Page 1 :
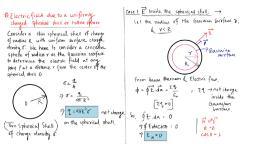
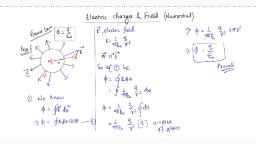
Electrostatic Potential & Capacitance, , Simple Physics, , 1. ELECTROSTATICS OF CONDUCTORS, , , CONDUCTORS, , , , GAS, , Conductors contain mobile charge carriers. Electrons are the charge carriers in metalic, conductor. In metal, the outer electrons(valence electrons) are free to move. These electrons are, free within the metal, but not free to leave from the metal surface. Therefore, these electrons, are called free electrons., In gas free electrons collide with each other and with the ions and move randomly in, different directions., Nuclei bound the electrons to revolve in fixed orbits., , In an external electric field, the free electrons, are drifted against the direction of the field., , , ELECTROLYTIC CONDUCTOR, , , , CHARACTERISTICS, , In electrolytic conductor charge carriers are both positive ions and negative ions., , When a conductor is placed in an external electric field, the movement of the charge, carriers is affected by the external electric field. This is the electrostatics of conductor. Some, important results regarding electrostatics of conductors(only in static conditions) are noted, below., Inside a conductors, electrostatics field is zero. In other words, net electric field is zero in the, interior of the conductor., At the surface of a charged conductor, electrostatic field must be normal to the surface at, every piont., The interior of a conductor can have no excess charge in the static situation. Net charge in, the interior of a conductor is zero., Electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the conductor and has thesame, value(as inside) on the surface. In other words, potential is constant within and on the, surface of the conductor., Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to the surface charge, density., Electrostatic Shielding: Phenomenon of making an electric field free zone in the free space is, called electrostatic shielding. It is like a cavity, electric field free region., Whatever be the charge and electric field in outside, cavity in a conductor remains shiled, from outside electric influences i.e., electric field inside the cavity is always zero., , Yayati Keshari, , 1