Page 1 :
EVOLUTION
Page 2 :
Study of development of, organism from lower grade of, organisation to higher grade of, organisation is called as, evolution.
Page 3 :
We have to study........, , *, *, *, *, , Origin of life, Evidence of evolution, Theories of evolution, Modern concept of, evolution, * Human evolution
Page 4 :
Theories..., , , , , , , Origin Of Life, , Special creation, Spontaneous generation, Cosmozoic (panspermia) evolution, Chemical evolution
Page 5 :
Special creation, All life form that we see around us were, , created almost simultaneously., or, The life we see today created as such.
Page 6 :
Living things like insects ,rat worms etc…, , could arise spontaneously from mud dung, and earth., Franscisco Redi & Louis Pasteur disprove, , this theory and state that ……, LIFE COMES ONLY FROM PRE-EXISTING, , LIFE
Page 8 :
State that life, comes from, celestial object like, comets, ,
Page 9 :
Haldane from England., Inorganic molecule combine spontaneously, , in right proportion to give rise to organic, molecule in ancient Earth., In 1953 Stanly Miller and Harold Urey prove, , this theory
Page 12 :
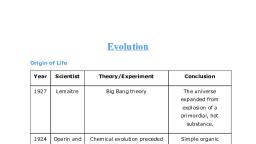
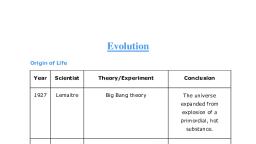
Origin of universe thought to be occur at, , about 20 million years back., Earth created by Big Bang(Modern, , theory), After that......, Universe expanded, Temperature comes down, Gas condensed
Page 13 :
That period, No atmosphere, Water exist as vapour, Methane vapour sufficient in atmosphere, Carbon dioxide rich in atmosphere, Heavy lightning and thunder going on for, , years, Volcano are rich in Earth
Page 14 :
ATMOSPHERE, Because free oxygen is ABSENT in, , atmosphere, These situation is artificially created by, , SL Miller in his experiment., And succeed to produce amino acid,, , sugars, nitrogen base, pigments etc…….
Page 15 :
, , THE BIO GENESIS STATES THAT THE, , , , ORIGIN OF LIFE FORMS FROM NON, , , , LIVING MOLECULES
Page 16 :
OPARIN state that the first living, , molecule may be Co-aservate…It may me, made up of carbohydrate compound, mostly.
Page 19 :
ALGAE, , PROTOZOA, Euglena like forms will be thought, to be first formed protozoa, , OZONE FORMATION, , Thought that O3 stop evolution
Page 20 :
1) INHERITANCE OF ACQUIRED, , CHARACTER, By, French naturalist, , LAMARK, Constant use of an organ results in, its better development while disuse, causes its reduction and degeneration., He cite examples like long neck of, Giraffe, the loss of limbs of snakes
Page 22 :
Beagle…, He visited around the world using voage by, HMS Beagle.
Page 23 :
Beagle…, He visited around the world using voage by, HMS Beagle.
Page 24 :
Galapagos Island and analyse, Alfred Wallace a naturalist who worked in Malay, Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions as, Darwin.
Page 25 :
Nature select the organism which is more, , adapted to its environment . Others were, extinct off……Let as look how it will take, place.
Page 26 :
, , In Nature the organism will produce, large number of offspring without, considering the possibility of survival the, phenomena is called Over production
Page 27 :
Thus these individuals develop competition for, Space, Food and, Mate., And thus develop a fight between them are, , called as Struggle for existence
Page 28 :
In a population the organisms are having two, , types of variations and can be classified as .., 1) USEFUL, , &, , 2) HARMFUL, , In struggle for existence the survival will be, , established the individual which are having, useful variation. This phenomena are called, survival of the fittest
Page 29 :
Variation and natural selection, removes unfit organisms and, establishes the better adapted, and fittest ones to survive in a, given environment., This leads to formation of new, species.
Page 30 :
1. Pale ontological evidence, 2. Comparative anatomical evidence, 3. Morphological evidence
Page 31 :
Branch of Biology deals with study of fossil is, , called Palaeontology., Fossils are remains (hard parts) of past, , organism preserved in sedimentary rocks, called fossils.
Page 32 :
modern organism and those in the lower layer are, from ancient organisms., The fossils of Dinosaurs have obtained and they, have become extinct.
Page 34 :
Comparative anatomical evidence, , Homologous organ
Page 35 :
category, for eg; Fore limb of Mammals, thorns and, tendrils., Similarity observed in the pattern of the, arrangement bone, muscle, blood vessels, nerve etc, But they perform different function.
Page 36 :
, , , , , , Organs that are similar in origin and, structure but dissimilar in function are, called, homologous organ(phenomenon is called, , homology., It indicate divergent evolution., It indicate common ancestry.
Page 37 :
Organs which are similar in function but, , dissimilar in structure and origin are called, analogous organ.
Page 39 :
It indicate convergent evolution or parallel, evolution., Example; wing of insects and wings of birds,, eyes of octopus and eyes of mammals,, sweet potato and potato.
Page 40 :
Divergent evolution, evolution, , Convergent
Page 41 :
, , The similarities in protein and genes give, clue that all the organisms have same, ancestry
Page 43 :
BEFORE INDUSTRIALISATION, (1850s), , AFTER INDUSTRIALISATION, (1920s), , There were more white-winged moth, on trees, , There were more dark winged moth on, trees, , Predators were spot dark winged moth Predators were spot the white winged, moth, So the dark winged moth did not, survive due to predators, , So the white winged moth did not, survive due to predators, , White coloured lichens covered over, the trees, , Pollution destroys the growth of, lichens
Page 44 :
, , Excess usage of pesticides and herbicides, result the selection of the chemical resist, variety of pests, , , , , , , The uncontrolled uses of antibiotics result, the selection of the drug resistant microbes