Page 1 :
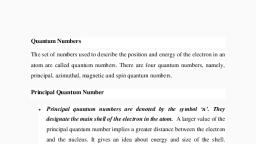
2021, GPTC KOTHAMANGALAM, , SELVARAJAN T R, SEM I, APPLIED CHEMISTRY, MODULE II, FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY, NOTES-PART II, VOLUMETRIC ANALYSIS, , Volumetric Analysis, Standard solution, Titration, End point, Indicators, Acid- base titrations, pH range of the, indicator, Selection /choice of indicators in acid base titrations, Normality Equation for, the titration
Page 2 :
2.2. Volumetric Analysis, Volumetric analysis involves the determination of the quantity of a substance in a solution, by reacting it with a standard solution of another substance by a process called titration., Pipette, burette and conical flasks are the equipments used for this process., , Standard solution: A solution of known strength (concentration) is called standard solution., Titration: The process of adding the solution taken in the burette drop wise to a fixed volume of, the other solution taken in the conical flask (titration flask) till the end point is called titration., End point: The stage at which the reaction is just completed during a titration is called the end, point., Indicators: The end point is detected with the help of some substance called indicators. Indicators, exhibit a marked colour change at the endpoint.
Page 3 :
Methyl orange and Phenolphthalein are the common indicators used in acid – base, titrations. These indicators are organic dyes which are either a weak acid or base. Methyl orange, is a weak base and Phenolphthalein is a weak acid. They have different colours in acidic and basic, medium. Because they exist as either ionized or unionized form in acidic or basic medium. Ionized, and unionized forms have different colours., Acid- base titrations:, Acid- base titrations are two types- i)Acidimetry and ii) Alkalimetry., Acidimetry is the determination of the quantity of a base in a solution by titrating it with a standard, acid solution., Alkalimetry is the determination of the quantity of an acid in a solution by titrating it with a, standard solution of Alkali (base)., pH range of the indicator, When an acid is gradually added to a base, its pH decreases. At a particular pH or within a, range of pH the indicator shows a colour change. The range of pH at which an indicator exhibits a, colour change during an acid-base titration is called pH range of the indicator., , Selection /choice of indicators in acid base titrations:, Depending upon the type of acid or base (whether it is strong or base ) suitable indicator is, selected for the titration., pH range of methyl orange is 3.1 to 4.5. This pH change occurs in acidic medium. So it is, used only when acid is strong. Base may be strong or weak., pH range of phenolphthalein is 8.3 to 10. This pH change occurs in basic medium. So it is, used only when the base is strong. Acid may be strong or weak.
Page 4 :
Therefore,, In the case of strong acid x strong base either phenolphthalein or methyl orange can be used., In the case of strong acid x weak base methyl orange is the suitable indicator. Phenolphthalein, cannot be used in this case, In the case of strong base x weak acid, phenolphthalein is the suitable indicator., Weak acid x weak base titrations are not conducted due to the difficulty in getting a sharp end, point., Strong acids: Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and Nitric acid(HNO3), Weak acid: Oxalic acid (H2C2O4.2H2O), Strong bases: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH), Weak bases: Ammonium hydroxide, Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and potassium carbonate, (K2CO3)., Normality Equation for the titration, If V1 ml of solution 1 having normality N1 is required to react completely with V2 ml of solution, 2 having normality N2 then, V1N1 =V2N2, This equation is called normality equation. The principle is that at the completion of the reaction,, the number of equivalents of both substance reacted are the same. That means number of, equivalents in V1 is same as the number of equivalents in V2 ., Knowing the normality of any one of the solution, normality of the other solution can be, determined using this equation. V1 and V2 are known. (measured using either pipette or burette)., The following equations are useful for solving problems.