Page 1 :
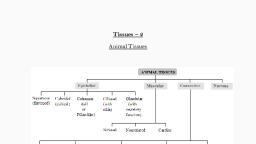
STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS, , Tissues, A group of similar cells with same structure and performing a specific function is, called tissue., Animal tissues, Based on functions, the tissues are classified into four types., 1. Epithelial tissue, 2. Connective tissue, 3. Muscular tissue, 4. Neural tissue, 1.Epithelial tissue, « Epithelial tissue serves as protective covering., * It covers the external surface of the body and internal surfaces of visceral organs,, body cavities and blood vessels., * Cells of epithelium are closely packed and separated by very little matrix., There are two types of epithelial tissue., A. Simple epithelium, B. Compound epithelium, A. SIMPLE EPITHELIUM, « Simple epithelium is composed of single layer of cells., ¢ It functions as lining for body cavities, ducts and tubes, On the basis of structural modification of cells simple epithelium is, further divided into 3 types., 1. Squamous epithelium, 2. Cuboidal epithelium, 3. Columnar epithelium, 1.Squamous epithelium, is made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries, ¢ They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved, ina functions like forming a diffusion boundary., , , , , , , , , , , , Flattened cell, 2.Cuboidal epithelium, formed of single layer of cube like cells., ¢ Itis commonly found in ducts of glands and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys., ¢ The main function are secretion and absorption., ¢ The epithelium of proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of nephron in the kidney has, microvilli which help in absorption.