point to, another on the charged conductor which, will violate is an electrostatic condition., Why two equipotential surfaces do not, intersect each other ?, Ans. Because if they intersect then at the, point of intersection there will be two, values of potential which is not possible., How the electrie field intensity (E) and the, ��, potential gradient, �� are related ?, −��, , Ans. E = ��, 29. Is there a point in an electric field where, electric field intensity is zero but not the, electric potential ?, Ans. Yes, at the midpoint between two, equal and similar charges., 30. Is there a point in an electric field where, electric potential is zero but not the electric, field intensity ?, Ans. Yes, at the midpoint of an electric, dipole., , Yayati Keshari, , Simple Physics, , II. Fill in the blank spaces, with appropriate answers:, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., , 12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., , 23., , SI unit of capacitance is _________., CGS electrostatic unit of capacitance is, ______., 1 Farad= ________ statfarad., SI unit of permittivity is ________., Dimensional formula of capacitance is, ______., Capacity of a conductor is the charge, per unit_______., Capacity of a capacitor is the charge, per_______ unit between the, conductors constituting the capacitor., For a parallel plate capacitor the, _______plate is preferably earth, connected., For a parallel plate capacitor the, capacity varies _______ as the area of, the plates., For a parallel plate capacitor the, capacity varies_______ as the, separation between the plates., For a parallel plate capacitor the, _______ as the relative permittivity of, the dielectric medium between the, plates., All dielectrics are basically ________., The molecules of dielectrics are, _________., The capacity of a capacitor________, when air is replaced by another, dielectric such as glass., Dielectric constant of a dielectric is also, called its ________ permittivity., Electric Potential is a ________quantity., The C.G.S electrostatic unit for The, measuring the electric potential is ____., The SI unit for measuring electric, potential is ______., 1volt is = ______statvolt., Electron Volt (eV) is the unit for, measuring electric ______., Electric potential is a______function., Electric potential at a point due to a as, the point charge varies _________ as, the distance between the point of, observation and the point charge., Electric potential due to an electric, dipole at an axial point varies______as, the square of the distance between the, centre of the dipole and the point off, observation., , 2
Page 3 :
Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance, , 24. Electric potential due to an electric, dipole is zero at a point on the _____, line., 25. A line of force intersects at _______, degree with an equipotential surface., 26. The electric potential at a point due to, more than one charges are added _____., 27. The surface of a charged conductor is an, ______surface., 28. For an isolated point charge both the, electric field intensity (E) and electric, potential (V) are zero only at ______., 29. In an electric field two equipotential, surfaces ______ intersect., 30. Work is done by a test charge when it, surfaces moves from, _____to_____potential1point., 31. Work is done on a test charge as it, moves from ____ to ____ potential, point., 32. When an external agent does work the, work is done _____ the test charge., 33. A test charge gains potential energy, when work is done _____ it by the, external agent., 34. A test charge gains potential energy as it, moves from a point at a _____ potential, to a point at _____ potential., 35. No work is done in moving a test charge, between two points at _____ potential., , ANSWER, , Simple Physics, , III. Correct the following, statements if required, changing the underlined, portion., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20., 21., , An isolated charged conductor has no, capacity to store positive charge., All insulators are basically dielectrics., Dielectric constant is same as relative, permittivity., Charge flows through a dielectric such as, glass, Work is not required to charge a capacitor., There is a net charge on a capacitor., Charges flow through a capacitor., A capacitor and a battery both operate on, the same principle., Potential difference exists only between, the capacitor plates but not across the, dielectric., The electric potential energy is stored, inside the dielectric., Dielectric constant of a dielectric varies, directly with the temperature., The effective capacitance increases when, number of capacitors are grouped in series., To decrease the effective capacitance, the, given capacitors are to be group, The molecules of all dielectrics are polar., In parallel plate capacitors the capacitance, decreases when the negative plate is, connected to the earth., The field properties (such as the field, intensity and the potential) can be, measured by the source charge itself., The surface of a charged conductor is an, equiintensity surface., Potential is a vector property of the field., Potential gradient is not related to, electricfield intensity., Moving down the potential gradient a test, charge gains electrie potential energy., −��, � = �� is correct., −��, , 22. �= �� can not be the correct relation., 23. An equipotentialsurface and lineof force in, an electric field are parallel to each other., 24. The angle between two equipotential, surfaces is 90 degrees., 25. Work has to be done in moving a test, charge from one point to another on an, equipotential surface., 26. Electricpotential at a point can not be zero, for a dipole., , Yayati Keshari, , 3
Page 4 :
Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance, , 27. Electron Volt is the unit of electric, potential., 28. The work done in moving a test charge, between two points in an electric field, depends on the path chosen., 29. Potentialat the centre of a hollow charged, sphere has to be zero., ������, ����, 30., = �2, �������, , IV., , 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., , ANSWER, , State whether following, statements are True (T) or, False(F):, , The conventional and convenient unit for, measuring capacitance is microfarad., Farad is a large unit for measuring the, capacitance., All insulators are dielectrics., All dielectricsnecessarily are insulators., An isolated charged conductor has no, electrical capacity., The minimum dielectricconstant is one for, air., Dielectricconstant of a dielectric is equal to, its permittivity., The relative permittivity of a dielectric, medium is same as its dielectric constant., A capacitor stores magnetic energy, between its plates., A capacitor stores electrostatic energy, inside its dielectric., The molecules of a dielectric may be polar, or non-polar., Water is the only dielectric with non- polar, molecules., An isolated charged conductor has no, electrical capacity., , Yayati Keshari, , Simple Physics, , 14. Charges do not flow through a dielectric, like conductors., 15. The electrical conductivity of dielectrics is, less than that for insulators., 16. Potential is a scalar quantity and hence o d, can be added algebraically., 17. Potential is a vector quantity., 18. Potential gradient is a scalar quantity., 19. The magnitude of electric field intensity is, numerically equal to the potential gradient., 20. An equipotential surface is a uniform field, region., 21. The potential at the centre of a hollow, charged sphere is zero., 22. Potential at any point on the surface of a, charged sphere is different from the, potential at the centre., 23. The potential at all points on the surface of, a charged conductor is same., 24. The surface of a charged conductor is an, equipotential surface., 25. Work has to be done in moving a test, charge from one point to another on a, charged conductor., 26. Volt = Joulex Coul., 27. The SI unit of potential gradientis, metre/volt, 28. NewtonVolt Coulomb m, 29. In an electric field due to an isolated point, charge the electric potential is a point, function., 30. The equipotential surfaces have to, intersectwith each other., 31. Equipotential surfaces are parallel to each, other., 32. Equipotentialsurfaces are parallel to, electrie lines of forces., 33. A test charge can be forced to move from, lower to higher potential point by an, external agent., 34. Work is done on the test charge when it, moves from higher to lower potential, point., 35. Electric potential due to a dipole is zero at, any point on its axial line., 36. Electric potential due to a dipole is zero at, any point on its equatorial line., , ANSWER, , 4