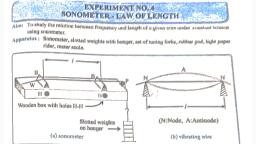
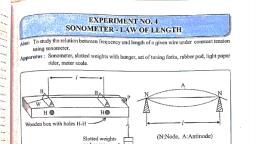
Page 1 :
INDEX, , LIST OF PHYSICS PRACTICALS, NAME OF EXPERIMENTS, , SPRING MA MASS OSCILLATOR, SURFACE TENSION |, , NEWTON’ Ss LAW OF COOLING, SONOMETER I LAW OF ' LENGTH, , SONOMETER uN LAW OF TENSION, , _| RESONANCE TUBE, , CURRENT SENSITIVITY, , LAWS OF RESISTANCES USING, METER BRIDGE, , RESISTANCE OF GALVANOMETER BY, KELVIN'S METHOD, , E, / E, USING POTENTIONMETER, INTERNAL RESISTANCE OF CELL, , u, / 1, BY SUSPENSION METHOD, CHARACTERISTICS OF ZENER DIODE, STUDY OF LOGIC GATES, , CHARACTERISTICS OF TRANSISTOR, , LIST OF ACTIVITIES, EFFECT OF DETERGENT ON SURFACE, TENSION, , SECONDS PENDULUM, , MELDE'S EXPERIMENT, , FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF, LOSS OF HEAT OF LIQUID, DIFFRACTION, , HOUSEHOLD CIRCUIT eae, VARIATION OF POTENTIAL DROP, , , , PAGE NO.| DATE SIGN, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , HUSEOR MULTIMETERS, LIGHT DEPENDENT RESISTOR | 3, QUESTIONS SLIPS FOR PRACTICAL EXAMINATION = 151 = |, , , , Scanned with CamScann
Page 3 :
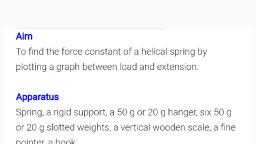
Where,, , R - Radius of spring, N - No. of turns in the spring, 7 = Radius of the wire used for spring, a ° Rigidity of the material of the spring, T z Time period of oscillation, Ref: Advanced Practical Physics for students by B. L. Warsnop & Flint, , Procedure:, PART - A To find force constant (K) & (P.E), , 1) Weigh the hanger and determine the mass of the hanger (m,)., , 2) Clamp the given spiral spring to a rigid support and attach the hanger with pointer at its lower, end., , 3) Add asuitable mass to the hanger so that the spring is stretched to about triple of the unstretched, length. i.e each tum of the spring will be free from each other., , 4) Note down total mass attached to the spring (M) and also note down the reading (S,) i. e., , mean position on the scale according to position of the pointer., , Add one slotted weight of 50g in the hanger and note the position of the pointer say S. Repeat, , the procedure twice by adding weights in steps of 50g. (m is more than M.), , 6) Remove weights from the hanger and bring the pointer to its mean position S,. Take three, readings by reducing weights in steps of 50g. (m less than M), , 7) Determine the extension (S, - S) = x in each case., , 8) Plot the graph of F against x. and determine slope of the graph. Slope of the graph is force, constant (k) lL 3 is), , 9) Calculate the potential energy (Se } for each value of extension,x, and plot the graph of, , ny, , potential energy against extension x., , PART - B To find mass of the spring m,, , 1) Put suitable weights in the hanger and determine the time to complete 20 oscillations by using, stop watch. Repeat this step two times, hence calculate mean time (t) for 20 oscillations., , 2) Calculate the periodic time (T)., , 3) Note down the next four observations by changing the mass in steps of 50g. Find the time for, 20 oscillations in each case. Where, total mass M (mass of the hanger + mass kept in the, hanger). a. 7, , 3) Determine mean time (t) in each case. Calculate periodic time (T) for each mass.- =, , 4) Plot the graph of T? against M and hence find the mass of the spring m,, , Observations : :, PART-A_ To determine force constant (k) and Potential Energy (P.E.): |, , , , : ee tae =! =, g, so that spring gets stretched to about triple of its, unstretched length. TI herefore totat-mass attached M “(yt m,) ™ Ne Bs, 3. Position of the pointer when the spring is stretched to about triple of the unstretched length S,, = seas cm., =<, _~ scanned witn Gamscann
Page 5 :
qe, , Agraph of F against x: . Agraph of P.E, against x:, , , , Tew, .E.=—KX°, z 2, , k=Islope I, , , , net ret qjcpeess ~~ ~A-graph of,.T? against M: ...... . ie tee, Ts’, , , , , , , , , , , , -” 0 Minkg, x intercept, J, Result, 1._Foree-constant-ofthe-given-spring (= same dyne+em—, , 2. Mass of the given spring (m,) from the etic af rT cigs M=.\0..g, , 3.—Fhe-graph-shows that potential energy of oseillator ehanges-with distance x from equilibrium_, Precautions :, , Record the mean position of the pointer carefully., , Oscillations of the spring mass oscillator should be in a vertical plane., , The pointer should move freely over the scale such that it should not touch the scale., Spiral spring should not be stretched beyond the elastic limit., , __D~, , ry, , Po NM, , scanned with Camscann