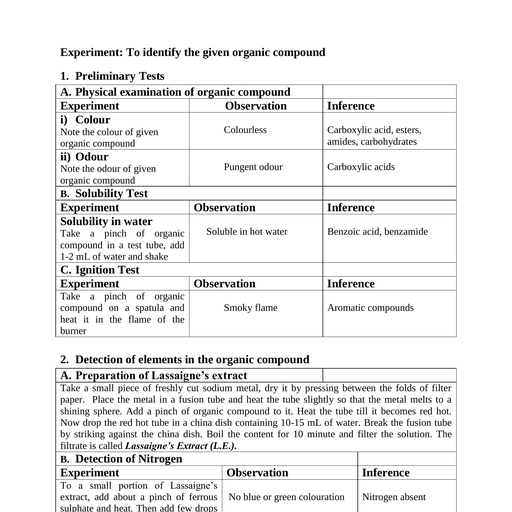
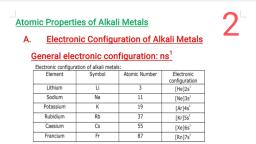
Page 1 :
IThe first ionization energy for sodium is lower than that of magnesium:, , Na(g) > Na‘(g) + &} IE, = 495 kt}, Mgte) > Mg’) + &} IE, = 735 kJ, , Jowever the second ionization energy for sodium is much higher than that of magnesium:, Na’ (g) > Na*() + &} TE, = 4560 k}, Mg’) > Mg”(@) + &; IE, = 1445 kJ, , , , First lonization energy, |, , |, e The first ionization energy of alkaline earth metals is the energy, needed for the removal of the first electron from the neutral atom. It, is larger than that of the alkali metal atom for two reasons:, , > Due to smaller radii and the electrons being held tightly by the, higher nuclear charge, and, , » Electron being removed from a fully filled and hence a stable, subshell., , Second lonization Energy, , e The second ionization energy of alkaline earth metals is more than, the first ionization energy of the atom, but less than any second, ionization of alkali metal., , e In spite of the high ionization energy, removal of both electrons are, feasible because,, , » Atom gets a noble gas configuration, , » The smaller size and higher charge help to overcome the higher, ionization energy by higher lattice energy arising due to the close, packing of atoms or ions in solids., , » Higher hydration energy in liquids due to larger solvation., , e So group two alkaline earth elements are all divalent electropositive, metals and exhibit a fixed oxidation state of +2., , e lonization energy needed for the removal of the valence electron will, be highest for the small beryllium atom., , e With increasing atomic size, the valence electron gets shielded by, the inner electrons and becomes easily removable with less energy, requirement. Hence the ionization energy decreases with an, increasing atomic number or atomic size., , Example: Ese > IEwg > IEca > IEsr > IEsa, , Why Solubility of Alkaline Earth Metals decreases down the, Group?, , > Beryllium ion is the most soluble and the solubility decreases with, increasing size., , |, , > Barium ion is the least water-soluble alkaline earth metal ion., Solubility in water is related to the ionic nature and size., , > Smaller ions have higher charge density and can be solvated by, more water molecules. This releases a higher enthalpy of hydration, and makes the hydrated ions more stable.