Page 1 :
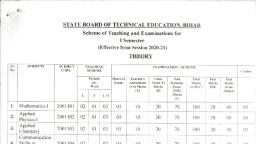
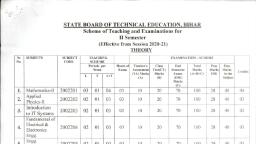
STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION. BIHAR, , Scheme of Teaching and Examinations for, I Semester, , (Effective from Session 2020-21), IHEDRY, Sr., No., , SUBJECrS, , SUBJECT, , TEACHING, , CODE, , EXAMINATION - SCHEME, , SCHEME, , Credits, , Periods, per, , Hours of, , Teacher's, , Class, , End, , Total, , Pass, , Pass, , Exam., , Assessment, , Test{CT), , Semester, , Marks, , Marks, , Marks, , (TA) Marks, (A), , Marks, , Exam., , (A+B+C), , ESE, , (B), , (ESE), , Week, , L, , T, , la the, , Subject, , Marks, , L+T, , (C), , Mathematics-I, , 1., , Applied, , 2., , Physics-I, , Applied, Chemistry, , 3., , 2001101, , 02, , 01, , 03, , 03, , 10, , 20, , 70, , 100, , 28, , 40, , 03, , 2001102, , 02, , 01, , 03, , 03, , 10, , 20, , 70, , 100, , 28, , 40, , 03, , 2001103, , 02, , 01, , 03, , 03, , 10, , 20, , 70, , 100, , 28, , 40, , 03, , 2001104, , 02, , 02, , 03, , 10, , 20, , 70, , 100, , 28, , 40, , 02, , 2001105, , 03, , 03, , 03, , 10, , 20, , 70, , 100, , 28, , 40, , 02, , Total:-, , 11, , 350, , 500, , Communication, Skills in, , 4., , -, , English, , Engg. Graphics, , 5., , 03, , 14, , 13, , PRACTTrAI,, Sr., , SUBJECTS, , Nu., , SUBJI.CT, COD, , 6., 7., 8., , Applied Physics Lab-1, Applied Chemistry Lab, Communication Skills in, , English Lab, , TEACHING, , EXAMI.NATION - SCHEME, , SCHEME, , Periods per, , Hours of, , Week, , Exam., , 2001106, , 03, , Practical (ESE), , Internal(A), , External(B), , Total, , Pass Marks, , Marks, , in the, , (A+B), , Subject, , Credits, , 03, , 15, , 35, , 50, , 20, , 02, , 2001107, , 03, , 03, , 15, , 35, , 50, , 20, , 02, , 2001108, , 03, , 03, , 15, , 35, , 50, , 20, , 02, , Total:-, , 09, , 150, , 06, , TERM WORK, Sr., , SUBJECTS, , No., , SUBJECT, , TEACHING, , CODE, , SCHEME, , EXAMINATION - SCHEME, , Periods per, , Marks of, , Marks of, , Total, , week, , Internal, , External, , Marks, , in the, , Examiner (X), , Examiner, , (X+Y), , Subject, , Pass Marks, , Credits, , (V), , 9., 10., 11., , Engg. Workshop Practice, Sports and Yoga, , 2001109, , 06, , 07, , 18, , 25, , 10, , 02, , 2001110, , 02, , 07, , 18, , 25, , 10, , 02, , 15, , 35, , 50, , 20, , 01, , C/KYP/IT, , 2001111, , Essential / Python*, , Total:-, , 08, , 100, , 05, , Total Periods per week Each of duration, One Hour, , 31, , Total Marks = 750, , 24, , iilMi
Page 2 :
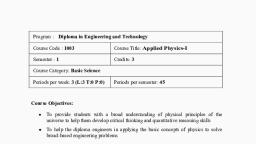
MATHEMATICS-1, No of Periods in One Session ; 45, , Subject Code, 2001101, , No. of Periods Per Week, L, 02, , T, , Full Marks, , P/S, , 01, , Credits, , 100, 70, , ESE, TA, , :, , 10, , CT, , 1, , 20, , 03, , -, , Course Objectives:, , This course is designed to give acomprehensive coverage at an introductory level to the, subject of Trigonometry, Co-ordinate Geometry, Basic elements of algebra and Matrices., Course Content:, , UNIT-I: Trigonometry, , I 09 1, , Concept of angles, measurement of angles in degrees, grades and radians and their conversions, T-Rat,os of, Allied angles (without proof), Sum, difference formulae and their applications (without proof). Product formulae, (Transformation of product to sum, difference and vice versa). T- Ratios of multiple angles, sub-multiple angles, [2A, 3A, A/2). Graphs of sin x, cos x, tan xand e^. Concept of inverse circular function., UNIT - II: Co-Ordinate Geometry, , \ 17 1, , ^, , Equation ofstraight line in various standard forms [without proof), intersection of two straight lines,, Angle between two lines. Parallel and perpendicular lines, perpendicular distance formula., General equation of acircle and its characteristics. To find the equation of acircle, given;, i. Centre and radius,, , ii. Three points lying on it and, lii. Coordinales of end points of a diameter;, , Definition of conies (Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola) their standard equations (without proof). Problems, on conics when their foci, directoriesor vertices are given., UNIT-III: Algebra, , Complex Numbers: Definition, real and imaginary parts ofaComplex number, polar and cartesian [0 ], representation of acomplex number and its conversion from one form to other, conjugate of acomplex, number, modulus and amplitude of acomplex number. Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division, of complex numbers, De-moivre's theorem (without proof) and its application., , Partial fractions: Definition of polynomial fraction, proper &improper fraelions and definition | 03 |, of partial fractions. To resolve proper fraction into partial fraction with denominator containing, non-repeated linear factors, repealed linear iactors and irreducible non-repeated quadratic iactors., To resolve improper fraction into parliai fraction., , Permutations and Combinations: Definition of Factorial Notation, Introduction of, , I 1, , Permutation & Combination, Value of nPr and nCT., , Binomial theorem; Binomial theorem (without proof) for positive integral index (expansion, , [04 ], , and general form); binomial theorem for any index (expansion without proof) first and second binomial, approximation with applications to engineering problems
Page 3 :
Determinants and Matrices, , f, , 1, , Elementary properties ofdeterminants up to 3rd order, consistency of equations, Crammer's rule., Algebra of matrices, Transpose of a matrix. Adjoint of a matrix. Inverse of a matrix, [by adjoint, method}, matrix inverse method to solve a system oflinear equations in2 or 3 variables., References:, , 1., 2., 3., , B.S. Grcwal, Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 40,h Edition, 2007., Rccna Garg. Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishing House, New Delhi (Revised Ed. 2018), Malhemalies Today -XI &XTl (Pail 1) by Lalji Prasad (Paramount Publication. Govind Mitra Road)., , 4., , AText BookofMathematics-Xl & XII (Vol-1) by K.C. Sinha-Rastogi Publication. Meemt, , 5, , Reena Garg &Chandrika Prasad. Advanced Engineering Mathematics. Khanna, , Publishing, , House. New Delhi, Course Outcomes:, , Bythe end of the course, the students are expected to learn, , (i), , The students are expected to acquire necessary background in Trigonometry to appreciate the, importance ofthe geometric study as well as for the calculation and the mathematical analysis., , (ii) The ability to find the effects of changing conditions on a system., , (iij) the coordinate geometry provides a connection between algebra and geometry through graphs ot lines, and curves., , (iv) Complex numbers enter into studies of physical phenomena in ways that most people cannot, imagine., , (v) The students are expected to acquire necessary background in Determinants and Matrices so as to appreciate the, importance ofthe Determinants are the factors that scale different parameterizations so that they all produce same, overall integrals, i.e. they are capable ofencoding the inherent geometry ofthe original shape.
Page 4 :
APPLIED PHYSICS !, Theory, , Subject Code, 2001102, , No of Periods in One Session : 45, , No. of Periods Per Week, , L, , T, , 02, , 01, , -, , -, , P/S, -, , -, , Full .Marks, , 100, , ESE, , 70, , TA, , 10, , CT, , 20, , Credits, , 03, , Course Objectives:, , Applied Physics includes the study of a large number of diverse topics all related to materials/things that exist in, the world around us. It aims to give an understanding of this world both by observation and by prediction of the, , wayin which such objects behave.Concrete use of physical principles and analysis in various fields of engineering, and technology are given prominence in the course content. The course will help the diploma engineers to apply, the basic concepts and principles to solve broad- based engineering problems and to understand different, technology based applications., , Teaching Approach:, , •, , Teachers should give examples from daily routine as well as, engineering/technology applications on, various concepts and principles in each topic so that students are able to understand and grasp these, concepts and principles. In all contents. SI units should be followed., , •, , Use of demonstration can make the subject interesting and develop scientific temper in the students., Student activities should be planned on all the topics., , •, , Activity- Theory - Demonstrate/practice approach may be followed throughout the course so that, learning may be outcome and employability based., , Course Content:, , Unit 1; Physical world. Units and Measurements, , ( 05 ], , Physical quantities: fundamental and derived, Units and systems of units (FPS, COS and SI units). Dimensions, , and dimensional formulae of physical quantities, Principle of homogeneity of dimensions, Dimensional, equations and their applications (conversion from one system of units to other, checking of dimensional, equations and derivation of simple equations). Limitations of dimensional analysis., Measurements: Need, measuring instruments, least count, types of measurement (direct, indirect), Errors in, measurements (systematic and random), absolute error, relative error, error propagation, error estimation, and significant figures., , Unit 2: Force and Motion, [09], Scalar and Vector quantities - examples, representation of vector, types of vectors. Addition and Subtraction, of Vectors, Triangle and Parallelogram law (Statement only). Scalar and Vector Product, Resolution of a, Vector and its application to inclined plane and lawn roller., Force, Momentum, Statement and derivation of conservation of linear momentum, its applications such as, recoil of gun, rockets. Impulse and its applications., Circular motion, definition of angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, frequency, time, , period. Relation between linear and angular velocity, linear acceleration and angular acceleration (related, numerical). Centripetal and Centrifugal forces with live examples, Expression and applications such as, banking of roads and bending of cyclist.
Page 5 :
Unit 3: Work, Power and Energy, [09], Work: Concept and units, examples of zero work, positive work and negative work Friction: concept, types,, laws of limiting friction, coefficient of friction, reducing friction and its engineering applications, Workdone, in movingan object on horizontal and inclined plane for rough and plane surfaces and related applications., Energy and its units, kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy with examples and derivations, mechanical, , energy, conservation of mechanical energy for freely falling bodies, transformation of energy [examples)., Powerand its units, power and work relationship, calculation of power (numerical problems)., , Unit 4: Rotational Motion, , [ 08 ], , Translational and rotational motions with examples. Definition of torque and angular momentum and their, examples. Conservation of angular momentum (quantitative) and its applications., , Moment of inertia and its physical significance, radius of gyration for rigid body. Theorems of parallel and, , perpendicular axes (statements only], Moment of inertia of rod. disc, ring and sphere (hollow and solid);, (Formulae only)., , Unit 5: Properties of Matter, , [08], , Elasticity: definition ofstress and strain, modulus of elasticity, Hooke's law,significance of stre.ss-strain, curve., , Pressure: definition, units, atmospheric pressure, gauge pressure, absolute pressure, Fortin's Barometer and, its applications., , Surface tension: concept, units, cohesive and adhesive forces, angle of contact, Ascent Formula (No, derivation), applications of surface tension, effect oftemperature and impurityon surface tension., Viscosity and coefficient ofviscosity: Terminal velocity. Stokes lawand effect oftemperature, on viscosity, application in hydraulic systems., , Hydrodynamics: Fluid motion, stream line and turbulent flow, Reynolds number Equation of continuity,, Bernoulli's Theorem (only formula and numerical) and its applications., , Unit 6: Heatand Thermometry, , [06], , Concept of heat and temperature, modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection and radiation with, , examples), specific heats, scales of temperature and their relationship. Types of Thermometer (Mercury, thermometer. Bimetallic thermometer. Platinum resistance thermometer. Pyrometer) andtheir uses., Expansion ofsolids, liquids and gases, coefficient oflinear, surface and cubical expansions and relation, amongst them, Co-efficient of thermal conductivity, engineeringapplications., Learning Outcome:, After undergoing this subject, the student will be able to:, , •, , Identify physical quantities, select their units for use in engineering solutions, and make, measurements with accuracy by minimizingdifferent types oferrors., , • Represent physical quantities as scalar and vectors and solve real life relevant problems., • Analyse type of motions and apply the formulation to understand banking of roads/railway tracks and, conservation of momentum principle to describe rocket propulsion, recoil of gun etc., , • Define scientific work, energy and power and their units. Derive relationships for work, energy and
Page 6 :
power and solve related problems., , • Describe forms of friction and methods to minimize friction between different surfaces., , • State the principle ot conservation ofenergy. Identify various forms ofenergy, and energy, transformations., , • Compare and relate physical properties associated with linear motion and rotational motion and apply, conservation of angular momentum principle to known problems., , • Describe the phenomenon of surface tension, effects of temperature on surface tension and solve, statics problems that involve surface tension related forces., , •, , Describe the viscosity ofliquids, coefffcient of viscosity and the various factors affecting its, value. Determine viscosity of an unknown fluid using Stokes' Law and the terminal velocity., , • Define stress and strain. State Hooke's law and elastic limits, stress-strain diagram, determine; (a) the, modulus of elasticity, (b) the yield strength (c) the tensile strength, and (d) estimate the percent, elongation., , • Illustrate the terms; heat and temperature, measure temperature in various processes on, different scales [Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin etc.), , • Distinguish between conduction, convection and radiation; identify different methods for reducing heal, losses and mode of heat transfer between bodies at differenttemperatures., • State specific heats and measure the specific heat capacity ofsolids and liquids., References:, , 1 Text Book of Physics for Class X1& XII (Part-I. Part-11); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi, , Z Applied Physics, Vol. 1and Vol. II, TTTI Publications, Tata McGraw Hill, Delhi., 3. Concepts in Physics by HC Verma, Vol. 1& II, Bharti Bhawan Ltd. New Delhi, , 4. Engineering Physics by PV Naik, Pearson Education Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, , S Engineering Physics by DK Bhhatacharya & PoonamTandan; Oxford University Press, New, Delhi., , e. Comprehensive Practical Physics, Vol, I&II, JN Jaiswal, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 7. Practical Physics by C. L. Arora, S. Chand Publication., , a e-books/e-tools/ learning physics software/websites etc.
Page 7 :
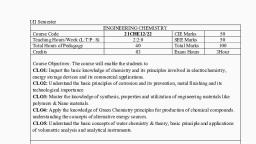
V,-, , APPLIED CHEMISTRY, Theory, , No of Periods in One Session : 4.5, Full Marks, 100, , No. of Periods Per Week, , Subject Code, 2001103, , L, , T, , 02, , 01, , -, , -, , P/S, -, , -, , ESE, , 70, , TA, , 10, , CT, , ;, , Credits, , 03, , 20, , Course Objectives:, , There are numerous number materials used In fabricating andmanufacturing devices for the comfort, , of life. The selection, characterization and suitability assessment of natural raw materials essentially, requires principles and concepts ofApplied Chemistry for students. On successful completion ofthis, course, , • The students will be able to understand, ascertain and analyse the properties of natural raw, materials required for producing economical and eco-friendly finished products., , • Solve various engineering problems applying the basic knowledge of atomic structure and, chemical bonding., , • Use relevant water treatment method to solve domestic and industrial problems., , • Solve the engineering problems using knowledge ofengineering materials and properties., • Use relevant fuel and lubricants for domestic and Industrial applications, • Solve the engineering problems using concept of Electrochemistry and Corrosion., Course Content:, UNIT-I, , Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding., , [ 10), , Rutherford Model of Atom, Photoelectric Effect, Bohr's Theory {Expression of Energy and, Radius to be omitted) and hydrogen spectrum explanation based on Bohr's Model of Atom, Wave, , Mechanical model of atom, de Brogiie relationship, Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, Quantum, Number,, , Shapes of Atomic Orbitals, Pauli's Exclusion Principle, Hund's Rule of Maximum, , Multiplicity, Aufbau Principle, Electronic Configuration (till atomic number 30)., , Concept of Chemical bonding - Cause of chemical bonding, Types of Bonds ; Ionic Bond (NaCl,, CaCb. MgO), Covalent Bond, Polar and Non polar Covalent Bonds (H2, F2, HF, HCl) & Co-ordinate, Bond (CO, NH4+, O3, H2SO4), Dipoie Moment (NH3, NF3), Hydrogen bonding, Anamalous properties, of NH3,H20 due to Hydrogen Bonding., , Concept of Hybridisation, Structure and Shape of Simple Inorganic Molecule e.g. BeCb, BF3,, CH4, NH3, H2O on the basis of hybridisation., UNIT-II, , Water, , | 08 ], , Introduction, Sources of Water, Hardness of Water, Degree of Hardness (In terms of CaC03, , equivalent), Unit of Hardness, Quantitative Measurement of Water Hardness by EDTA method., Municipal supply of Water, Disinfection of Water., , Water Softening Technique-Soda Lime Process, Determination of Dissolved Oxygen,, Water Quality Index - Biological Oxygen Demand, Chemical Oxygen Demand, Simple Numerical, Problems., , UNIT-lII, , Engineering Materials., , [ 08 ], , Natural Occurrence of Metals, Metallurgy —briefaccount of general principles of Metallurgy,, , Gangue, Flux and Slag, Extraction ofAluminum, Iron and Copper from their important ores along with
Page 8 :
reactions., , Alloys - Definition, Purpose of Alloying, Ferrous and Non Ferrous Alloy with suitable examples,, Composition, Properties and Applications., , Polymers-Homopolymers and Copolymers, Addition and Condensation Polymerization e.g., , Polythene, Orion, Terylene, Nylon 66, Nylon 6, Bakelite, Thermoplastic and Thermosetting plastic,, Rubber and Vulcanization of Rubber with Chemical Reaction., , UNIT-IV Chemistry of Fuel and Lubricants., , [ 09 ], , Definition of Fuel, Characteristics of an Ideal Fuel, Classification of Fuel, Calorific Values, (HCV and LCV), Determination of Calorific Value by using Bomb Calorimeter, Calculation of HCV, , and LCV using Dulong's formula., Petrol and Diesel-Fuel Rating (Octane and Cetane Number), Chemical Composition, Calorific Values, and Application of LPG, CNG and Biogas., , Lubricants-Functions and Properties of Good Lubricant, Viscosity & Viscosity Index, Flash, point, Fire point, Cloud & Pour point, Classification of Lubricants with examples., , UNIT-V, , Electrochemistry., , [ 10 ], , Introduction, Electrolyte and Non electrolyte, Arrhenius Theory of lonization. Electrolytic and, , Metallic Conduction, Factors affecting Electrolytic Conductance, Ohm's law. Molar Conductivity and, Equivalent Conductivity, Variation of Molar Conductivity, Kohlrausch's law. Electrolysis, Faraday's, Laws of Electrolysis and simple numerical problems., , Galvanic Cell, Electrode Potential, Measurement of Electrode Potential NHE (Normal, Hydrogen electrode) EMF, Electrochemical Series, Nernst Equation for Electrode Potential., , Batteries, (Commercial Cells) - Primary cells-Dry cell, Secondary cell -Lead storage battery,, Fuel cells., , Corrosion as an Electrochemical Process., , Learning Outcomes, At the end of the course student will be able to, , 1. Understand the classification and general properties of engineering materials such as metal, alloys,, and composite materials using knowledge of chemical bonding., , 2. Understand and assess the suitability of water source for domestic and industrial application,, effluents and minimize water pollution., , 3. Qualitatively analyze the engineering materials and understand their properties and applications., 4. Choose fuel and lubricants suitable for economical industrial processing to obtain eco-friendly finished, products., , 5. a) Ascertain construction, mechanism efficiency of electrochemical cells, solar cell fuel cells, , b) Understand corrosion and develop economical prevention techniques.
Page 9 :
References/Suggested Learning Resources:, (a) Books :, , 1) Text Book of Chemistry for Class XI& Xli (Part-I, Part-ll); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi. 2017-18., , 2) Agrawal. &Shikha. Engineering Chemistry. Cambridge University Press; New Delhi, 2015., 3), 4), 5), 6), 7), , C.N. R. Rao, Understanding Chemistry, Universities Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., 2011., Data, S. S. &Dr.S.S.Umare, Engineering Chemistry. S.Chand. Publication. New Delhi. 2015., Jain &Jain, Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai and Sons; New Delhi, 2015., Dr. Vairam, S.. Engineering Chemistry. Wiley India Pvt.Ltd., New Delhi, 2013., Dr. G. H. Hugar &Prof A. N. Pathak. Applied Chemistry Laboratory Praetices, Vol. Iand, Vol. 11, NITTTR, Chandigarh, Publications. 2013-14., , 8) Agnihotri, Rajesh, Chemistry for Engineers, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd.. 2014., (b)Open sourcesoftware and website address:, , 1 www.chemgujde.co.uk/atommenu.html (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), 2 www.visionleaming.com (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), 3 www.chem I.com (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), , 4 https://www.wastewaterelearning.com/elearning/ (Water Treatment), 5 www.capital-refractories.com (Metals, Alloys. Cement, and Refractory Materials), 6 ^ww.em-ea.org/guide%20books/book-2/2.l%20fuels%20and%20combustion.pdf(Fueland, Combustion), , 7 www.chemcollective.org (Metals, Alloys), 8, , www.wqa.org(Water Treatment)
Page 10 :
COMMUNICATION SKILLS IN ENGLISH, No of Periods in One Session : 30, , Theory, No. of Periods Per Week, L, , Subject Code, , T, , P/S, , Full Marks, ESE, , Credits, , 100, , :, , 70, , •, , {50Eng.+, , 2001104, , 20 Hindi), 02, -, , -, , -, , TA, , ;, , 10, , CT, , :, , 20, , 02, , Course Objectives:, Communication skills play an important role in career development This course aims at introducing basic, concepts of communication skills with an emphasis on developing personality of the students. Thus, the main, objectives of this course are:, , To develop confidence in speaking English with correct pronunciation;, To develop communication skills of the students i.e. listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; and, To introduce the need for personality development., Focus will be on developing certain qualities which will aid students in handling personal and career, challenges, leadership skills etc., Course Content:, , Part - A (English), UNIT -1, ♦, , F.M. - 50(English), 1041, , COMMUNICATION: THEORY AND PRACTICE, , Basics of Communication: Introduction, Meaning and Definition, Process of Communication,, , Elements of Communication: Sender-Message-Channel-Receiver-Feedback & Context,, , Feedback: Definition & Importance., Types of Communication: Formal and Informal, Verbal-Non-verbal, Types of Verbal, , Communication: Oral and Written, Non-Verbal Codes such as Kinesics, Proxemics, Haptics,, Vocalics, Chronemics, Physical Appearance; Tables, Charts and Graphs in Graphic, Communication Oral and Written., UNIT-2, ♦, , EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION AND COMMUNICATION BARRIERS, , [041, , Concept, 7 Cs for Effective Communication (Considerate, Concrete, Concise, Clear,, Complete, Correct, Courteous);, , Art of Effective Communication: Choosing Words, Voice, Modulation, Clarity, Time,, Simplification of Words., ♦, , UNIT - 3, ♦, , Different Barriers to Communication, Ways to Remove/Minimize., READING COMPREHENSION, , j 031, , Comprehension and Vocabulary enhancement based on reading of the following texts:, SECTION-1, , Malgudi Days:, , R.K. Narayan, , What Students Can Do:, , Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, , The Secret of Work :, , Swami Vivekanand
Page 11 :
SECTION-2, , Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening:, , Robert Frost, , Where the Mind Is without Fear:, , Rabindranath Tagore, , Ode on Solitude:, , Alexander Pope, , A Psalm of Life:, , H,W. Longfellow, , UNIT - 4 FORMAL WRITTEN SKILLS/PROFESSIONAL WRITING, , [ 04 ], , ♦, , Application to Principal/Librarian., , ♦, , Drafting E-mails, Messages and Notices., , ♦, , Business Letters: Enquiry Letter, Order Letter, Complaint Letter, Adjustment Letter., , ♦, , Application / Official Letter Writing., , ♦, , Report Writing., , UNIT-5, , VOCABULARY AND GRAMMAR, , [05], , ♦, , Vocabulary of Common Words., , ♦, , One Word Substitution, Common Idioms and Phrases., , ♦, , Use of Synonyms & Antonyms., , ♦, , Parts of Speech, Simple Sentence and Question, Adding Question-Tags, Removal of 'Too*,, , Active Voice into Passive Voice, Direct Speech into Indirect Speech (in cases of Simple, Sentence and Question), Punctuation., , Part-B (Hindi), , UNlT-l., , ^-20 ^, , ^ ciJci^K, , 2. TOTW?TT^>HJ-Cl'HU|, , [021, , TJ^c^renrR, , 3., , 3iicim,, , 'HI-Hd'KI,, , 4., , UNIT-2. . ci|M41|f2lct,, 1., , [02], , - <icha?|efi ^TFT W ciJci^K, , 2., , 3. ofid<r| chl^lcH - 3TTr3T alRTF^icn", 4., , o, , 5. c^qpK ^IFT^, , 3TTr3T, , 3i«rich<Hir|'?riddl, XJW, o *s, , -^FcT
Page 12 :
UNIT - 3. ^, , ^, , Rt/iRd, , amnrr, , l (121, , -, , (^^jTrac^#cb^|Pl4-, , ^#TTrr, , (^sT) ^f^5=5»^TTV S^ftT # T'cRT-STH" oT^ ST^T ^ ?TW^, O, , UNIT-4., , | 02 1, , 1., , 2. aMrnft^ ^TT, , 3., , xrgcZTWrf^ ^ . TTWI^, , SI^^TWfr TT5|-^^, , c^^<ri - ^J^RTT, «ii<ilsici, PiRm c^oi,, , UNIT-5. 5lc<ilcj<^l TOciljch^Uj, , [02], , 1. dWk-il ^Kldc^l, 2., , 4. R'tliH Ro"?, 5., , o, , References:, , 1. J.D.O'Connor. Better English Pronunciation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1980., Lindley Murray.An English Grammar: Comprehending Principles and Rules. London:, , 2, , Wilson and Sons, 1908., , 3. Kulbhushan Kumar, Effective Communication Skills, Khanna Publishing House, New Delhi, (Re- vised Edition 2018), , 4. Margaret M. Md\sor\. Examine your English. Orient Longman: New Delhi, 1964., 5. M. Ashraf Rizvi. Effective Technical Communication. Mc-Graw Hill: Delhi, 2002., 6. John Nielson. Effective Communication Skills. Xlibris, 2008., 7., , Oxford Dictionary, , 8. Roget's Thesaurus ofEnglish Words and Phrases, 9., , Collin s English Dictionary, , Course outcomes:, , At the end of this course, the participants will:, , •, , Develop basic speaking and writingskills including proper usage of language and vocabulary so, that they can become highly confident and skilled speakers and writers., , •, , Be informed of the latest trends in basic verbal activities such as presentations, facing, interviews and other forms of oral communication., , Develop non-verbal communication such as proper use of body language and gestures., , •, , Also develop skills of group presentation and communication in team., , •
Page 14 :
UNIT-V Computer aided drafting interface, , [08], , Computer Aided Drafting: concept. Hardware and various CAD software available., , System requirements and Understanding the interface., , Components of AutoCAD software window: Title bar, standard tool bar, menu bar, object, properties tool bar, draw tool bar, modify tool bar, cursor cross hair Command window, sta- tus, bar, drawing area, UCS icon., , File features: New file. Saving the file. Opening an existing drawing file, Creating templates., Quit., , Setting up new drawing: Units, Limits, Grid, Snap., Undoing and redoing action., , UNIT - VI Computer aided drafting, , [08 J, , Draw basic entities like Line, Circle, Arc, Polygon, Ellipse, Rectangle, Multiline, PolyLine., Method of Specifying points: Absolute coordinates. Relative Cartesian and Polar coordinates., , Modify andedit commands like trim, extend, delete, copy, offset, array, block, layers., Dimensioning: Linear, Horizontal Vertical, Aligned, Rotated. Baseline, Continuous, Diameter,, Radius, Angular Dimensions., Dim scale variable., , Editing dimensions., Text: Single line Text, Multiline text., , Standard sizes of sheet. Selecting Various plotting parameters such as Paper size, paper units, Drawing, orientation, plot scale, plot offset, plot area, print preview., S. No., , Exercises, , Unit, , No., 1, , Draw horizontal, Vertical, 30 degree, 45 degree, 60 and 75 degrees lines, different, types of lines, dimensioning styles using Tee and Set squares/ drafter, (do this exercise, , 1, , in sketch book), 2, , Write alphabets and numerical (Vertical only) (do this exercise in sketch book), , 1, , 3, , Draw regular geometric constructions and redraw the given figure (do this exercise in, , 11, , sketch book) Part 1, 4, , Draw regular geometric construction and redraw the given figure (do this exercise in, , 11, , sketch book) Part II, 5, , Draw a problem on orthographic projections using first angle method of projection, having plain surfaces and slanting. Part 1, , 6, , Draw another problem on orthographic projections using first angle method of, , 111, , 111, , projection having slanting surfaces with slots. Part 11, 7, , Draw two problems on orthographic projections using first angle method ofprojection, , III, , having cylindrical surfaces, ribs. Part 1, 8, , Draw two problems on Isometric view ofsimple objects having plain and slanting, , IV, , surface by using natural scale. Part 1, 9, , Draw some problems on Isometric projection ofsimple objects having cylindrical, surface by using isometric scale. Part 1, , IV
Page 17 :
APPLIED PHYSICS LAB-I, Practical, , Subject Code, 2001106, , L, , No of Periods in One Session : 45, , No. of Periods Per Week, , Full Marks, , SO, , T, , Internal Comm., External Comm., , 3S, , -, , P/S, 03, , IS, , 02, , Course Objectives, , Study of Applied Physics aims to give an understanding of physical world by observations and predic, tions. Concrete use ofphysical principles and analysis in various fields ofengineering and technology is, , very prominence. The course aims to supplement the factual knowledge gained in the lecture by first, , hand manipulation of apparatus. This will develop scientific temper and help to apply the basic, , concepts and principles in solving engineering and technology based problems. In addition, students, getnecessary confidence in handling equipment and thus learn various skills inmeasurement., , List ofPracticars (To perform minimum 10 practicaPs)., , 1, , To measure length, radius ofa given cylinder, a test tube and a beaker using a Vernier, caliper and find volume of each object., , 2 To determine diameter ofawire, asolid ball and thickness ofcardboard using ascrew, gauge., , 3. To determine radius ofcurvature ofaconvex and aconcave mirror/surface using aspherometer., , 4., , Toverify triangle and parallelogram law of forces., , 5., , To find the co-efficient offriction between wood and glass using a horizontal board., , &, , To determine force constant of a spring using Hook's Law., , 7., , To verify law ofconservation ofmechanical energy (PE to KE)., , 8., , To find the moment of inertia of a flywheel., , 9., , To find the viscosity ofa given liquid (Glycerin) by Stokes law., , Id To find the coefficient of linear expansion of the material of a rod., , 11 To determine atmospheric pressure ata place using Fortin's barometer., , 12 To measure room temperature and temperature ofahot bath using mercury thermometer and, convert it into different scales., , Learning Outcome:, After undergoing this lab work, the student will be able to:, , • Select right kind of measuring tools (Meter scale. Vernier caliper. Screw gauge, Spherometer etc.), for determining dimensions of physical quantities and make measurements with accuracy and, precision., , • Differentiate various shapes and determine dimensions ofplane, curved and regular surfaces/bodies., • Apply and Verify laws offorces and determine resultant force acting on abody., •, , Appreciate role of friction and measure co-efficient of friction between different surfaces., , • Describe and verify Hook's law and determine force constant ofspring body., , • Identify various forms of energy, energy transformations and verify law ofconservation of energy., • Understand rotational motion and determine M.l. ofa rotating body (flywheel), , • Understand Stokes law for viscous liquids and determine viscosity ofa given liquid., • Understand how materials expand on heating and determine linear expansion coefficient for
Page 18 :
r', , . Understand use ofthermometers to measure temperature under different conditions and, ditterent scales oftemperature measurements., , SUGGESTED STUDENT ACTIVITES &STRATEGIES, , Apart from classroom and laboratory learning follow,ng are the suggested student related, , act,v.t,es wh,ch can he undertahen to accelerate the attainment ofvarious outcomes ofthe, course, , a. Make survey ofdifferent physical p,-oducts and compare the following points, •, , Measurements of dimensions, , •, , Properties, , •, , Applications, , b. Library survey regarding engineering materials/products used in diffe,-ent industries, c. Seminar on any relevant topic., , Teachers should use fonowiug strategies to achieve the various outcomes ofthe course, ferent methods ofteaching and media to be used to attain classroom attention., , . Massive open online courses (MOOCs) may be used to teach va,-ious topics/sub topics., • 15-200/. otMhe topics which are relatively simpler ofdescriptive in nature should be given, O estu ents lor self-lea,rung and assess the development of competency through, classroom presentations., , Micro-projects may be given to group ofstudents for hand-on experiences., References:, , 1 Text Book of Physics for Class XI& XII (Part-I, Part-ll); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi, 2. Comprehensive Practical Physics, I ^ ii JN, m Jaiswai,, i•, rnysics, Vnl, Vol, I&H., , Laxmi Publications (P)Ltd, , T Practical Physics by C. L. Arora, S. Chand Publication., , 4. e-books/e-tools/ learning physics software/YouTube videos/websites etc.
Page 19 :
APPLIED CHEMISTRY LAB, Practical, , Subject Code, , No of Periods in One Session : 4.S, , No. of Periods Per Week, , 2001107, , L, , T, , Full Marks, , Credits, , 50, , P/S, , Internal Comm., , 15, , 03, , External Comm., , 35, , 02, , Course Objectives:, , There are numerous number ofmaterials used in fabricating and manufacturing devices for the comfort of, , life. The selection, characterization and suitability assessment of natural raw materials essentially requires, principles and concepts of Applied Chemistry for students. The course aims to supplement the factual, , knowledge gained in the lectures by first hand manipulation of processes and apparatus. This will develop, , scientific temper and help to apply the basic concepts and principles in solving technology based problems., In addition, students will get necessary confidence inhandling equipments and thus learn various skills in, measurement., , List pf Practi^ls..: Perform, 1., , Preparation of 250ml N/10 Oxalic acid Solution., , 2., , Preparation of 250ml N/10 Sodium Carbonate Solution., , 3., , To determine the strength ofSodium Hydroxide Solution by Titrating against Oxalic Acid, Solution., , 4., , Determination of Temporary Hardness ofTap Water., , 5., 6., , Gravimetric Estimation of Moisture in given Coal Sample., Determination of Percentage of Water of Crystallization in Barium Chloride., , 7., , Preparation of Cupric Oxide from Copper Sulphate., , 8., , Preparation of Barium Sulphate from Barium Chloride., , 9-11., , Qualitative Analysis of Three Solutions containing One Basic and One Acid radicals, Listed below., , 12., , Basic radicals - NH4^ Pb'"^ Cu"'^Nr^ Zn'"^ Fe^l, Acid radicals - Cl", Br", T, NOb", C0{^, SOT^,, Determination ofViscosity of Lubricating Oil Using Ostwald Viscometer., , 13., , To Verify Faradays First Law of Electrolysis., , 14., , To determine pH of given solution by pH meter., , 15., , Prepare Phenol Formaldehyde Resin (Bakelite), , 16., , To Determine Dissolved Oxygen in given Sample of Water., , Learning Outcomes:, At the end of the course student will be able to, , • Toexpress quantitative measurements accurately., • Topractice and adapt good measuringtechniques., • To use various apparatus for precise measurements., , • To understand and differentiate different methods of quantitative analysis., • To know and understand principles of quantitative analysis using instruments.
Page 20 :
• To construct different electrochemical cells used in developing batteries., • To understand and appreciate methods ofcorrosion abetnients., Reference Books:, , I. Tea Book orcheaiooj forCI.e, XI i Xll (P.„.|. p.,,.|,x nc.E RT,, DelM, 2017-18, Z Dr C., , p„„ ^, , Vol. II, NITTTR, Chandigarh, Publications, 2013-14., , 3. Agnihotri, Rajesh, Chemistry for Engineers, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd., 2014., , 4. Jain &Jain, Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai and Sons; New Delhi, 2015.
Page 21 :
•», , COMMUNICATION SKILLS IN ENGLISH LAB, Practical, , Subject Code, 2001108, , No of Periods in One Session : 45, , No. of Periods Per Week, L, , T, , Full Marks, , Credits, , SO, , P/S, , Internal Comm., , 15, , 03, , External Comm., , 35, , 02, , Communication skills play an important role in career development. This lab course aims at actively involving, students in various activities to improve their communication skills with an emphasis on developing personality, of the students. Thus, the objectives of this course are:, , 1. Todevelop listening skills for enhancing communication., , 2. To develop speaking skills with a focus on correct pronunciation and fluency., , 3. To introduce the need for Personality development- Focus will be on developing certain qualities which, will help students in handling personal and career challenges, leadership skills etc. For that purpose, group discussion, extempore and other activities should be conducted during lab classes., Course Content:, , UNIT-1 Listening Skills, , Listening Process and Practice: Introduction to recorded lectures, poems, interviews and, speeches, listening tests., UNIT-11, , Introduction to Phonetics, , Sounds: consonant, vowel, diphthongs, etc. transcription of words (IPA), weak forms, syllable, division, word stress, intonation, voice etc., , UNIT- III Speaking Skills, , Standard and formal speech: Group discussion, oral presentations, public speaking, extempore speech,, business presentations conversation practice and role playing, mock interviewsetc., UNIT-IV Building Vocabulary, Etymological study of words and construction of words, phrasal verbs. Idioms and phrases., Jargon/ Register related to organizational set up, word exercises and word games to enhance selfexpression and vocabulary of participants., , Recommended Readings:, 1. Daniel Jones. The Pronunciation ofEnglish. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1956., , 2. James Hartman& et al. Ed. English Pronouncing Dictionary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006., , 3., , Kulbhushan Kumar, Effective Communication Skills, Khanna Publishing House. New Delhi, (Revised Ed. 2018), , 4., 5., , J.D.O'Connor. Better English Pronunciation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1980., Lindley Murray. An English Grammar: Comprehending Principles and Rides. l>ondon: Wilson, and Sons. 1908., , 6., , Margaret M. Maison. Examineyour English. Orient Longman: New Delhi. 1964., , 7., , J.Sethi & et al. A Practice Course in English Pronunciation. New Delhi: Prentice Hall, 2004., , 8., , Pfeiffer, William Sanborn and T.V.S Padmaja. Technical Communication: A Practical, Approach, b'^ed. Delhi: Pearson, 2007.
Page 22 :
1*, , Learning Outcome;, , • At the end ofthis course thestudents will be able tocommunicate effectively with an increase, in their confidence to read, write and speak English fluently., , • They will also demonstrate a significant increase in word power., , • The variety of exercises and activities that will be conducted in the Language Lab will, devel- op their skills needed to participate in a conversation like listening carefully and, respectfully to others' viewpoints: articulating their own ideas and questions clearly and, over all students will be able to prepare, organize, and deliver an engaging oral, presentation., , • They will also develop non-verbal communication such as proper use of body language, and gestures.
Page 23 :
'«•, , ENGINEERING WORKSHOP PRACTICE, No of Periods in One Session : 90, , Term Work, , Subject Code, 2001109, , Full Marks, , 25, , P/S, , Internal, , 07, , 06, , External Comm., , 18, , No. of Periods Per Week, L, , T, , Credits, 02, , Course Objectives:, •, , To understand basic engineering processes for manufacturing and assembly., , •, , To understand, identify, select and use various marking, measuring, and holding, striking and cutting, tools and equipment's, , •, , To understand and interpret job drawings, produce jobs, and inspect the job for specified, dimensions, , •, , To understand the various types of wiring systems and acquire skills in house wiring, To understand, operate, control different machines and equipment's adopting safety practices Course, Content:, , Course Content:, I, , Carpentry: i) Demonstration of different wood working tools/machines., , [ 16], , ii) Demonstration of different wood working processes, like plaining, marking, chiseling, grooving,, turning of wood etc. iii) One simple job involving any one joint like mortise and tenon dovetail,, bridle, half lap etc., 11, , Fitting: i) Demonstration of different fitting tools and drilling machines and power tools, , 1161, , ii) Demonstration of different operations like chipping, filing, drilling, tapping, sawing, cutting etc., iii) One simple fitting job involving practice of chipping, filing, drilling, tapping, cutting etc, III, , Welding: i) Demonstration of different welding tools / machines, ii) Demonstration on Arc [16|, ISjWelding, Gas Welding. MIG, MAG welding, gas cutting and rebuilding of broken parts with, welding, iii) One simple job involving butt and lap joint, , IV, , Sheet Metal Working: i) Demonstration of different sheet metal tools / machines., , [ 16 ], , ii) Demonstration of different sheet metal operations like sheet cutting, bending, edging, end, curling, lancing, soldering, brazing, and riveting, iii) One simple job involving sheet metal, operations and soldering and riveting., , Electrical House Wiring; Practice on simple lamp circuits (i) one lamp controlled by one, , [ 16), , switch by surface conduit wiring, (ii) Lamp circuits- connection of lamp and socket by separate, switches, (iii) Connection of Fluorescent lamp/tube light, (iv) simple lamp circuits-in- stall bedroom, lighting. And (v) Simple lamp circuits- install stair case wiring., VI, , Demonstration: i) Demonstration of measurement of Current, Voltage, Power and Energy., , (10 ], , ii) Demonstration of advance power tools, pneumatic tools, electrical wiring tools and accessories, iii), Tools for Cutting and drilling
Page 24 :
References:, , 1. S.K.. Hajara Chaudhary, Workshop rechnology. Media Promoters and Publishers, New Delhi,, 2015, , 2. B.S. Raghuwanshi, Workshop Technology, Dhanpat Rai and sons, New Delhi 2014, , 3. K. Venkat Reddy, Workshop Practice Manual, BS Publications, Hyderabad 2014, 4. Kents Mechanical Engineering Hand book, John Wiley and Sons, New York Course outcomes, At the end of the course, the student will be able to:, , QQj, , Acquire skills in basic engineering practice to identify, select and use various marking,, measuring, and holding, striking and cutting tools & equipment's and machines, , C02, , Understand job drawing and complete jobs as per specifications in allotted time, , €03, , Inspect the job for the desired dimensions and shape, , €04, , Operate, control different machines and equipment's adopting safety practices
Page 25 :
Yoga& Lifestyle, o, , Asanas as Preventive Measures., , o Hypertension: Tadasana, Vajrasana, Pavan Muklasana, Ardha Chakrasana,, Bhujangasana, Sharasana., , o Obesity: Procedure, Benefits & Contraindications for Vajrasana., o, , Back Pain: Tadasana, Ardh Matsyendrasana, Bhujangasana., , o, , Diabetes: Procedure, Benefits & Contraindications for Bhujangasana, Paschimottasana., , Ardh Matsyendrasana., , o, , Asthma: Procedure. Benefits & Contraindications for Sukhasana, Bhujangasana ,, , Matsyasana., , Psychology & Sports, , o Psychological Benefits of Exercise,, , o Anxiety & Fear and Its Effects on Sports Performance,, o, , Motivation, its types & Techniques,, , o, , Understanding Stress & Coping Strategies., •, , Sports / Games, , Following sub topics related to any one Game/Sport of choice of student out of: Athletics,, Badminton, Chess, Cricket, Kabaddi, Table Tennis, Volleyball, Yoga etc., , o, , History of the Games/Sport., , o, , Latest General Rules of the Games/Sports., , o Specifications of Play Fields and Related Sports Equipment., o, , Important Tournaments and Venues., , o, , Sports Personalities., , References:, , 1., , Modern Trends and Physical Education by Prof. Ajmer Singh., , 2., , Light On Yoga By B.K.S. lyengar., , 3., , Health and Physical Education-NCERT (11th and 12th Classes), , Course Outcomes:, , On successful completion of the course the students will be able to:, , (i), , Practice Physical activities and Hatha Yoga focusing on Yoga for strength, flexibility,, and relaxation., , (ii), , Learn techniques for increasing concentration and decreasing anxiety which leads to, stronger academic performance., , (iii), , Learn breathing exercises and healthy fitness activities, , fiv), , Understand basic skills associated with yoga and physical activities including strength and, flexibility, balance and coordination.
Page 26 :
SPORTS AND YOGA, Term Work, , Subject Code, 2001110, , No of Periods in One Session : 30, , No. of Periods Per Week, L, , T, , Full Marks, , 25, , P/S, , Internal, , 07, , 02, , External Comm., , 18, , Credits, 02, , Course Objectives:, , • To make the students understand the importance of sound health and fitness principles, as they relate to better health., , • To expose the students to a variety of physical and yogic activities aimed at stimulating their, continued inquiry about Yoga, physical education, health and fitness., , • To create a safe, progressive, methodical and efficient activity based plan to enhance, improvement and minimize risk of injury., , • Todevelop among students an appreciation of physical activity as a lifetime pursuit and a means, to better health., Course Content:, , •, , Introduction to Sports, , o Meaning & Definition of Sports, o Aims & Objectives of Physical Education, , o Awards and Honours in the Field of Sports in India (Dronacharya Award. Arjuna Award,, Dhayanchand Award, Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award etc.], •, , Physical Fitness, Weliness & Lifestyle, o Meaning & Importance of Physical Fitness & Weliness, o, , Components of Physical Fitness, , o, , Components of Weliness, , o Preventing Health Threats through Lifestyle Change, o Concept of Positive Lifestyle, •, , Postures, , o Meaning and Concept of Postures,, , •, , o, , Causes of Bad Posture,, , o, , Concept & Advantages of Correct Posture., , Yoga, , o Meaning & Importance of Yoga, o, , Elements of Yoga, , o Introduction - Asanas, Pranayama, Meditation & Yogic Kriyas, o Yoga for Concentration & Related Asanas (Sukha.sana; Tadasana; Padmasana & Shashankasana)
Page 27 :
I, , M, , Perform Yoga movements in various combination and forms., , (vO, , Assess current personal fitness levels., , (vii), , Identify opportunities for participation in Yoga and Sports activities., , (viii), , Develop understanding of health-related fitness components: cardiorespiratory, endurance, flexibility and body composition etc., , fix), , Improve personal fitness through participation in Sports and Yogic activities., , (x), , Develop understanding of psychological problems associated with the age and lifestyle., , (xl), , Demonstrate an understanding of sound nutritional practices as related to health, and physical performance., , (xn), , (xi), , Assess Yoga activities in terms of fitness value., , Identify and apply injury prevention principles related to Yoga and physical, fitness activities., , (wv), , Understand and correctly apply biomechanical and physiological principles, related to exercise and training.
Page 28 :
C / KYP / IT ESSENTIAL / PYTHON, Term Work, , Subject Code, 2001111, , No of Periods in One Session : 30, , No. of Periods Per Week, L, , T, -, , P/S, , Full Marks, , Credits, , 50, , Internal, , 15, , External Comm., , 35, , 02, , j